|
List Of Chinese Terrestrial Ungulates
This is a list of Chinese terrestrial ungulates, including both extinct and extant types. Ungulates are mammals which are endothermic amniote animals distinguished from reptiles and birds by the possession of hair, three middle ear bones, mammary glands, and a neocortex (a region of the brain). The mammalian brain regulates body temperature and the circulatory system, including the four-chambered heart. The mammals include the largest animals on the planet, the rorquals and some other whales, as well as some of the most intelligent, such as elephants, some primates and some cetaceans. The basic body type is a four-legged land-borne animal, but some mammals are adapted for life at sea, in the air, in the trees, or on two legs. The largest group of mammals, the placentals, have a placenta which feeds the offspring during pregnancy. China for the purposes of this list article refers to a geographic area, now primarily politically identified with a modern nation state. Writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Territories Of Dynasties In China
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal. In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or an administrative division is usually an area that is under the jurisdiction of a sovereign state. As a subdivision a territory is in most countries an organized division of an area that is controlled by a country but is not formally developed into, or incorporated into, a political unit of the country that is of equal status to other political units that may often be referred to by words such as "provinces" or "regions" or "states". In its narrower sense, it is "a geographic region, such as a colonial possession, that is dependent on an external government." Etymology The origins of the word "territory" begin with the Proto-Indo-European root ''ters'' ('to dry'). From this emerged the Latin word ''terra'' ('earth, land') and later the La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including humans). Primates arose 85–55 million years ago first from small terrestrial mammals, which adapted to living in the trees of tropical forests: many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging environment, including large brains, visual acuity, color vision, a shoulder girdle allowing a large degree of movement in the shoulder joint, and dextrous hands. Primates range in size from Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, which weighs , to the eastern gorilla, weighing over . There are 376–524 species of living primates, depending on which classification is used. New primate species continue to be discovered: over 25 species were described in the 2000s, 36 in the 2010s, and three in the 2020s. Primates have large bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system). Civilizations are intimately associated with additional characteristics such as centralization, the domestication of plant and animal species (including humans), specialization of labour, culturally-ingrained ideologies of progress, monumental architecture, taxation, societal dependence upon farming, and expansionism. Historically, a civilization has often been understood as a larger and "more advanced" culture, in implied contrast to smaller, supposedly less advanced cultures. In this broad sense, a civilization contrasts with non-centralized tribal societies, including the cultures of nomadic pastoralists, Neolithic societies or hunter-gatherers; however, sometimes it also contrasts with the cultures found within civilizations themselv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest list of rivers of Asia, river in Asia, the list of rivers by length, third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows in a generally easterly direction to the East China Sea. It is the List of rivers by discharge, seventh-largest river by discharge volume in the world. Its drainage basin comprises one-fifth of the land area of China, and is home to nearly one-third of the demographics of China, country's population. The Yangtze has played a major role in the history of China, history, culture of China, culture, and economy of China. For thousands of years, the river has been used for water, irrigation, sanitation, transportation, industry, boundary-marking, and war. The prosperous Yangtze Delta generates as much as 20% of historical GDP of China, China's GDP. The Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze is the list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Standard Beijing Mandarin, Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Har Mountains in Qinghai province of Western China, it flows through nine provinces, and it empties into the Bohai Sea near the city of Dongying in Shandong province. The Yellow River basin has an east–west extent of about and a north–south extent of about . Its total drainage area is about . The Yellow River's basin was the Yellow River civilization, birthplace of ancient Chinese, and, by extension, Far East, Far Eastern civilization, and it was the most prosperous region in early Chinese history. There are frequent devastating natural disasters in China, floods and course changes produced by the continual elevation of the river bed, sometimes above the level of its surrounding farm fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
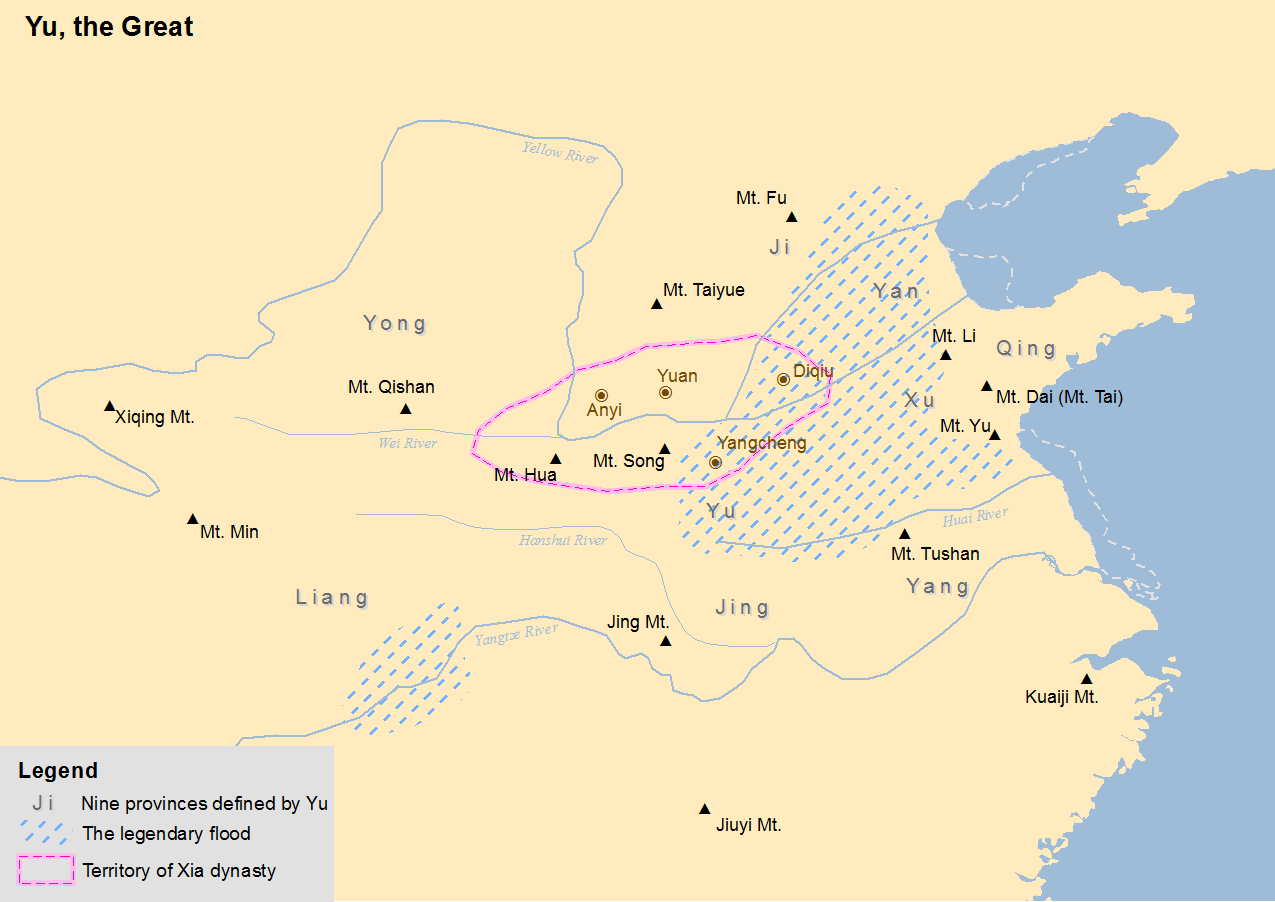
Xia Dynasty
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In traditional historiography, the Xia was later succeeded by the Shang dynasty. There are no contemporaneous records of the Xia, who are not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts, since the earliest oracle bone inscriptions date from the late Shang period (13th century BC). The earliest mentions occur in the oldest chapters of the '' Book of Documents'', which report speeches from the early Western Zhou period and are accepted by most scholars as dating from that time. The speeches justify the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the passing of the Mandate of Heaven and liken it to the succession of the Xia by the Shang. That political philosophy was promoted by the Confucian school in the Eastern Zhou period. The succession of dynasties was incorporat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamboo Annals
The ''Bamboo Annals'' (), also known as the ''Ji Tomb Annals'' (), is a chronicle of ancient China. It begins in the earliest legendary time (the age of the Yellow Emperor) and extends to 299 BC, with the later centuries focusing on the history of the State of Wei in the Warring States period. It thus covers a similar period to Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (91 BC). The original may have been lost during the Song dynasty, and the text is known today in two versions, a "current text" (or "modern text") of disputed authenticity and an incomplete "ancient text". Textual history The original text was interred with King Xiang of Wei (died 296 BC) and re-discovered nearly six centuries later in 281 AD (Western Jin dynasty) in the Jizhong discovery. For this reason, the chronicle survived the burning of the books by Emperor Qin Shi Huang. Other texts recovered from the same tomb included '' Guoyu'', '' I Ching'', and the '' Tale of King Mu''. They were written on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Grand Historian
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese historian Sima Qian, whose father Sima Tan had begun it several decades earlier. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Records'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and the First Emperor of Qin, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Records'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historical works, the ''Records'' do not treat history as "a cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shang Dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou dynasty. The classic account of the Shang comes from texts such as the '' Book of Documents'', '' Bamboo Annals'' and '' Records of the Grand Historian''. According to the traditional chronology based on calculations made approximately 2,000 years ago by Liu Xin, the Shang ruled from 1766 to 1122 BC, but according to the chronology based upon the "current text" of ''Bamboo Annals'', they ruled from 1556 to 1046 BC. Comparing the same text with dates of five-planet conjunctions, David Pankenier, supported by David Nivison, proposed dates of the establishment of the dynasty to 1554 BC. The Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project dated the establishment to c. 1600 BC based on the carbon-14 dates of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
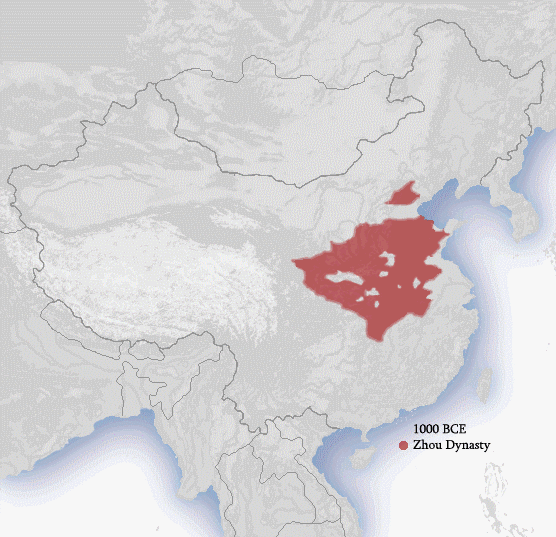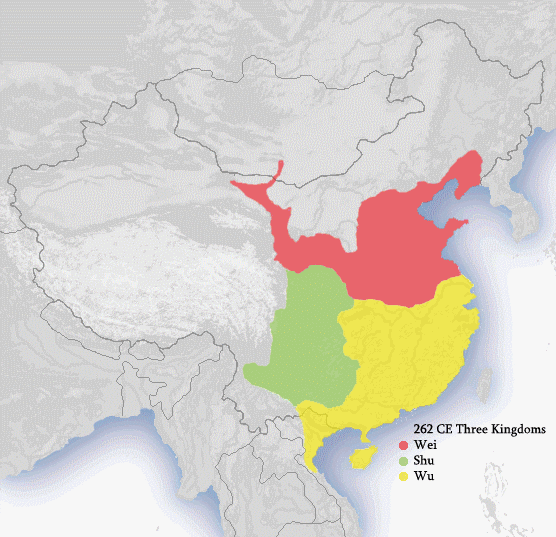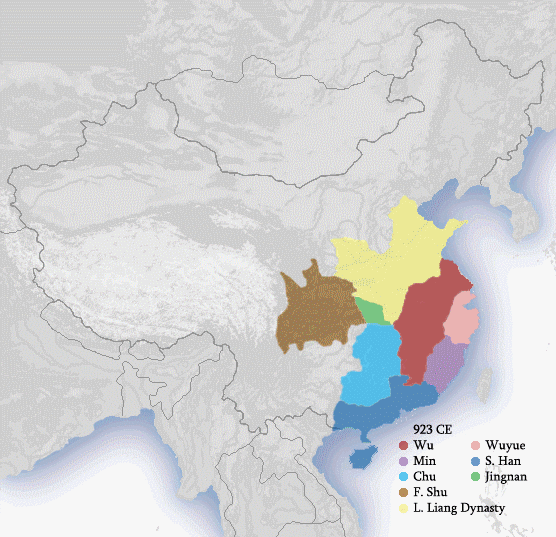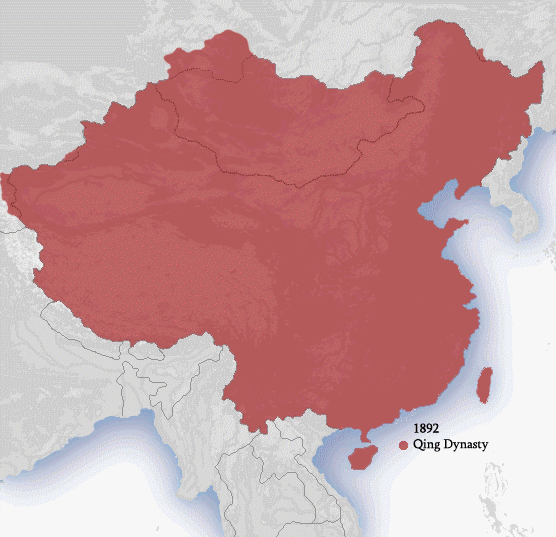
History Of China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapters, 11th century BC), the '' Bamboo Annals'' (c. 296 BC) and the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (c. 91 BC) describe a Xia dynasty before the Shang, but no writing is known from the period, and Shang writings do not indicate the existence of the Xia. The Shang ruled in the Yellow River valley, which is commonly held to be the cradle of Chinese civilization. However, Neolithic civilizations originated at various cultural centers along both the Yellow River and Yangtze River. These Yellow River and Yangtze civilizations arose millennia before the Shang. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is among the world's oldest civilizations and is regarded as one of the cradles of civilization. The Zhou dynasty (1046–256 BC) supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)