|
List Of Tlatelolco Rulers
This is a list of the '' tlatoque'' of the pre-Columbian era ''altepetl'' of Tlatelolco. Pre-Hispanic rulers Colonial rulers See also * List of rulers of Tenochtitlan * List of rulers of Tetzcoco * Family tree of Aztec monarchs *Aztec Empire The Aztec Empire or the Triple Alliance ( nci, áxcán Tlahtéléyán, jûˋùòkaùnäË tëÀè˜aòtoùùlû°ùjaùnäË was an alliance of three Nahua city-states: , , and . These three city-states ruled that area in and around the Valley of Mexic ... Notes References *{{cite book , author=Chimalpahin Cuauhtlehuanitzin, Domingo Francisco de San Antû°n MuûÝû°n , authorlink=Chimalpahin , year=1997 , title=Codex Chimalpahin: society and politics in Mexico Tenochtitlan, Tlatelolco, Texcoco, Culhuacan, and other Nahua altepetl in central Mexico: the Nahuatl and Spanish annals and accounts collected and recorded by don Domingo de San Antû°n MuûÝû°n Chimalpahin Quauhtlehuanitzin , others=edited and translated by Arthur J. O. Anderson and Sus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlatoani
''Tlatoani'' ( , "one who speaks, ruler"; plural ' or tlatoque) is the Classical Nahuatl term for the ruler of an , a pre-Hispanic state. It is the noun form of the verb "tlahtoa" meaning "speak, command, rule". As a result, it has been variously translated in English as "king", "ruler", or "speaker" in the political sense. Above a tlahtoani is the ''Weyi Tlahtoani,'' sometimes translated as "Great Speaker", though more usually as "Emperor" (the term is often seen as the equivalent to the European " great king"). A ' () is a female ruler, or queen regnant. The term refers to "vice-leader". The leaders of the Mexica prior to their settlement are sometimes referred to as , as well as colonial rulers who were not descended from the ruling dynasty. The ruler's lands were called , and the ruler's house was called ''Nahuatl dictionary'' (1997). Wired humanities project. Retrieved January 1, 2012, frolink/ref> The city-states of the Aztec Empire each had their own tlatoani, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
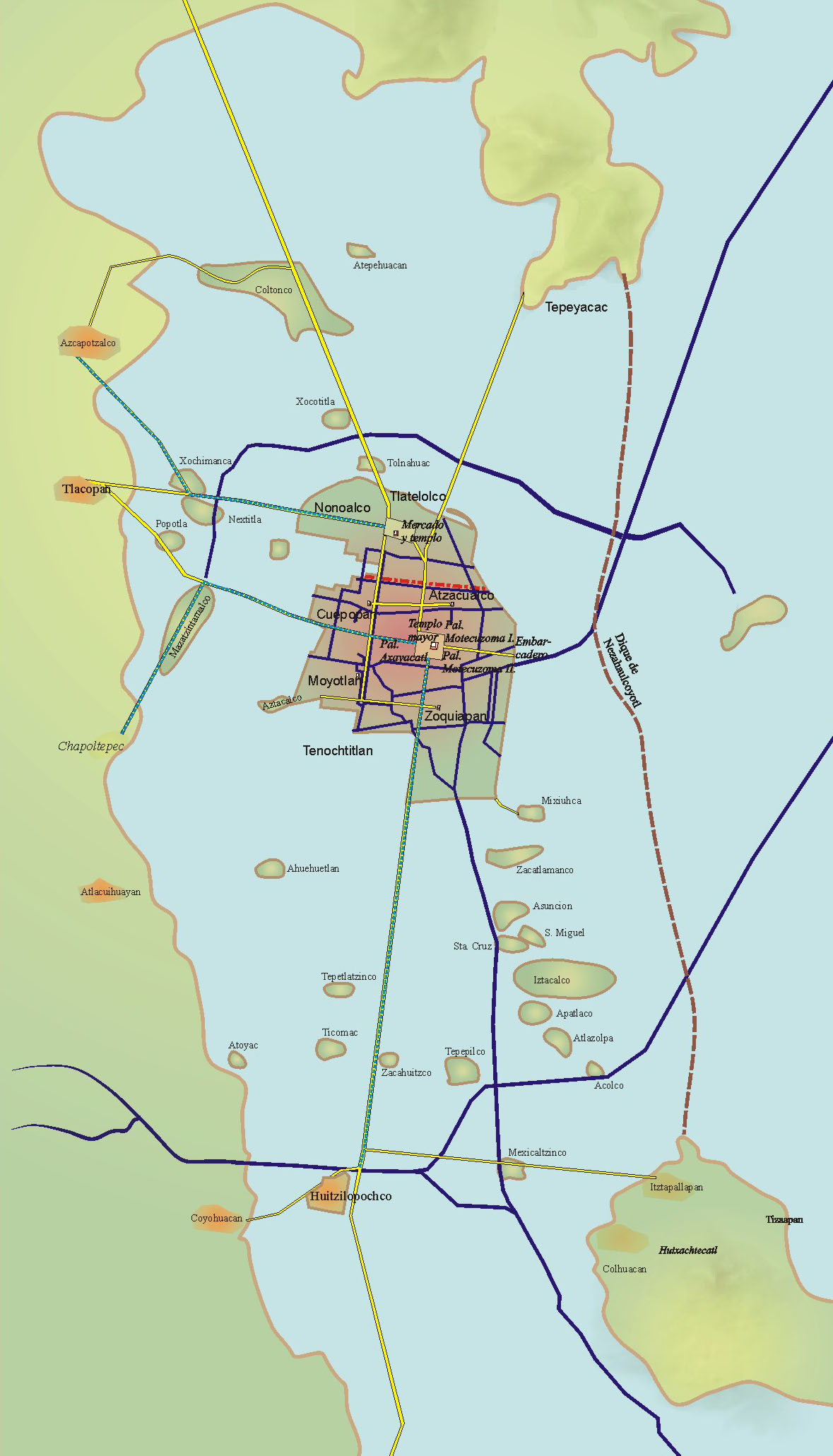
Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, Mûˋxico-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was captured by the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a '' cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or polities) on the island, the other being . The city is located in modern-day Mexico City. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
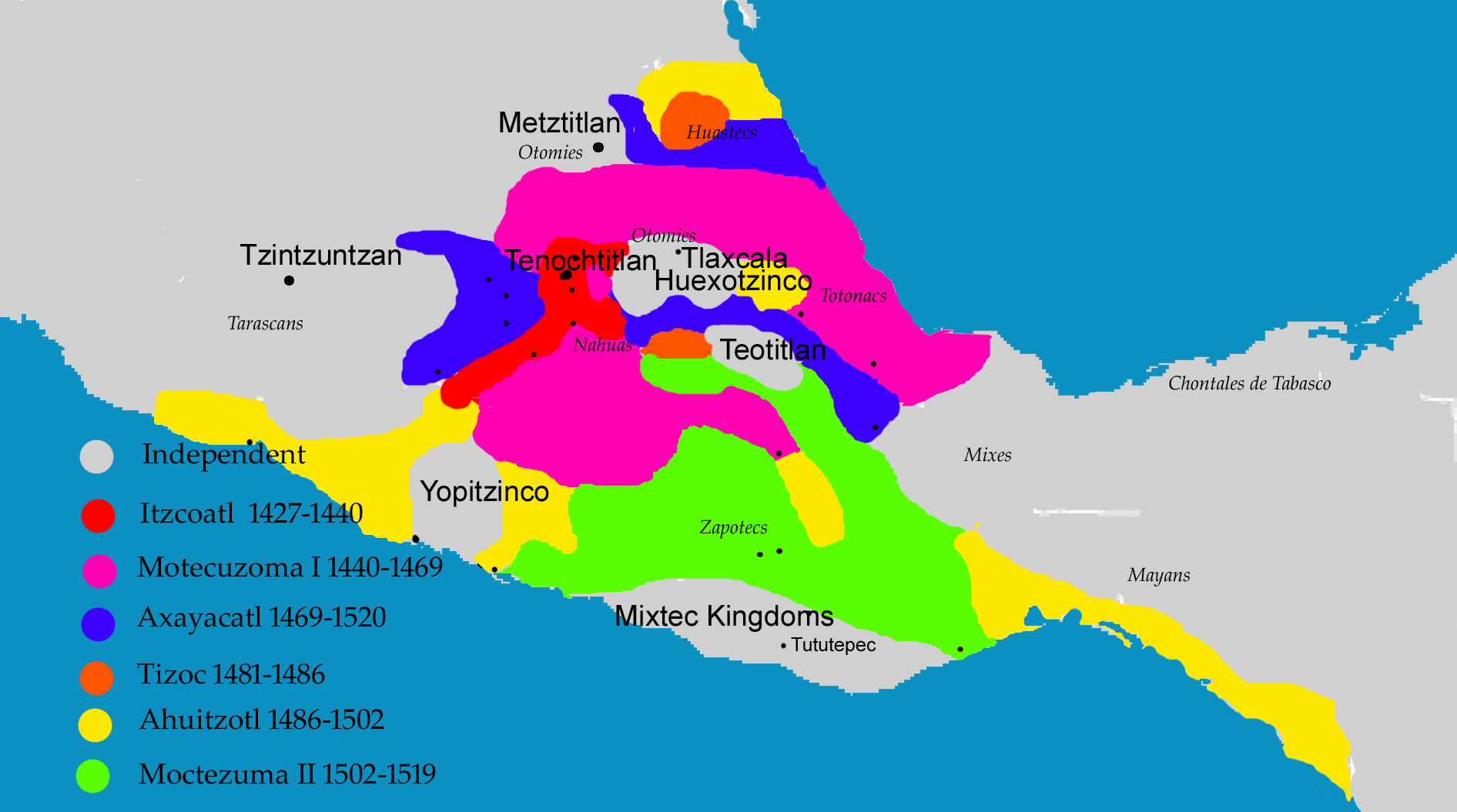
Aztec Empire
The Aztec Empire or the Triple Alliance ( nci, áxcán Tlahtéléyán, jûˋùòkaùnäË tëÀè˜aòtoùùlû°ùjaùnäË was an alliance of three Nahua city-states: , , and . These three city-states ruled that area in and around the Valley of Mexico from 1428 until the combined forces of the Spanish and their native allies who ruled under defeated them in 1521. The alliance was formed from the victorious factions of a civil war fought between the city of and its former tributary provinces. Despite the initial conception of the empire as an alliance of three self-governed city-states, the capital became dominant militarily. By the time the Spanish arrived in 1519, the lands of the alliance were effectively ruled from , while other partners of the alliance had taken subsidiary roles. The alliance waged wars of conquest and expanded after its formation. The alliance controlled most of central Mexico at its height, as well as some more distant territories within Mesoamerica, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Tree Of Aztec Monarchs
The following is a family tree of the Mexica Emperors from 1376 to 1525. See also *List of Tenochtitlan rulers {{Aristocratic family trees Aztec The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ... Mexican noble families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rulers Of Tetzcoco
This is a list of Mesoamerican rulers of the ''altepetl'' of Tetzcoco from the time the city began being ruled by ''tlatoque'' in 1298 to the end of the line of indigenous rulers. From the early 15th century to 1521, Tetzcoco was one of the three leading members of the Triple Alliance, commonly known as the Aztec Empire, but was often subservient to the rulers of Tenochtitlan. The Aztec Empire was conquered by Spain in 1521, but the Spanish colonial authorities continued to appoint ''tlatoque'' of Tetzcoco until the office was abolished in 1564. Pre-colonial rulers (1298ã1521) Early Tetzcoco (1298ã1431) The ''tlatoque'' of Tetzcoco were descendants and successors of earlier ''tlatoque'' of the Chichimeca, succeeding Xolotl (1172ã1232), Nopaltzin (1232ã1263) and Tlotzin (1263ã1298). In the Triple Alliance (1431ã1521) Colonial period (1521ã1564) The line of ''tlatoque'' continued in Tetzococo after the Spanish conquest. Adept at navigating the new Spani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rulers Of Tenochtitlan
This is a list of Mesoamerican rulers of the ''altepetl'' of Tenochtitlan (modern Mexico City) from its foundation in 1325 until the end of the line of indigenous rulers. From c. 1375 onwards, the rulers of Tenochtitlan were monarchs and used the title ''tlatoani''. From 1427 to 1521, the ''tlatoque'' of Tenochtitlan were alongside those of the cities Tetzcoco and Tlacopan the leaders of the powerful Triple Alliance, commonly known as the Aztec Empire. The rulers of Tenochtitlan were always pre-eminent and gradually transitioned into the sole rulers of the empire; under either Tizoc (1481ã1486) or Ahuitzotl (1486ã1502), the ''tlatoque'' of Tenochtitlan assumed the grander title ''huehuetlatoani'' ("supreme ''tlatoani''") to indicate their superiority over the other ''tlatoque'' in the alliance. The evolution into full autocracy was finished by 1502, when Moctezuma II was elected as ''huehuetlatoani'' of Tenochtitlan without the traditional input from Tetzoco and Tlacopan. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diego De Mendoza
Diego de Mendoza ( 4 House (1549)Chimalpahin (1997): pp. 172ã173. ã 5 Rabbit (1562)Chimalpahin (1997): pp. 174ã175, 236ã237.) was a ''tlatoani'' (king) of the Nahua city Tlatelolco. Name His name is a Spanish version of Yaò£áqébh (Jacob). ''Mendoza'' means ''cold mountain''. Life He was a colonial ruler, son of Zayoltzin. He died on 20 December, 5 Rabbit (1562). His successor was the last ruler of Tlatelolco - Miguel GarcûÙa Oquiztzin This is a list of the '' tlatoque'' of the pre-Columbian era ''altepetl'' of Tlatelolco. Pre-Hispanic rulers Colonial rulers See also * List of rulers of Tenochtitlan * List of rulers of Tetzcoco * Family tree of Aztec monarchs *Aztec Empire .... Notes {{reflist Tlatoque of Tlatelolco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quauhtlatoani
''Cuáuhtlahtoáni'' or ''CuûÊuhtlahtoh'' is a titular office of governorship and political administration, used within certain city-states and provinces among the Aztecs of pre-Columbian central Mexico in the Late Postclassic period. The office of ''cuauhtlatoani'' (a Nahuatl word meaning approximately, "the one who speaks like eagle") carried the connotation of "military ruler" or "appointed administrator". During the rise of the Aztec Empire the title was given by the ruling Mexica- Tenochca to the governors they imposed on conquered city-states in central provinces. A Tlatoani ("the one who speaks") was an independent ruler of an Aztec/Mexica polity (altepetl). Cuauhtlatoani were appointed by a Tlatoani to rule conquered areas or areas whose independence was lost such as the city Tlatelolco following the 1473 CE defeat of its last Tlatoani, Moquihuix, by Tenochtitlan. Tlatelolco was governed by Cuauhtlatoque until the death of Itzquauhtzin in 1520 CE. The title is also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance ethnic group native to Spain. Within Spain, there are a number of national and regional ethnic identities that reflect the country's complex history, including a number of different languages, both indigenous and local linguistic descendants of the Roman-imposed Latin language, of which Spanish is the largest and the only one that is official throughout the whole country. Commonly spoken regional languages include, most notably, the sole surviving indigenous language of Iberia, Basque, as well as other Latin-descended Romance languages like Spanish itself, Catalan and Galician. Many populations outside Spain have ancestors who emigrated from Spain and share elements of a Hispanic culture. The most notable of these comprise Hispanic America in the Western Hemisphere. The Roman Republic conquered Iberia during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC. Hispania, the name given to Iberia by the Romans as a province of their Empire, became highly accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moctezuma And Itzquauhtzin
Montezuma or Moctezuma may refer to: People * Moctezuma I (1398ã1469), the second Aztec emperor and fifth king of Tenochtitlan * Moctezuma II (c. 1460ã1520), ninth Aztec emperor ** Pedro Moctezuma, a son of Montezuma II ** Isabel Moctezuma (1509/1510ã1550/1551), a daughter of Montezuma II *** Leonor Cortûˋs Moctezuma (c. 1528ã?), daughter of HernûÀn Cortûˋs and Isabel Montezuma **** Isabel de Tolosa Cortûˋs de Moctezuma (1568ã1619/1620), Mexican heiress, great-granddaughter of Montezuma II * Duke of Moctezuma de Tultengo, a Spanish hereditary title held by descendants of Moctezuma II * Carlos Montezuma (c. 1860ã1923), Yavapai/Apache Native American activist * Carlos Lû°pez Moctezuma (1909ã1980), Mexican film actor * Eduardo Matos Moctezuma (born 1940), Mexican archaeologist * Esteban Moctezuma (born 1954), Mexican politician * Julio Rodolfo Moctezuma (1927ã2000), Mexican lawyer, politician and banker * Leonidas de Montezuma (1869ã1937), English cricketer * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itzquauhtzin
Itzquauhtzin ( 9 Reed (1475)Chimalpahin (1997): pp. 140ã141. ã 2 Flint (1520)Chimalpahin (1997): pp. 158ã159.) was a king (''tlatoani'') of Nahua ''altepetl'' Tlatelolco. He was mentioned in '' Chimalpahin Codex''. Biography Itzquauhtzin was a son of the king Tlacateotl and his aunt Xiuhcanahualtzin and grandson of Quaquapitzahuac and queen Acxocueitl. His brother was king Tezozomoctli. He was a '' quauhtlatoani'' (interim ruler). He was installed by Emperor Axayacatl of Tenochtitlan , ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, Mûˋxico-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was ... and killed by the Spaniards.Chimalpahin (1997): pp. 158ã159 His successor was Diego de Mendoza. Notes {{reflist Tlatoque of Tlatelolco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axayacatl
Axayacatl (; nci, áxáyacatl ; es, AxayûÀcatl ; meaning "face of water"; ã1481) was the sixth of the of Tenochtitlan and Emperor of the Aztec Triple Alliance. Biography Early life and background Axayacatl was a son of the princess Atotoztli II and her cousin, prince Tezozomoc. He was a grandson of the Emperors Moctezuma I and Itzcoatl. He was a descendant of the king Cuauhtototzin. He was a successor of Moctezuma and his brothers were Emperors Tizoc and Ahuitzotl and his sister was the Queen Chalchiuhnenetzin. He was an uncle of the Emperor Cuauhtûˋmoc and father of Emperors Moctezuma II and CuitlûÀhuac. Rise to power During his youth, his military prowess gained him the favor influential figures such as Nezahualcoyotl and Tlacaelel I, and thus, upon the death of Moctezuma I in 1469, he was chosen to ascend to the throne, much to the displeasure of his two older brothers, Tizoc and Ahuitzotl. It is also important that the Great Sun Stone, also known as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |