|
List Of NATO Reporting Names For Air-to-surface Missiles
NATO reporting name for AS series air-to-surface missiles, with Soviet designations: Note: The Soviet / Russian designation is a Cyrillic letter " Х", which is translated as "Kh" or "H". Also, sometimes a combination ("complex") of a missile with its aircraft is marked with a letter "K" (for example, a missile Kh-22 with an aircraft is a "complex K-22"). The Cyrillic "X" (read "Kh") in the designation of Soviet ASMs is in fact a Latin " X" ("ecks") for Xperimental, as used by the design bureau. With passing time, however, this was ignored and used in Soviet/Russian as well as foreign literature as the Cyrillic Kh. * AS-1 "Kennel" (KS-1 ''Kometa'') * AS-2 "Kipper" (K-10S ''Yen'') * AS-3 "Kangaroo" (Kh-20) * AS-4 "Kitchen" (Kh-22 Burya) * AS-5 "Kelt" (Kh-11/KSR-2) * AS-6 "Kingfish" (Kh-26/KSR-5) * AS-7 "Kerry" (Kh-66, Kh-23 ''Grom'') * AS-8 (9M114V ''Shturm-V'') * AS-9 "Kyle" (Kh-28) * AS-10 "Karen" (Kh-25) * AS-11 "Kilter" (Kh-58 ''Izdeliye D-7'') * AS-12 "Kegler" (Kh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NATO Reporting Name
NATO reporting names are code names for military equipment from Russia, China, and historically, the Eastern Bloc (Soviet Union and other nations of the Warsaw Pact). They provide unambiguous and easily understood English words in a uniform manner in place of the original designations, which either may have been unknown to the Western world at the time or easily confused codes. For example, the Russian bomber jet Tupolev Tu-160 is simply called "Blackjack". NATO maintains lists of the names. The assignment of the names for the Russian and Chinese aircraft was once managed by the five-nation Air Standardization Coordinating Committee (ASCC), but that is no longer the case. American variations The United States Department of Defense (DOD) expands on the NATO reporting names in some cases. NATO refers to surface-to-air missile systems mounted on ships or submarines with the same names as the corresponding land-based systems, but the US DoD assigns a different series of numbers with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
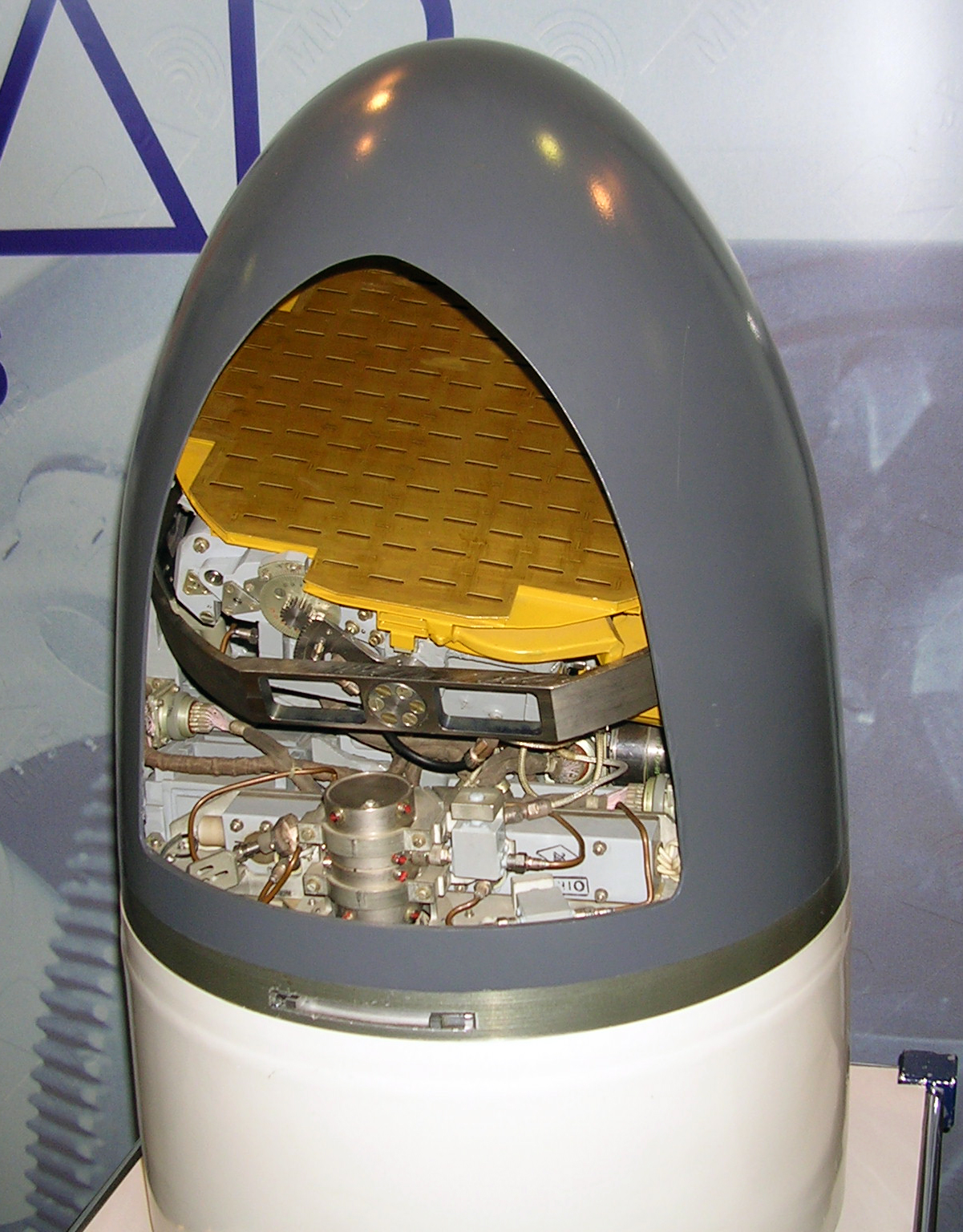
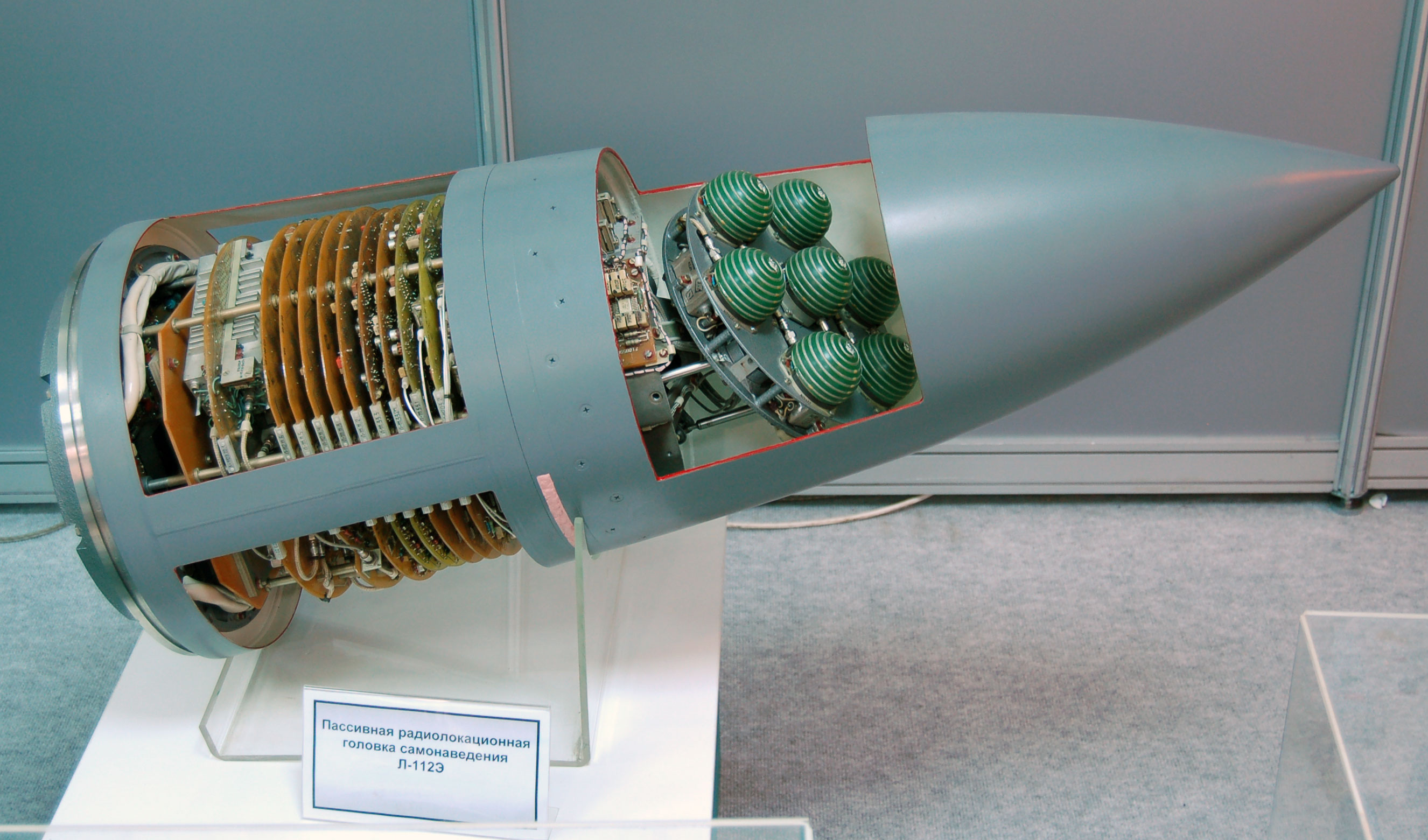
AS-11 Kilter
The Kh-58 (russian: Kha (Cyrillic), Х-58; NATO reporting name, NATO:AS-11 'Kilter') is a Soviet anti-radiation missile with a range of 120 km. the Kh-58U variant was still the primary anti-radiation missile of Russia and its allies. It is being superseded by the Kh-31. The NATO reporting name is "Kilter". Development The Bereznyak design bureau had developed the liquid-fuelled Kh-28 (AS-9 ‘Kyle’) and the KSR-5P (AS-6) anti-radiation missiles. They merged with Raduga in 1967, so Raduga was given the contract in the early 1970s to develop a solid-fuel successor to the Kh-28 to equip the new Su-24M 'Fencer-D' attack aircraft. Consequently, the project was initially designated the Kh-24, before becoming the Kh-58. During the 1980s a longer-range variant was developed, the Kh-58U, with lock-on-after-launch capability. Since the fall of the Soviet Union, Raduga have offered several versions for export. Design It was designed to be used in conjunction with the Su-24's L-086A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kh-55
The Kh-55 (russian: Х-55, also known as RKV-500; NATO reporting name: AS-15 "Kent") is a Soviet/Russian subsonic air-launched cruise missile, designed by MKB Raduga in the 1970s. It has a range of up to and can carry nuclear warheads. Kh-55 is launched exclusively from bomber aircraft and has spawned a number of conventionally armed variants mainly for tactical use, such as the Kh-65SE and Kh-SD, but only the Kh-101 and Kh-555 appear to have been put into service. Contrary to popular belief, the Kh-55 was not the basis of the submarine and ground-launched S-10 Granat or RK-55 ''Relief'' (SS-N-21"Sampson" and SSC-X-4"Slingshot") designed by NPO Novator. The RK-55 is very similar to the air-launched Kh-55 (AS-15 "Kent") but the Kh-55 has a drop-down turbofan engine and was designed by MKB Raduga. Development In the late 1960s, the "Ekho" study conducted by the GosNIIAS institute concluded that it would be more effective to deploy many small, subsonic cruise missiles than th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kh-90
The Kh-90 GELA (russian: ГЭЛА (гиперзвуковой экспериментальный летательный аппарат), Hypersonic Experimental Flight Vehicle) is a Soviet/Russian air-to-surface cruise missile. It was supposed to replace subsonic intermediate range missiles in the Soviet inventory. The missile was an ambitious project, as the main objective was to develop it into a hypersonic missile. It was to be a successor to the Kh-45, which never entered service. The missile was designed by Raduga. It was equipped with a one-megaton thermonuclear warhead and used inertial navigation with mid-course update via data link. It had a maximum range of 3,000 km. It was developed at the beginning of 1980, following the Kh-80 and Kholod projects. It was shown to the public an MAKS Airshow 1995. See also *Ra'ad * SOM * Ya-Ali *Shahab-3 *Fajr-3 *Shaheen-III *Ashoura (missile) *Sejjil *Ghauri-I The Ghauri–I ( ur, غوری-ا; official codename: Hatf–V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AS-20 Kayak
The Zvezda Kh-35 (russian: Х-35 , AS-20 'Kayak') is a Soviet turbojet subsonic cruise anti-ship missile. The missile can be launched from helicopters, surface ships and coastal defence batteries with the help of a rocket booster, in which case it is known as ''Uran'' ('Uranus', SS-N-25 'Switchblade', GRAU The Main Missile and Artillery Directorate of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation (), commonly referred to by its transliterated Russian acronym GRAU (), is a department of the Russian Ministry of Defense. It is subordinate to the ... 3M24) or ''Bal'' (SSC-6 'Sennight', GRAU 3K60). It is designed to attack vessels up to 5,000 tonnes. Development The previous anti-ship missiles made in USSR were highly capable, but they also were large and expensive. Therefore, the Soviet Navy found that a similar, small and very low flying missile would be useful. This new system was planned as small, cheap, and easy to install missile for a variety of platforms. This new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kh-80
The Kh-80 Meteorit-A ( GRAU-code: 3M25A, NATO: AS-X-19 Koala), the RK-75 Meteorit-N ''(GRAU:'' 3M25N, ''NATO:'' SS-NX-24 Scorpion) and the P-750 Meteorit-M (Russian: П-750 Гром, ''GRAU:'' 3М25, ''NATO'': SSC-X-5) was a Soviet cruise missile which was supposed to replace subsonic intermediate range missiles in Soviet inventory. Development of three variants of this cruise missile was authorized on 9 December 1976. The Meteorit-M strategic version would be deployed from Project 667M submarines with 12 launchers per boat. The air-launched Meteorit-A would be launched from Tu-95 bombers. The land-based version was designated Meteorit-N. The missile was also sometimes referred to by the code-name Grom. The first test launch, on 20 May 1980, was unsuccessful, as were the next three attempts. The first successful flight did not come until 16 December 1981. The first launch from a 667M Andromeda submarine took place on 26 December 1983 from the Barents Sea. The missile was design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AS-18 Kazoo
The Kh-59 ''Ovod'' (russian: Х-59 Овод 'Gadfly'; AS-13 'Kingbolt') is a Russian TV-guided cruise missile with a two-stage solid-fuel propulsion system and 200 km range. The Kh-59M ''Ovod-M'' (AS-18 'Kazoo') is a variant with a bigger warhead and turbojet engine. It is primarily a land-attack missile but the Kh-59MK variant targets ships. Development The initial design was based on the Raduga Kh-58 (AS-11 'Kilter'), but it had to be abandoned because the missile speed was too high for visual target acquisition. Raduga OKB developed the Kh-59 in the 1970s as a longer ranged version of the Kh-25 (AS-10 'Karen'), as a precision stand-off weapon for the Su-24M and late-model MiG-27's. The electro-optical sensors for this and other weapons such as the Kh-29 (AS-14 'Kedge') and KAB-500KR bombs were developed by S. A. Zverev NPO in Krasnogorsk. It is believed that development of the Kh-59M started in the 1980s. Details of the Kh-59M were first revealed in the early 1990s. Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AS-17 Krypton
The Kh-31 (russian: Х-31; AS-17 'Krypton') is a Russian air-to-surface missile carried by aircraft such as the MiG-29 or Su-27. It is capable of Mach 3.5 and was the first supersonic anti-ship missile that could be launched by tactical aircraft. There are several variants; the Kh-31 is best known as an anti-radiation missile (ARM) but there are also anti-shipping and target drone versions. There has been talk of adapting it to make an " AWACS killer", a long-range air-to-air missile. Development The proliferation of surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) has made the Suppression of Enemy Air Defences (SEAD) a priority for any modern air force intending offensive action. Knocking out air search radars and fire control radars is an essential part of this mission. ARMs must have sufficient range that the launch platform is out of range of the SAMs, high speed to reduce the risk of being shot down and a seeker that can detect a range of radar types, but they do not need a particularly b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AS-16 Kickback
The Raduga Kh-15 or RKV-15 (russian: Х-15; NATO: AS-16 "Kickback"; GRAU:) is a Russian hypersonic aero-ballistic air-to-ground missile carried by the Tupolev Tu-22M and other bombers. Originally developed as a standoff nuclear air-to-ground missile similar to the U.S. Air Force's AGM-69 SRAM, versions with conventional warheads have been developed. As of early 2019, it was uncertain whether the Kh-15 was in service, with rumors that it had been retired or placed in storage. Development In 1967, MKB Raduga started developing the Kh-2000 as a replacement for the Kh-22 ( NATO reporting name AS-4 Kitchen) heavy anti-shipping missile. Development of the Kh-15 started some time in the early 1970s. The sophistication of the design made it suitable for other roles, and a nuclear-tipped version was developed in tandem with the conventionally armed variant. An upgrade under development was cancelled in 1991, but reports in 1998 suggested an upgraded Kh-15 might be fitted to Su-35 (F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AS-15 Kent
The Kh-55 (russian: Х-55, also known as RKV-500; NATO reporting name: AS-15 "Kent") is a Soviet/Russian subsonic air-launched cruise missile, designed by MKB Raduga in the 1970s. It has a range of up to and can carry nuclear warheads. Kh-55 is launched exclusively from bomber aircraft and has spawned a number of conventionally armed variants mainly for tactical use, such as the Kh-65SE and Kh-SD, but only the Kh-101 and Kh-555 appear to have been put into service. Contrary to popular belief, the Kh-55 was not the basis of the submarine and ground-launched S-10 Granat or RK-55 ''Relief'' (SS-N-21"Sampson" and SSC-X-4"Slingshot") designed by NPO Novator. The RK-55 is very similar to the air-launched Kh-55 (AS-15 "Kent") but the Kh-55 has a drop-down turbofan engine and was designed by MKB Raduga. Development In the late 1960s, the "Ekho" study conducted by the GosNIIAS institute concluded that it would be more effective to deploy many small, subsonic cruise missiles than t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kh-29
The Kh-29 (russian: Х-29; NATO: AS-14 'Kedge; GRAU: 9M721) is a Soviet air-to-surface missile with a range of 10–30 km. It has a large warhead of 320 kg, has a choice of laser, infrared, active radar or TV guidance, and is typically carried by tactical aircraft such as the Su-24, Su-30, MiG-29K as well as the Su-25, giving these aircraft an expanded standoff capability. The Kh-29 is intended for primary use against larger battlefield targets and infrastructure such as industrial buildings, depots and bridges, but can also be used against ships up to 10,000 tonnes, hardened aircraft shelters and concrete runways. Development Design started in the late 1970s at the Molniya design bureau in Ukraine on what would be their only air-to-ground munition, but when they moved exclusively to space work Vympel took over development of the Kh-29. The first firing of the missile took place in 1976 and after extensive trials the Kh-29 was accepted into service in 1980. Design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kh-59
The Kh-59 ''Ovod'' (russian: Х-59 Овод ' Gadfly'; AS-13 'Kingbolt') is a Russian TV-guided cruise missile with a two-stage solid-fuel propulsion system and 200 km range. The Kh-59M ''Ovod-M'' (AS-18 'Kazoo') is a variant with a bigger warhead and turbojet engine. It is primarily a land-attack missile but the Kh-59MK variant targets ships. Development The initial design was based on the Raduga Kh-58 (AS-11 'Kilter'), but it had to be abandoned because the missile speed was too high for visual target acquisition. Raduga OKB developed the Kh-59 in the 1970s as a longer ranged version of the Kh-25 (AS-10 'Karen'), as a precision stand-off weapon for the Su-24M and late-model MiG-27's. The electro-optical sensors for this and other weapons such as the Kh-29 (AS-14 'Kedge') and KAB-500KR bombs were developed by S. A. Zverev NPO in Krasnogorsk. It is believed that development of the Kh-59M started in the 1980s. Details of the Kh-59M were first revealed in the early 1990s. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(524-20).jpg)