|
List Of PET Radiotracers
This is a list of positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracers. These are chemical compounds in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a short-lived, positron emitting radioisotope. Cardiology * 15Owater *[Nitrogen-13">13N">Oxygen-15">15O">Oxygen-15.html" ;"title="/nowiki> 15Owater *[Nitrogen-13">13Nammonia *[Rubidium-82">82Rb">Oxygen-15">15Owater *[Nitrogen-13">13Nammonia *[Rubidium-82">82RbRubidium-82 chloride *[Carbon-11, 11C] Acetate (Also used in oncology) Neurology * 11C">sup>11C25B-NBOMe (Cimbi-36) * 18F">sup>18FAltanserin * 11C">sup>11C Carfentanil * 11C">sup>11C DASB * 11C">sup>11CDTBZ or 18F">sup>18Fluoropropyl-DTBZ * 11C">sup>11C 11C">sup>11CME@HAPTHI * 18F">sup>18FFallypride * 18F">sup>18F Florbetaben * 18F">sup>18F Flubatine * 18F">sup>18F Fluspidine * 18F">sup>18F Florbetapir * 18F">sup>18For 11C">sup>11C Flumazenil * 18F">sup>18F Flutemetamol * 18F">sup>18FFluorodopa * 18F">sup>18FDesmethoxyfallypride * 18F">sup>18FMefway * 18F">sup>18FMPPF * 18F" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
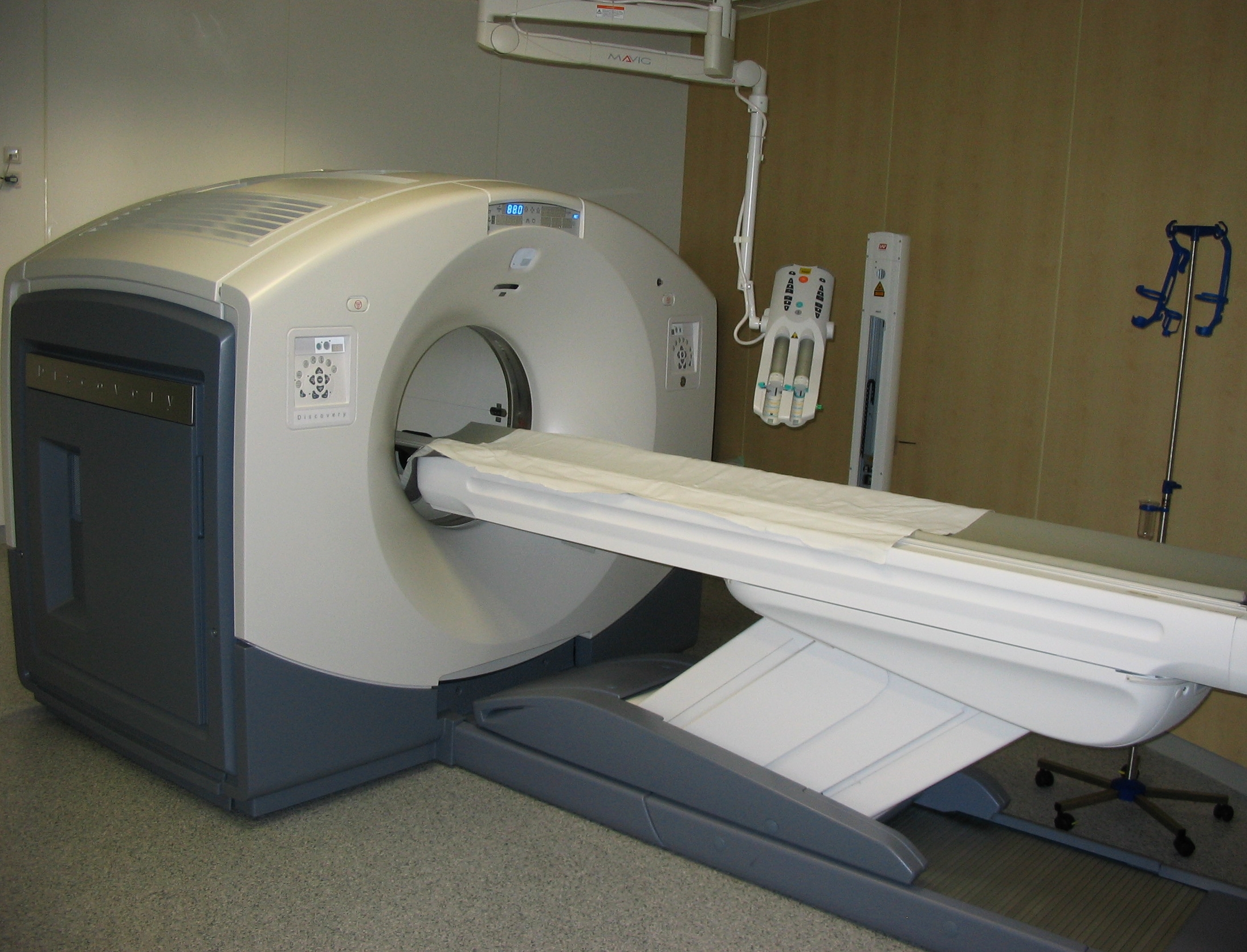
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in Metabolism, metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example, 18F-FDG, -FDG is commonly used to detect cancer, Sodium fluoride#Medical imaging, NaF is widely used for detecting bone formation, and Isotopes of oxygen#Oxygen-15, oxygen-15 is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common medical imaging, imaging technique, a Scintigraphy#Process, medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical, radiopharmaceutical — a radioisotope attached to a drug — is injected into the body as a radioactive tracer, tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florbetaben
Florbetaben, a fluorine-18 (18F)-labeled stilbene derivative (formerly known as BAY-949172), trade name NeuraCeq, is a diagnostic radiotracer developed for routine clinical application to visualize β-amyloid plaques in the brain. It is indicated for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging of β-amyloid neuritic plaque density in the brains of adult patients with cognitive impairment who are being evaluated for Alzheimer's disease Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term me ... (AD) and other causes of cognitive impairment. β-amyloid is a key neuropathological hallmark of AD, so markers of β-amyloid plaque accumulation in the brain are useful in distinguishing AD from other causes of dementia. The tracer successfully completed a global multicenter phase 0–III develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setoperone
Setoperone is a compound that is a ligand to the 5-HT2A receptor. It can be radiolabeled with the radioisotope fluorine-18 and used as a radioligand with positron emission tomography (PET). Several research studies have used the radiolabeled setoperone in neuroimaging for the studying neuropsychiatric disorders, such as depression or schizophrenia. Synthesis The starting material is called 6-(2-hydroxyethyl)-7-methyl-2,3-dihydro- ,3hiazolo ,2-ayrimidin-5-oneCID:15586462(1). Halogenation of this with hydrobromic acid in acetic acid giveCID:15586463(2). Sn2 alkylation with 4-(4-fluorobenzoyl)piperidine 6346-57-7(3) under Finkelstein reaction conditions affords setoperone (4). See also * Altanserin * Ketanserin * Pirenperone Pirenperone (, , ; developmental code names R-47456, R-50656) is a serotonin receptor antagonist described as an antipsychotic and tranquilizer which was never marketed. It is a relatively selective antagonist of the serotonin 5-HT2 recepto ... * R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raclopride
Raclopride is a typical antipsychotic. It acts as a selective antagonist on D2 dopamine receptors. It has been used in trials studying Parkinson Disease. Its selectivity to the cerebral D2 receptors is characterized by its respective Ki-values, which are as follows: 1.8, 3.5, 2400 and 18000 nM for D2, D3, D4 and D1 receptors respectively. It can be radiolabelled with radioisotopes, e.g. 3H or 11C and used as a tracer for '' in vitro'' imaging (autoradiography) as well as '' in vivo'' imaging positron emission tomography (PET). Images obtained by cerebral PET scanning (e.g. PET/CT or PET/MRI) allow the non-invasive assessment of the binding capacity of the cerebral D2 dopamine receptor, which can be useful for the diagnosis of movement disorders. In particular, cerebral D2 receptor binding as measured by carbon-11-raclopride (11C-raclopride) has shown to reflect disease severity of Huntington's disease, a genetic disease characterized by selective degeneration of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittsburgh Compound B
Pittsburgh compound B (PiB) is a radioactive analog of thioflavin T, which can be used in positron emission tomography scans to image beta-amyloid plaques in neuronal tissue. Due to this property, Pittsburgh compound B may be used in investigational studies of Alzheimer's disease. History The definitive diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease can only be made following the demonstration of the presence of beta-amyloid (Aβ) plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, the pathologic hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease in brain tissue, typically at autopsy. While the cognitive impairments of the disease could be monitored throughout the disease course, clinicians had no reliable way to monitor the pathologic progression of the disease. Due to this fact, a clear understanding of the process of amyloid deposition and how amyloid deposits relate to the cognitive symptoms of Alzheimer's disease remains to be elucidated. While sophisticated centers for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease are ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nifene
Nifene is a high affinity, selective nicotinic α4β2* receptor partial agonist used in medical research for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, usually in the form of nifene ( 18F) as a positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer. Nifene has been used to assess the efficacy of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in animal models, because the neurotransmitter acetylcholine competes with the binding of nifene at the nicotinic receptor site. Learning and behavior studies in animal models using nifene have suggested a potential role of the nicotinic receptors located in distinct white matter tracts. Nifene studies in animal models of lung cancer have suggested an upregulation of the nicotinic receptor in the lung tumors. Novel PET and SPECT imaging agents as potential receptor antagonists A receptor antagonist is a type of Receptor (biochemistry), receptor ligand (biochemistry), ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a Receptor (bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPPF
MPPF, with the full name 2'-methoxyphenyl-(''N''-2'-pyridinyl)-''p''-fluoro-benzamidoethyipiperazine, is a compound that binds to the serotonin-1A receptor. Labeled with fluorine-18 it has been used as a radioligand with positron emission tomography. It has, e.g., been used to examine the difference in neuroreceptor binding in the human brain across sex and age. See also * WAY-100,635 References Phenol ethers Phenylpiperazines Fluoroarenes Benzamides 2-Pyridyl compounds {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mefway
Mefway is a serotonin 5-HT1A receptor antagonist used in medical research, usually in the form of mefway ( 18F) as a positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer. Chemistry Mefway is closely related to the research compound WAY-100,635. The compound adds a fluoromethyl group to the cyclohexyl ring of WAY-100,635 and it is effectively prepared with automation module. There are two isomers with regard to the cyclohexane ring, of which the ''trans'' conformation has the higher 5-HT1A specificity. Animal PET studies In one study the uptake and retention of mefway (18F) was found to be similar to that found for 11C-WAY-100,635. Head-to-head comparison of mefway (18F) and 11C-WAY-100,635 have been evaluated. Since 11C-WAY-100,635 is the current 'gold standard' and difficult to synthesize, a suitable fluorine-18 replacement as in mefway is highly desired. In addition, mefway (18F) showed comparable brain uptake and the target-to-reference ratios compared to fcway(18F) The ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmethoxyfallypride
Desmethoxyfallypride is a moderate affinity dopamine D2 receptor/D3 receptor antagonist used in medical research, usually in the form of the radiopharmaceuticals desmethoxyfallypride or DMFP( 18F) and has been used in human studies as a positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a chemical compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide so by virtue of its radioactive decay it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tr .... References External links ChemSpider {{Dopaminergics Typical antipsychotics Salicylamide ethers Pyrrolidines D2 antagonists Organofluorides Radiopharmaceuticals Allyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorodopa
Fluorodopa, also known as FDOPA, is a fluorinated form of L-DOPA primarily synthesized as its fluorine-18 isotopologue for use as a radiotracer in positron emission tomography (PET). The most common side effects are injection site pain. Medical uses Fluorodopa is indicated for use in positron emission tomography (PET) to visualize dopaminergic nerve terminals in the striatum for the evaluation of adults with suspected Parkinsonian syndromes (PS). History In October 2019, Fluorodopa was approved in the United States for the visual detection of certain nerve cells in adult patients with suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes (PS). The U.S. Food and Drug Administration The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ... (FDA) approved Fluorodopa F 18 based on evidence from one cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flutemetamol
Flutemetamol (18F) (trade name Vizamyl, by GE Healthcare) is a PET scanning radiopharmaceutical containing the radionuclide fluorine-18, used as a diagnostic tool for Alzheimer's disease. Adverse effects Adverse effects of flutemetamol include headache, nausea, dizziness, flushing and increased blood pressure. Mechanism of action After the substance is given intravenously, it accumulates in beta amyloid plaques in the patient's brain, which thus become visible via positron emission tomography (PET). Manufacturing and distribution Flutemetamol (18F) can be produced within five to six hours. It then undergoes a quality check and is ready to be distributed immediately after. The product must be used within a certain time frame for maximum efficacy. Because of the limited time window, flutemetamol is not produced until an order has been placed. Flutemetamol is typically administered intravenously in 1 to 10 mL doses. Average costs for PET scans without insurance covera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flumazenil
Flumazenil (also known as flumazepil, code name Ro 15-1788) is a selective GABAA receptor antagonist administered via injection, otic insertion, or intranasally. Therapeutically, it acts as both an antagonist and antidote to benzodiazepines (particularly in cases of overdose), through competitive inhibition. It was first characterized in 1981, and was first marketed in 1987 by Hoffmann-La Roche under the trade name Anexate. However, it did not receive FDA approval until December 20, 1991. The developer lost its exclusive patent rights in 2008; so at present, generic formulations of this drug are available. Intravenous flumazenil is primarily used to treat benzodiazepine overdoses and to help reverse anesthesia. Administration of flumazenil by sublingual lozenge and topical cream has also been tested. Medical uses Flumazenil benefits patients who become excessively drowsy after use of benzodiazepines for either diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. The drug has been used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |