|
List Of Microorganisms Found In Sourdough
Sourdough is a mixture of flour and water inhabited by a symbiosis of Lactic acid bacteria and yeasts. It is used in baking to leaven and acidify bread. Yeasts *''Candida milleri, Candida humilis'' (formerly ''C. milleri'') *''Candida krusei'' *''Kazachstania exigua'' *''Pichia saitoi'' *''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' *''Torulopsis holmii'' Lactic acid bacteria *''Lactobacillus acetotolerans'' *''Lactobacillus acidophilus'' *''Lactobacillus alimentarius'' *''Lactobacillus brevis'' *''Lactobacillus buchneri'' *''Lactobacillus casei'' *''Lactobacillus crustorum'' *''Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, Lactobacillus delbrueckii'' *''Lactobacillus farciminis'' *''Lactobacillus fermenti'' *''Lactobacillus fermentum'' *''Lactobacillus fructivorans'' *''Lactobacillus frumenti'' *''Lactobacillus hilgardii'' *''Lactobacillus leichmannii'' *''Lactobacillus mindensis'' *''Lactobacillus panis'' *''Lactobacillus paralimentarius'' *''Lactobacillus pastorianus'' *''Lactobacillus plantarum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sourdough
Sourdough or sourdough bread is a bread made by the fermentation of dough using wild lactobacillaceae and yeast. Lactic acid from fermentation imparts a sour taste and improves keeping qualities. History In the ''Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology'', Michael Gaenzle writes: "The origins of bread-making are so ancient that everything said about them must be pure speculation. One of the oldest sourdough breads dates from 3700 BCE and was excavated in Switzerland, but the origin of sourdough fermentation likely relates to the origin of agriculture in the Fertile Crescent and Egypt several thousand years earlier", which was confirmed a few years later by archeological evidence. ... "Bread production relied on the use of sourdough as a leavening agent for most of human history; the use of baker's yeast as a leavening agent dates back less than 150 years." Pliny the Elder described the sourdough method in his '' Natural History'': Sourdough remained the usual form of leavening do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
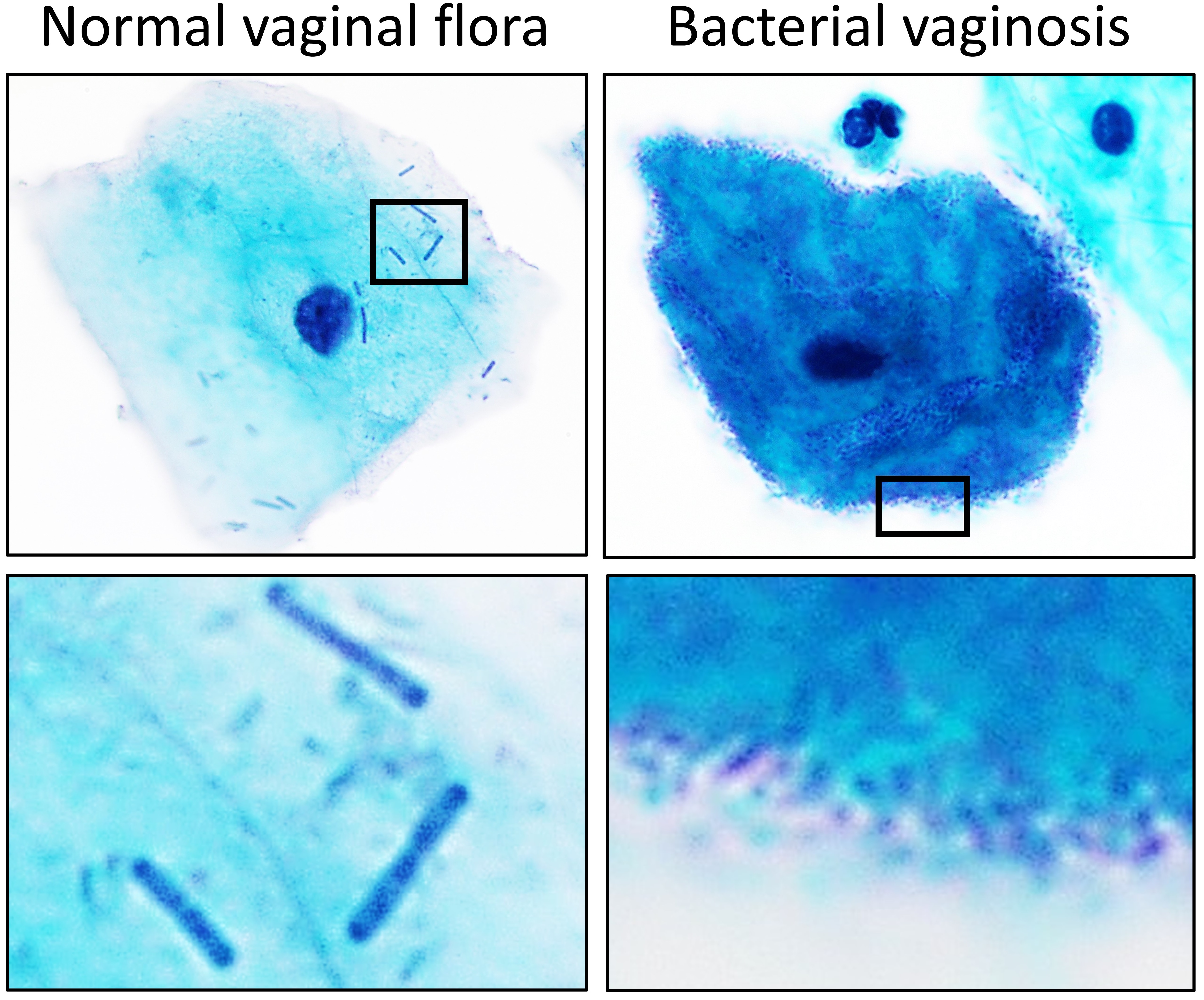
Lactobacillus Delbrueckii Subsp
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nutrients. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Pontis
''Limosilactobacillus pontis'' is a rod-shaped, Gram-positive facultatively anaerobic bacterium. Along with other '' Lactobacillus'' species, it is capable of converting sugars, such as lactose, into lactic acid. ''Limosilactobacillus pontis'' is classified under the phylum Bacillota, class Bacilli, and is a member of the family Lactobacillaceae and is found to be responsible for the fermentation of sourdough, along with many other '' Lactobacillus'' species. This microorganism produces lactic acid during the process of fermentation, which gives sourdough bread its characteristic sour taste. History and discovery In 1994, ''Limosilactobacillus pontis'' was discovered during an experiment focusing on the microflora found in sourdough preparations for making sourdough bread. Scientists isolated ''Limosilactobacillus pontis'' as well as many common species such as ''Limosilactobacillus reuteri'', '' Levilactobacillus brevis'', and ''Fructilactobacillus sanfranciscensis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Plantarum
''Lactiplantibacillus plantarum'' (formerly ''Lactobacillus arabinosus'' and ''Lactobacillus plantarum'') is a widespread member of the genus ''Lactiplantibacillus'' and commonly found in many fermented food products as well as anaerobic plant matter. ''L. plantarum'' was first isolated from saliva. Based on its ability to temporarily persist in plants, the insect intestine and in the intestinal tract of vertebrate animals, it was designated as a nomadic organism. ''L. plantarum'' is Gram positive, bacilli shaped bacterium. ''L. plantarum'' cells are rods with rounded ends, straight, generally 0.9–1.2 μm wide and 3–8 μm long, occurring singly, in pairs or in short chains. ''L. plantarum'' has one of the largest genomes known among the lactic acid bacteria and is a very flexible and versatile species. It is estimated to grow between pH 3.4 and 8.8. ''Lactiplantibacillus plantarum'' can grow in the temperature range 12 °C to 40 °C. The viable counts of the "L. plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Pastorianus
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Paralimentarius
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nutrients. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Panis
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Mindensis
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Leichmannii
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nutrients. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Hilgardii
''Lentilactobacillus hilgardii'' is a species of bacterium found in wine, dairy products, and wine musts. Its morphology is consistent (on a cellular level) of rods that are 0.5–0.8 micrometres of both single short chains and long filament like structures. On a colony level, the bacteria appears glossy, round and white. For study, the bacteria requires malt agar and can ferment maltose, but often also requires yeast extract in order to ferment properly. To study ''L. hilgardii'' in liquid requires growing it in Elliker broth so it can show turbidity and gas formation. On staining with Gram's iodine, the bacillus is Gram positive. ''L. hilgardii'' is considered a negative catalase (enzyme that decomposes hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water) and creates lactic acid, ethanol/acetic acid, and carbon dioxide. Along with this it is capable of sometimes producing biogenic amines or histamine and ethyl carbamate, which causes health risks. Its role in the fermentation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Frumenti
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Fructivorans
''Fructilactobacillus fructivorans'' is a gram-positive bacteria and a member of the genus '' Fructilactobacillus'' in the family Lactobacillaceae. It is found in wine, beer, grape must, dairy, sauerkraut, meat, and fish. They are facultative anaerobics and experience best growth in environments with 5-10% CO2. Temperature for growth is between 2 °C and 53 °C, with the optimum temperature between 30 °C and 40 °C and a pH level between 5.5 and 6.2. The bacterium is rod shaped and can be found in the following forms: single, pairs, chains of varying lengths, or long curved filaments. Lactobacillus fructivorans is non-motile. The main end product of the metabolic process is lactate, although ethanol, acetate, formate, CO2, and succinate may also be produced. Food production The bacteria have several metabolic properties that allow them to function as starter cultures in the production of fermented dairy, meat, and vegetable products and beverages. ''F. f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |