|
List Of People Convicted Of Treason
This is a list of people convicted of treason. Some countries have a high constitutional hurdle to conviction for treason, while many countries have less stringent definitions. Armenia * Meruzhan Artzruni, Lord Prince of Vaspurakan (? – 369), for conspiring with one of the Great Persian Kings, Shapur II against his liege-lord, Armenian King Arsaces II (Arshak II), whom he betrayed to Persia. He was captured by Arsaces II's son King Papas (Pap) and executed. Austria * Count Lajos Batthyány de Németújvár, for involvement in the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. Executed by firing squad on the same day as the 13 Martyrs of Arad. Austria-Hungary * Nedeljko Čabrinović, for conspiring to assassinate Archduke Franz Ferdinand * Vaso Čubrilović, for conspiring to assassinate Archduke Franz Ferdinand * Veljko Čubrilović, for conspiring to assassinate Archduke Franz Ferdinand * Trifko Grabez, for conspiring to assassinate Archduke Franz Ferdinand * Danilo Ilić, for consp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplomats, or its secret services for a hostile and foreign power, or attempting to kill its head of state. A person who commits treason is known in law as a traitor. Historically, in common law countries, treason also covered the murder of specific social superiors, such as the murder of a husband by his wife or that of a master by his servant. Treason (i.e. disloyalty) against one's monarch was known as ''high treason'' and treason against a lesser superior was ''petty treason''. As jurisdictions around the world abolished petty treason, "treason" came to refer to what was historically known as high treason. At times, the term ''traitor'' has been used as a political epithet, regardless of any verifiable treasonable action. In a civil war or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gavrilo Princip
Gavrilo Princip ( sr-Cyrl, Гаврило Принцип, ; 25 July 189428 April 1918) was a Bosnian Serb student who assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria and his wife Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg, in Sarajevo on 28 June 1914. Princip was born in western Bosnia to a poor Serb family. At the age of 13, he was sent to Sarajevo, the capital of Austrian-occupied Bosnia, to study at the Merchants’ School before transferring to the gymnasium where he became politically aware. In 1911, he joined Young Bosnia, a secret local society aiming to free Bosnia from Austrian rule and achieve the unification of the South Slavs. After attending anti-Austrian demonstrations in Sarajevo, he was expelled from school and walked to Belgrade, Serbia to continue his education. During the First Balkan War, Princip traveled to Southern Serbia to volunteer with the Serbian army's irregular forces fighting against the Ottoman Empire but was rejected for being too small and weak. In 1913 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor of Japan as supreme commander of the army and the Imperial Japanese Navy. Later an Inspectorate General of Aviation became the third agency with oversight of the army. During wartime or national emergencies, the nominal command functions of the emperor would be centralized in an Imperial General Headquarters (IGHQ), an ad hoc body consisting of the chief and vice chief of the Army General Staff, the Minister of the Army, the chief and vice chief of the Naval General Staff, the Inspector General of Aviation, and the Inspector General of Military Training. History Origins (1868–1871) In the mid-19th century, Japan had no unified national army and the country was made up of feudal domains (''han'') with the Tokugawa shogunate (''bakufu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergeant
Sergeant (abbreviated to Sgt. and capitalized when used as a named person's title) is a rank in many uniformed organizations, principally military and policing forces. The alternative spelling, ''serjeant'', is used in The Rifles and other units that draw their heritage from the British light infantry. Its origin is the Latin , 'one who serves', through the French term . The term ''sergeant'' refers to a non-commissioned officer placed above the rank of a corporal, and a police officer immediately below a lieutenant in the US, and below an inspector in the UK. In most armies, the rank of sergeant corresponds to command of a squad (or section). In Commonwealth armies, it is a more senior rank, corresponding roughly to a platoon second-in-command. In the United States Army, sergeant is a more junior rank corresponding to a squad- (12 person) or platoon- (36 person) leader. More senior non-commissioned ranks are often variations on sergeant, for example staff sergeant, gunn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamloops
Kamloops ( ) is a city in south-central British Columbia, Canada, at the confluence of the South flowing North Thompson River and the West flowing Thompson River, east of Kamloops Lake. It is located in the Thompson-Nicola Regional District, whose district offices are based here. The surrounding region is sometimes referred to as the Thompson Country. The city was incorporated in 1893 with about 500 residents. The Canadian Pacific Railroad was completed through downtown in 1886, and the Canadian National arrived in 1912, making Kamloops an important transportation hub. With a 2021 population of 97,902, it is the twelfth largest municipality in the province. The Kamloops census agglomeration is ranked 36th among census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada with a 2021 population of 114,142. Kamloops is promoted as the ''Tournament Capital of Canada''. It hosts more than 100 sporting tournaments each year (hockey, baseball, curling, etc) at world-class sports fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanao Inouye
Kanao Inouye (May 24, 1916 – August 27, 1947) was a Canadian citizen of Japanese descent, convicted of high treason and war crimes for his actions during World War II. Known as the "Kamloops Kid", he served as an interpreter and prison camp guard for the Imperial Japanese Army and the Kenpeitai political police. Early life in Canada A Nisei (second-generation Japanese-Canadian), Kanao Inouye was born to immigrant parents in Kamloops, British Columbia. His father, Tadashi Inouye, had emigrated to British Columbia from Tokyo, and had been a decorated Canadian soldier during World War I.Brode P,Canada's war criminal Kanao Inouye, ''Esprit de Corps'', December 2002. Although his father died in 1926, Inouye at his first trial described his life in Canada as happy. His family nevertheless maintained close ties to Japan, where his grandfather, Chotahara Inouye, was a Member of Parliament in the House of Peers. After he graduated from Vancouver Technical School, Inouye's family urge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
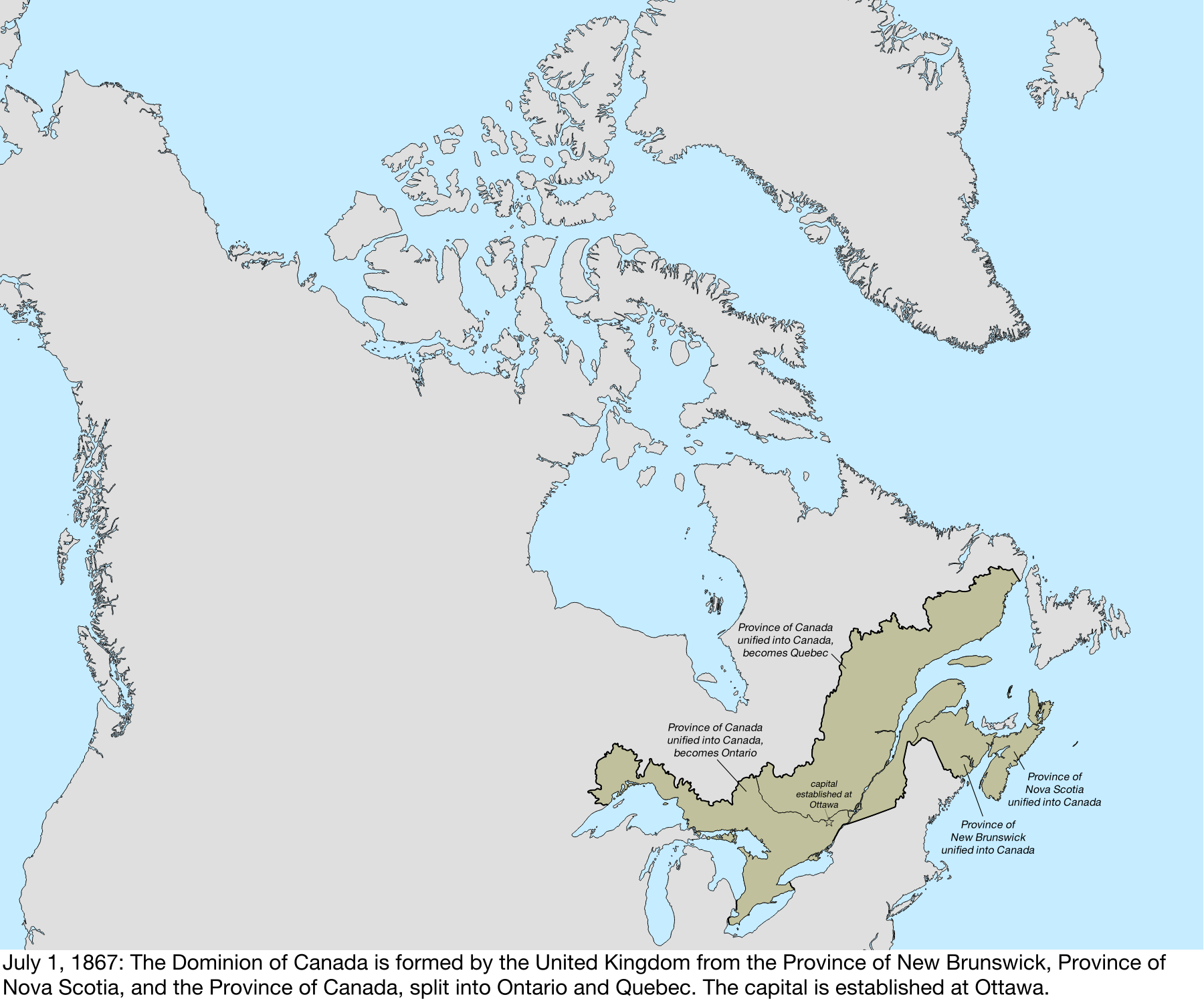
Territorial Evolution Of Canada
The history of post-confederation Canada began on July 1, 1867, when the British North American colonies of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia were united to form a single Dominion within the British Empire. Upon Confederation, the United Province of Canada was immediately split into the provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The colonies of Prince Edward Island and British Columbia joined shortly after, and Canada acquired the vast expanse of the continent controlled by the Hudson's Bay Company, which was eventually divided into new territories and provinces. Canada evolved into a fully sovereign state by 1982. Before being part of British North America, the constituents of Canada consisted of the former colonies of Canada and Acadia from within New France which had been ceded to Great Britain in 1763 as part of the Treaty of Paris. French Canadian nationality was maintained as one of the "two founding nations" and legally through the Quebec Act which ensured the maintenance of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North-West Rebellion
The North-West Rebellion (french: Rébellion du Nord-Ouest), also known as the North-West Resistance, was a resistance by the Métis people under Louis Riel and an associated uprising by First Nations Cree and Assiniboine of the District of Saskatchewan against the Canadian government. Many Métis felt that Canada was not protecting their rights, their land, and their survival as a distinct people. Riel had been invited to lead the movement of protest; he turned it into a military action with a heavily religious tone. That alienated Catholic clergy, whites, most Indigenous tribes, and some Métis, but he had the allegiance of 200 armed Métis, a smaller number of other Indigenous warriors, and at least one white man at Batoche in May 1885, who confronted 900 Canadian militia and some armed local residents. About 91 people would die in the fighting that occurred that spring before the resistance's collapse. Despite some notable early victories at Duck Lake, Fish Creek, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Métis People (Canada)
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United States. They have a shared history and culture which derives from specific mixed European (primarily French) and Indigenous ancestry which became a distinct culture through ethnogenesis by the mid-18th century, during the early years of the North American fur trade. In Canada, the Métis, with a population of 624,220 as of 2021, are one of three major groups of Indigenous peoples that were legally recognized in the Constitution Act of 1982, the other two groups being the First Nations and Inuit. Smaller communities who self-identify as Métis exist in Canada and the United States, such as the Little Shell Tribe of Chippewa Indians of Montana. The United States recognizes the Little Shell Tribe as an Ojibwe Native American tribe. Alberta is the only Canadian province with a recognized Métis Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Riel
Louis Riel (; ; 22 October 1844 – 16 November 1885) was a Canadian politician, a founder of the province of Manitoba, and a political leader of the Métis people. He led two resistance movements against the Government of Canada and its first prime minister John A. Macdonald. Riel sought to defend Métis rights and identity as the Northwest Territories came progressively under the Canadian sphere of influence. The first resistance movement led by Riel was the Red River Resistance of 1869–1870. The provisional government established by Riel ultimately negotiated the terms under which the new province of Manitoba entered the Canadian Confederation. However, while carrying out the resistance, Riel had a Canadian nationalist, Thomas Scott, executed. Riel soon fled to the United States to escape prosecution. He was elected three times as member of the House of Commons, but, fearing for his life, he could never take his seat. During these years in exile he came to believe that he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_frontispiece_-_BL.jpg)