|
List Of Telescope Types
The following are lists of devices categorized as types of telescopes or devices associated with telescopes. They are broken into major classifications with many variations due to professional, amateur, and commercial sub-types. Telescopes can be classified by optical design or mechanical design/construction. Telescopes can also be classified by where they are placed, such as space telescopes. One major determining factor is type of light, or particle being observed including devices referred to as "telescopes" that do not form an image or use optics. Some telescopes are classified by the task they perform; for example Solar telescopes are all designs that look at the Sun, Dobsonian telescopes are designed to be low cost and portable, Aerial telescopes overcame the optical shortcomings of 17th-century objective lenses, etc. List of optical telescope types Optical telescopes can be classified by three primary optical designs (refractor, reflector, or catadioptric), by sub-designs o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects, the word ''telescope'' now refers to a wide range of instruments capable of detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors. The first known practical telescopes were refracting telescopes with glass lenses and were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 17th century. They were used for both terrestrial applications and astronomy. The reflecting telescope, which uses mirrors to collect and focus light, was invented within a few decades of the first refracting telescope. In the 20th century, many new types of telescopes were invented, including radio telescopes in the 1930s and infrared telescopes in the 1960s. Etymology The word ''telescope'' was coin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-achromatic Objective
A non-achromatic objective is an objective lens which is not corrected for chromatic aberration. In telescopes they can a be pre-18th century simple single element objective lenses which were used before the invention of doublet achromatic lenses. They can also be specialty monochromatic lenses used in modern research telescopes and other instruments. Non-achromatic telescope objectives Early non-achromatic objectives Early telescope objective, such as those built by Johannes Hevelius and Christiaan Huygens and his brother Constantijn Huygens, Jr., utilized single small (2"-8") positive lenses with enormous focal lengths (up to 150 feet in length in tube telescopes and up to 600 feet in non-tube aerial telescopes). This allowed the observer to use higher magnification while limiting the interfering rainbow halos caused by chromatic aberration (the uncorrected chromatic aberration fell within the large diffraction pattern at focus). Modern non-achromatic objectives Modern instrumen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Liquid Mirror Telescope
Liquid-mirror telescopes are telescopes with mirrors made with a reflective liquid. The most common liquid used is mercury, but other liquids will work as well (for example, low-melting alloys of gallium). The liquid and its container are rotated at a constant speed around a vertical axis, which causes the surface of the liquid to assume a paraboloidal shape. This parabolic reflector can serve as the primary mirror of a reflecting telescope. The rotating liquid assumes the same surface shape regardless of the container's shape; to reduce the amount of liquid metal needed, and thus weight, a rotating mercury mirror uses a container that is as close to the necessary parabolic shape as possible. Liquid mirrors can be a low-cost alternative to conventional large telescopes. Compared to a solid glass mirror that must be cast, ground, and polished, a rotating liquid-metal mirror is much less expensive to manufacture. Isaac Newton noted that the free surface of a rotating liquid forms a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregorian Telescope
The Gregorian telescope is a type of reflecting telescope designed by Scottish mathematician and astronomer James Gregory in the 17th century, and first built in 1673 by Robert Hooke. James Gregory was a contemporary of Isaac Newton. Both often worked simultaneously on similar projects. Gregory's design was published in 1663 and pre-dates the first practical reflecting telescope, the Newtonian telescope, built by Sir Isaac Newton in 1668."Isaac Newton: adventurer in thought", by Alfred Rupert Hallpage 67 However, Gregory's design was only a theoretical description, and he never actually constructed the telescope. It was not successfully built until five years after Newton's first reflecting telescope. History The Gregorian telescope is named after the James Gregory design, which appeared in his 1663 publication (The Advance of Optics). Similar theoretical designs have been found in the writings of Bonaventura Cavalieri ( (On Burning Mirrors), 1632) and Marin Mersenne (, 1636). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossed Dragone
The Crossed Dragone Telescope is an off-axis telescope design consisting of a parabolic primary mirror and a large concave secondary mirror arranged so that the focal plane is at right angles to the incoming light. In this configuration the polarization of light is preserved through the optics. Other advantages of this design are a large field of view in a compact volume. Due to its off-axis nature the secondary mirror does not block any of the incoming light. At millimeter and submillimeter wavelengths this greatly decreases systematic effects due to diffraction. The main disadvantage is that the size of the secondary mirror is of similar size to the primary mirror making it expensive to make and heavy (requiring large supports). However, for professional applications where low systematic effects are critical (for example in cosmic microwave background In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
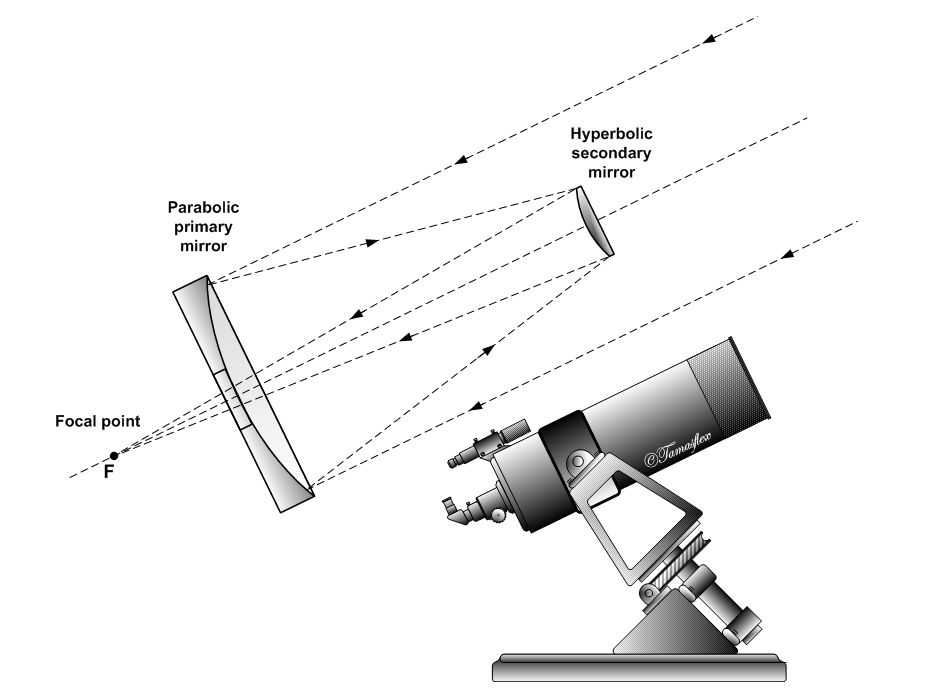
Ritchey–Chrétien Telescope
A Ritchey–Chrétien telescope (RCT or simply RC) is a specialized variant of the Cassegrain telescope that has a hyperbolic primary mirror and a hyperbolic secondary mirror designed to eliminate off-axis optical errors (coma). The RCT has a wider field of view free of optical errors compared to a more traditional reflecting telescope configuration. Since the mid 20th century, a majority of large professional research telescopes have been Ritchey–Chrétien configurations; some well-known examples are the Hubble Space Telescope, the Keck telescopes and the ESO Very Large Telescope. History The Ritchey–Chrétien telescope was invented in the early 1910s by American astronomer George Willis Ritchey and French astronomer Henri Chrétien. Ritchey constructed the first successful RCT, which had an aperture diameter of in 1927 (e.g. Ritchey 24-inch reflector). The second RCT was a instrument constructed by Ritchey for the United States Naval Observatory; that telescope is st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasmyth Telescope
The Nasmyth telescope, also called Nasmyth–Cassegrain or Cassegrain–Nasmyth, is a reflecting telescope developed by the Scottish inventor James Nasmyth. It is a modified form of a Cassegrain telescope, with light reflected sideways to an eyepiece. Scheme As in the Cassegrain telescope, the light falls on a concave primary mirror, then is reflected towards a convex secondary mirror. A comparatively small tertiary flat mirror reflects the light to one of the sides of the telescope. (The central hole in the primary mirror may still host a Cassegrain focus if the tertiary can be moved out of the way.) This flat mirror is placed on the altitude axis, so that the beam exits through a hole in the middle of the altitude bearing. This means the eyepiece or instrument does not need to move up and down with the telescope as the tertiary mirror's angle with the main telescope axis is adjustable as a function of the telescope's pointing and the star's elevation above the horizon; therefor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dall–Kirkham Telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Many variant forms are in use and some employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a catoptric telescope. From the time of Newton to the 1800s, the mirror itself was made of metal usually speculum metal. This type included Newton's first designs and even the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
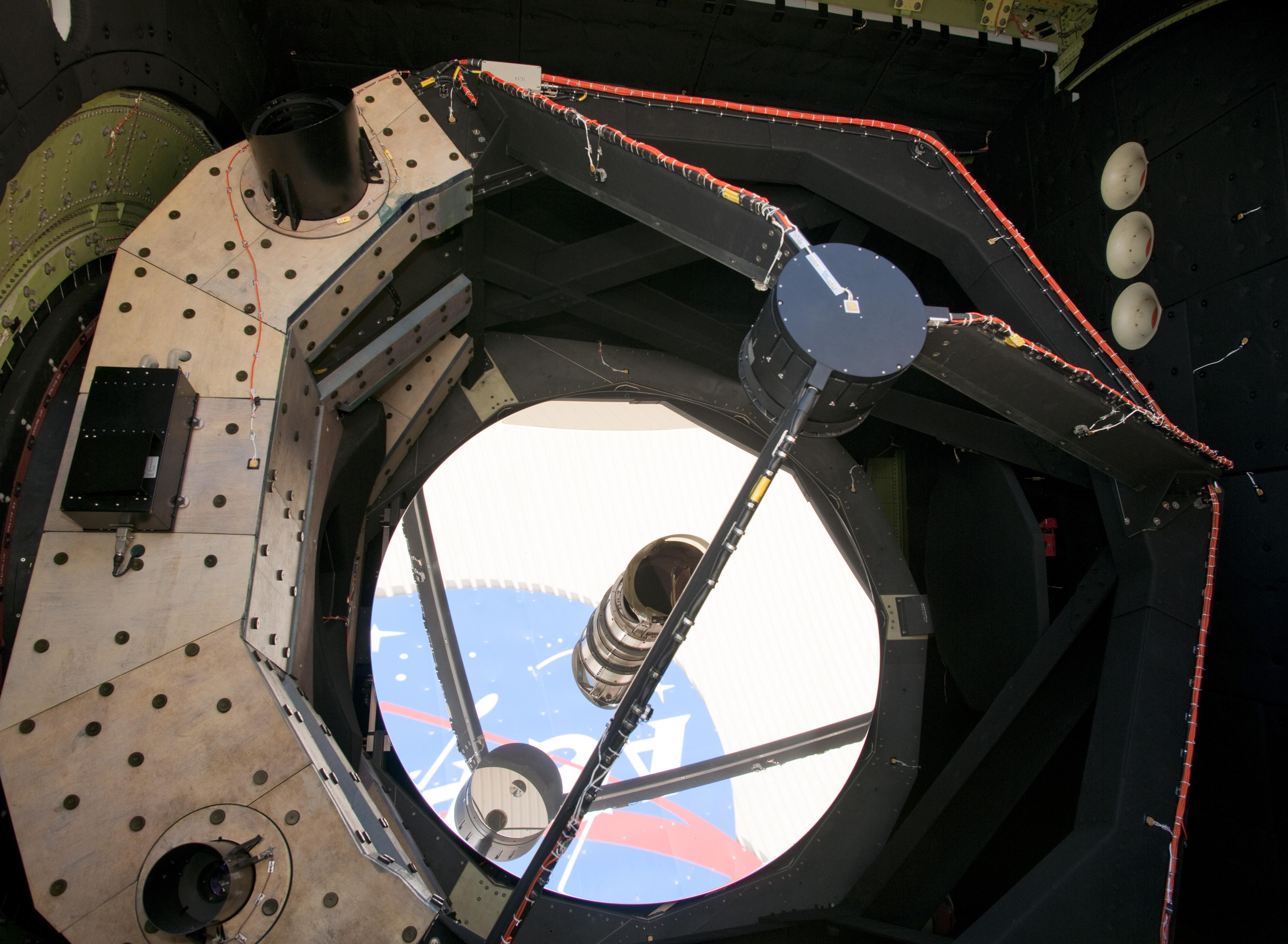
Cassegrain Telescope
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the primary mirror (or both). The classic Cassegrain co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catoptrics
Catoptrics (from grc-gre, κατοπτρικός ''katoptrikós'', "specular", from grc-gre, κάτοπτρον ''katoptron'' "mirror") deals with the phenomena of reflected light and image-forming optical systems using mirrors. A catoptric system is also called a ''catopter'' (''catoptre''). Ancient texts ''Catoptrics'' is the title of two texts from ancient Greece: *The Pseudo-Euclidean ''Catoptrics''. This book is attributed to Euclid, although the contents are a mixture of work dating from Euclid's time together with work which dates to the Roman period., accessed 31 January 2013 It has been argued that the book may have been compiled by the 4th century mathematician Theon of Alexandria. The book covers the mathematical theory of mirrors, particularly the images formed by plane and spherical concave mirrors. *Hero's ''Catoptrics''. Written by Hero of Alexandria, this work concerns the practical application of mirrors for visual effects. In the Middle Ages, this work was fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
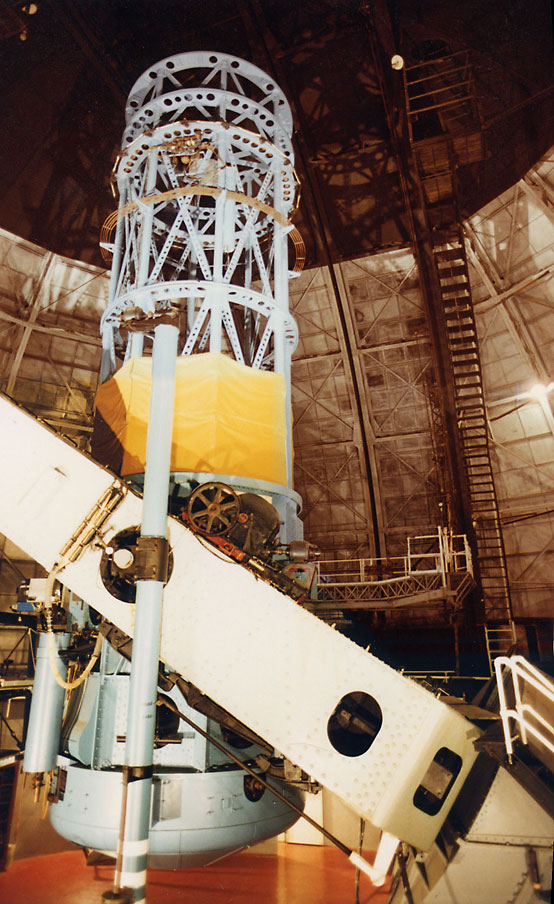
Reflecting Telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Many variant forms are in use and some employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a catoptrics, catoptric telescope. From the time of Newton to the 1800s, the mirror itself was made of metal usually speculum metal. This type included Newton's first designs and eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
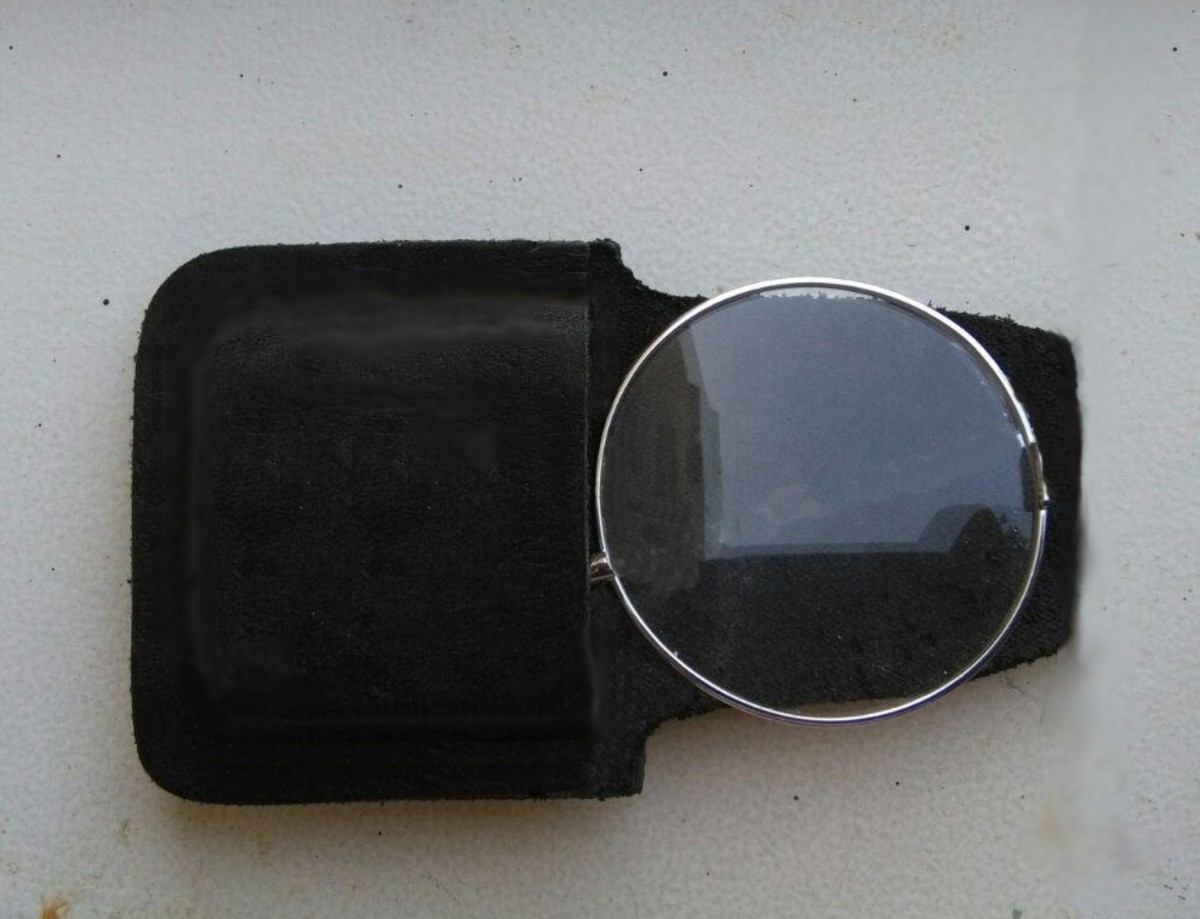
Baden-Powell's Unilens
The unilens monocular is a simple refracting telescope for field use, designed by Robert Baden-Powell, 1st Baron Baden-Powell, Robert Baden-Powell. Consisting of only one Lens (optics), lens, it is the simplest of all telescopes, and while occupying very little space can still magnify a distant image up to about four times. The nature of its operation however does not accommodate to everyone's visual acuity, with only three out of four people able to use it. Description and use The unilens monocular is simply a 2.5 inch (6.4 cm) diameter convex lens with a 6 foot (1.8 m) focal length, equivalent to +0.55 dioptres. In use the eye is closer than 6 feet to the lens (usually 3–4 feet) and thus between the lens and its principal focus. Accommodation (eye), Eye accommodation required is similar to that when viewing objects in the far distance, but more so as actual accommodation is made for somewhere beyond accommodation for infinity. Because of this unusual requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |