|
List Of African Dinosaurs
This is a list of dinosaurs whose remains have been recovered from Africa. Africa has a rich fossil record, but it is patchy and incomplete. It is rich in Triassic and Early Jurassic dinosaurs. African dinosaurs from these time periods include ''Coelophysis'', ''Dracovenator'', '' Melanorosaurus'', ''Massospondylus'', ''Euskelosaurus'', ''Heterodontosaurus'', ''Abrictosaurus'', and ''Lesothosaurus''. In the Middle Jurassic, the sauropods '' Atlasaurus'', ''Chebsaurus'', ''Jobaria'', and ''Spinophorosaurus'', flourished, as well as the theropod ''Afrovenator''. The Late Jurassic is well represented in Africa, mainly thanks to the spectacular Tendaguru Formation in Lindi Region of Tanzania. ''Veterupristisaurus'', ''Ostafrikasaurus'', ''Elaphrosaurus'', ''Giraffatitan'', ''Dicraeosaurus'', ''Janenschia'', ''Tornieria'', ''Tendaguria'', '' Kentrosaurus'', and '' Dysalotosaurus'' are among the dinosaurs whose remains have been recovered from Tendaguru. This fauna seems to show strong si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species, are among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afrovenator
''Afrovenator'' (; "African hunter") is a genus of megalosaurid theropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Period of northern Africa. Discovery and naming The remains of ''Afrovenator'' were discovered in 1993 in the Tiourarén Formation of the department of Agadez in Niger. The Tiourarén was originally thought to represent the Hauterivian to Barremian stages of the early Cretaceous Period, or approximately 132 to 125 million years ago (Sereno et al. 1994). However, re-interpretation of the sediments showed that they are probably Mid-Jurassic in age, dating ''Afrovenator'' to the Bathonian to Oxfordian stages, between 167 and 161 mya. The sauropod '' Jobaria'', whose remains were first mentioned in the same paper which named ''Afrovenator'', is also known from this formation. ''Afrovenator'' is known from a single relatively complete skeleton, holotype UC OBA 1, featuring most of the skull minus its top (likewise the mandible, or lower jaws, are lacking apart from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
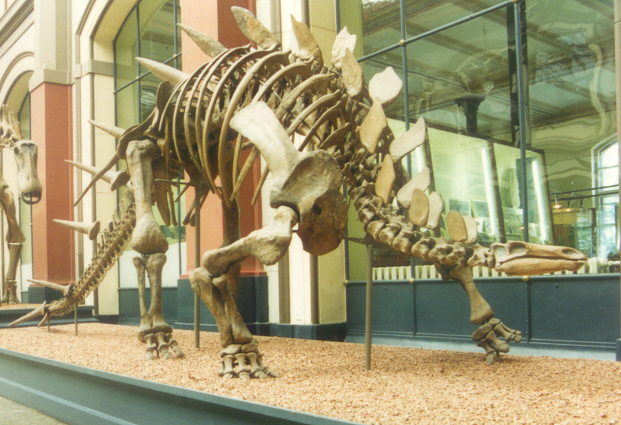
Kentrosaurus
''Kentrosaurus'' ( ; ) is a genus of stegosaurid dinosaur from the Late Jurassic in Lindi Region of Tanzania. The type species is ''K. aethiopicus'', named and described by German palaeontologist Edwin Hennig in 1915. Often thought to be a " primitive" member of the Stegosauria, several recent cladistic analyses find it as more derived than many other stegosaurs, and a close relative of ''Stegosaurus'' from the North American Morrison Formation within the Stegosauridae. Fossils of ''K. aethiopicus'' have been found only in the Tendaguru Formation, dated to the late Kimmeridgian and early Tithonian ages, about 152 million years ago. Hundreds of bones were unearthed by German expeditions to German East Africa between 1909 and 1912. Although no complete skeletons are known, the remains provided a nearly complete picture of the build of the animal. In the Tendaguru Formation, it coexisted with a variety of dinosaurs such as the carnivorous theropods ''Elaphrosaurus'' and ''Veterupris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
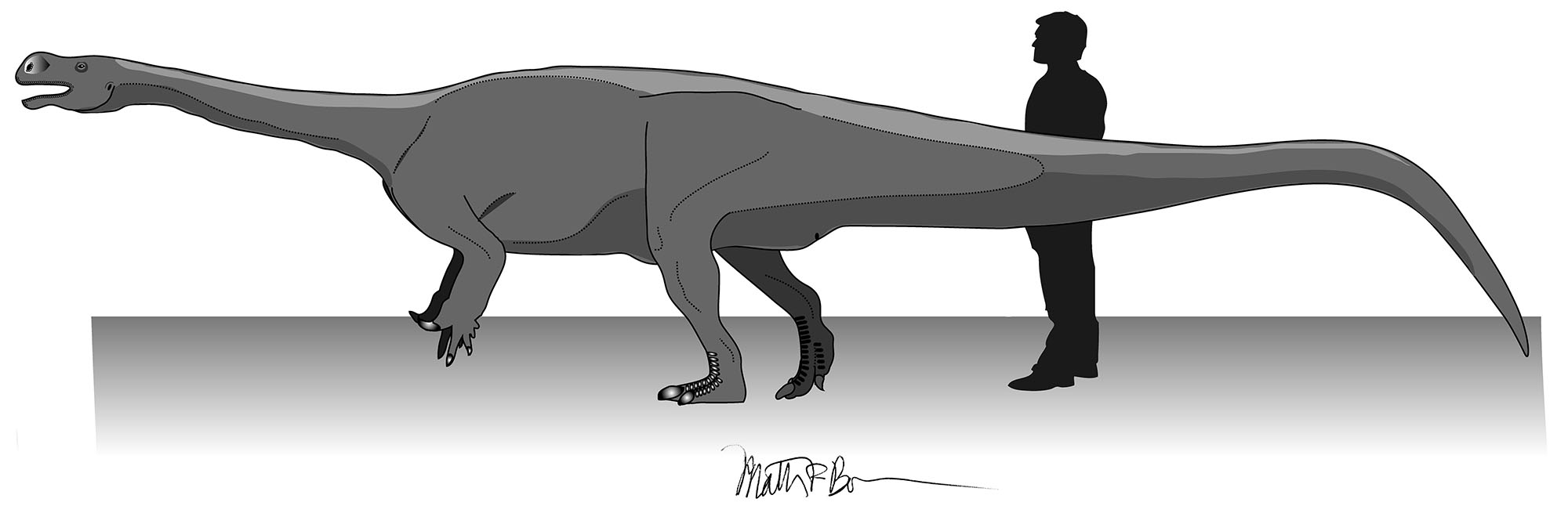
Tendaguria
''Tendaguria'' ( ; meaning "the Tendaguru one") is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic of Lindi Region, Tanzania. Discovery and naming In 1911, German geologist Wilhelm Bornhardt at Nambango in German East Africa discovered two sauropod vertebrae, fifteen kilometers (nine miles) southeast of Tendaguru Hill. These were described by Werner Janensch in 1929 but not named. The finds were formally named by José Fernando Bonaparte, Wolf-Dieter Heinrich and Rupert Wild in 2000. The type species is ''Tendaguria tanzaniensis'' () Bonaparte, Heinrich & Wild 2000. The generic name refers to the Tendaguru, the area of the great German palaeontological expeditions between 1909 and 1912. The specific name was "after Tanzania, the country where the holotype was collected".J.F. Bonaparte, W.-D. Heinrich, and R. Wild, 2000, "Review of ''Janenschia'' Wild, with the description of a new sauropod from the Tendaguru beds of Tanzania and a discussion on the systemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tornieria
''Tornieria'' ("for Tornier") is a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic in Lindi Region of Tanzania. It has a convoluted taxonomic history. Discovery and naming In 1907, German paleontologist Eberhard Fraas who was working the Tendaguru Beds in German East Africa (presently Tanzania), discovered two sauropod specimens at a single site ("Quarry A"). The two individuals, designated "Skeleton A" and "Skeleton B", each represented a different sauropod species. In 1908 he named these respectively ''Gigantosaurus africanus'' ("African giant lizard") and ''G. robustus'' ("Robust giant lizard"). A third, unrelated African species, "Gigantosaurus" ''dixeyi'', was named by Haughton in 1928, and has since been reassigned to ''Malawisaurus''. However, the name ''Gigantosaurus'' had already been used for the European sauropod ''Gigantosaurus megalonyx'' Seeley, 1869. Fraas, not intending to place his species in the same genus as this English form, had believed that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janenschia
''Janenschia'' (named after Werner Janensch) is a large herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Tendaguru Formation of Lindi Region, Tanzania around 155 million years ago. Discovery and naming ''Janenschia'' has had a convoluted nomenclatural history. In 1907, Eberhard Fraas at "site P", nine hundred metres to the southeast of Tendaguru Hill, discovered two skeletons of gigantic sauropods. They were designated as "Skeleton A" and "Skeleton B". The fossils were transported to the collection of the ''Stuttgarter Naturaliensammlung'' in Stuttgart, Germany. Fraas in 1908 decided to name both skeletons as different species of one genus, ''Gigantosaurus''. Skeleton A became ''Gigantosaurus africanus'' and skeleton B became ''Gigantosaurus robustus''. The latter species was based on the holotype partial skeleton SMNS 12144, consisting of a right hindlimb. The specific name was inspired by the heavy build of the animal. While doing so, Fraas knew full well that the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicraeosaurus
''Dicraeosaurus'' (Gr. , ' "bifurcated, double-headed" + Gr. , ' "lizard") is a genus of diplodocoid sauropod dinosaur that lived in what is now Lindi Region, Tanzania during the late Jurassic period. The genus was named for the neural spines on the back of its neck. The first fossil was described by paleontologist Werner Janensch in 1914. Description Unlike most diplodocoids, ''Dicraeosaurus'' had a comparatively large head with a relatively short and wide neck. The neck contained 12 unusually short vertebrae, likely indicating a low-level browser of vegetation no more than off the ground. ''Dicraeosaurus'' also lacked the "whiplash" tail tip typical of diplodocoids. It was smaller than many other diplodocoids, at only in length and , though this still makes it among the larger known members of the family Dicraeosauridae. The genus is notable for the rather tall neural spines protruding from its vertebrae, which it is named for. They were not straight as in some members of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
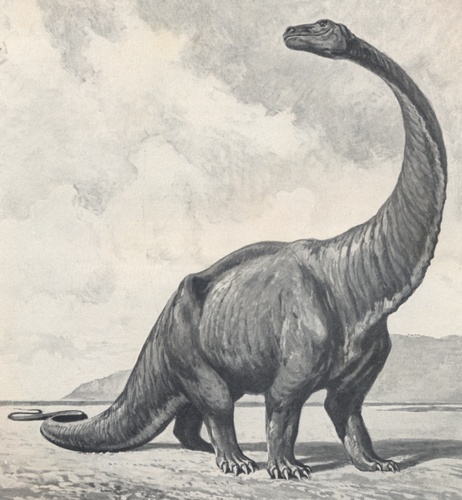
Giraffatitan
''Giraffatitan'' (name meaning "titanic giraffe") is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived during the late Jurassic Period (geology), Period (Kimmeridgian–Tithonian stages) in what is now Lindi Region, Tanzania. It was originally named as an African species of ''Brachiosaurus'' (''B. brancai''), but this has since been moved to its own genus. ''Giraffatitan'' was for many decades known as the largest dinosaur but recent discoveries of several larger dinosaurs prove otherwise; giant titanosaurians appear to have surpassed ''Giraffatitan'' in terms of sheer mass. Also, the sauropod dinosaur ''Sauroposeidon'' is estimated to be taller and possibly heavier than ''Giraffatitan''. Most size estimates for ''Giraffatitan'' are based on the specimen HMN SII, a subadult individual, but there is evidence supporting that these animals could grow larger; specimen HMN XV2, represented by a fibula 13% larger than the corresponding material on HMN SII, might have attained in length and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elaphrosaurus
''Elaphrosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of ceratosaurian theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 154 to 150 million years ago during the Late Jurassic Period in what is now Tanzania in Africa. ''Elaphrosaurus'' was a medium-sized but lightly built member of the group that could grow up to long. Morphologically, this dinosaur is significant in two ways. Firstly, it has a relatively long body but is very shallow-chested for a theropod of its size. Secondly, it has very short hindlimbs in comparison with its body. Phylogenetic analyses indicate that this genus is likely a ceratosaur. Earlier suggestions that it is a late surviving coelophysoid have been examined but generally dismissed. ''Elaphrosaurus'' is currently believed to be a very close relative of ''Limusaurus'', an unusual beaked ceratosaurian which may have been either herbivorous or omnivorous. Discovery The type specimen of ''Elaphrosaurus bambergi'' HMN Gr.S. 38–44 was recovered in the Middle Dinosaur Member of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostafrikasaurus
''Ostafrikasaurus'' is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic period of what is now Lindi Region, Tanzania. It is known only from fossil teeth discovered sometime between 1909 and 1912, during an expedition to the Tendaguru Formation by the Natural History Museum of Berlin. Eight teeth were originally attributed to the dubious dinosaur genus '' Labrosaurus'', and later to ''Ceratosaurus'', both known from the North American Morrison Formation. Subsequent studies attributed two of these teeth to a spinosaurid dinosaur, and in 2012, ''Ostafrikasaurus crassiserratus'' was named by French palaeontologist Eric Buffetaut, with one tooth as the holotype, and the other referred to the same species. The generic name comes from the German word for German East Africa, the former name of the colony in which the fossils were found, while the specific name comes from the Latin words for "thick" and "serrated", in reference to the form of the animal's teeth. ''Ostafrikasaurus'' h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veterupristisaurus
''Veterupristisaurus'' is an extinct genus of carcharodontosaurid theropod dinosaur known from the Jurassic of Tendaguru, Lindi Region of southeastern Tanzania. Discovery and naming ''Veterupristisaurus'' is known from the holotype specimen MB R 1938, an isolated middle caudal vertebra. Two partially fused posterior middle caudal vertebrae, MB R 2166, from the same locality as the holotype, are referred to this genus and most probably came from the same individual. The anterior caudal vertebra, MB R 1940, may also represent this genus. The holotype was collected in the St (EH) locality of the Tendaguru in German East Africa, from the Middle Dinosaur Member of the Tendaguru Formation, dating to the late Kimmeridgian to earliest Tithonian faunal stage of the Late Jurassic, about 154-150 million years ago. The holotype was originally referred to ''Ceratosaurus? roechlingi'' by Werner Janensch in 1925. ''Veterupristisaurus'' was named by Oliver W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to the south; Zambia to the southwest; and Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa's highest mountain, is in northeastern Tanzania. According to the United Nations, Tanzania has a population of million, making it the most populous country located entirely south of the equator. Many important hominid fossils have been found in Tanzania, such as 6-million-year-old Pliocene hominid fossils. The genus Australopithecus ranged across Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, and the oldest remains of the genus ''Homo'' are found near Lake Olduvai. Following the rise of '' Homo erectus'' 1.8 million years ago, humanity spread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)







