|
List Of Jewish Diaspora Languages
This is a list of languages and groups of languages that developed within Jewish diaspora communities through contact with surrounding languages. Afro-Asiatic languages Cushitic languages * Kayla dialect, Kayla * Qwara dialect, Qwara Semitic languages Arabic languages * Judeo-Arabic :* Judeo-Algerian Arabic (extinct) :* Judeo-Andalusian Arabic (extinct) :* Judeo-Egyptian Arabic (extinct) :* Judeo-Iraqi Arabic :* Judeo-Levantine Arabic (extinct) :* Judeo-Moroccan Arabic :* Judeo-Tripolitanian Arabic :* Judeo-Tunisian Arabic :* Judeo-Yemeni Arabic * Karaite Egyptian Arabic, based on old Egyptian Arabic Aramaic languages * Judeo-Aramaic :* Hulaulá, Hulaulá (Persian Kurdistani Jewish Neo-Aramaic) :* Jewish Palestinian Aramaic (extinct) ::* Galilean dialect (extinct) :* Lishana Deni, Lishana Deni (Zakho Jewish Neo-Aramaic) :* Lishan Didan, Lishan Didan (Persian Azerbaijani Jewish Neo-Aramaic) :* Lishanid Noshan, Lishanid Noshan (Arbil Jewish Neo-Aramaic) Other Afro- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Diaspora
The Jewish diaspora ( he, תְּפוּצָה, təfūṣā) or exile (Hebrew: ; Yiddish: ) is the dispersion of Israelites or Jews out of their ancient ancestral homeland (the Land of Israel) and their subsequent settlement in other parts of the globe. In terms of the Hebrew Bible, the term "Exile" denotes the fate of the Israelites who were taken into exile from the Kingdom of Israel during the 8th century BCE, and the Judahites from the Kingdom of Judah who were taken into exile during the 6th century BCE. While in exile, the Judahites became known as "Jews" (, or ), "Mordecai the Jew" from the Book of Esther being the first biblical mention of the term. The first exile was the Assyrian exile, the expulsion from the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria) begun by Tiglath-Pileser III of Assyria in 733 BCE. This process was completed by Sargon II with the destruction of the kingdom in 722 BCE, concluding a three-year siege of Samaria begun by Shalmaneser V. The next experience of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Gruyter
Walter de Gruyter GmbH, known as De Gruyter (), is a German scholarly publishing house specializing in academic literature. History The roots of the company go back to 1749 when Frederick the Great granted the Königliche Realschule in Berlin the royal privilege to open a bookstore and "to publish good and useful books". In 1800, the store was taken over by Georg Reimer (1776–1842), operating as the ''Reimer'sche Buchhandlung'' from 1817, while the school’s press eventually became the ''Georg Reimer Verlag''. From 1816, Reimer used the representative Sacken'sche Palace on Berlin's Wilhelmstraße for his family and the publishing house, whereby the wings contained his print shop and press. The building became a meeting point for Berlin salon life and later served as the official residence of the president of Germany. Born in Ruhrort in 1862, Walter de Gruyter took a position with Reimer Verlag in 1894. By 1897, at the age of 35, he had become sole proprietor of the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
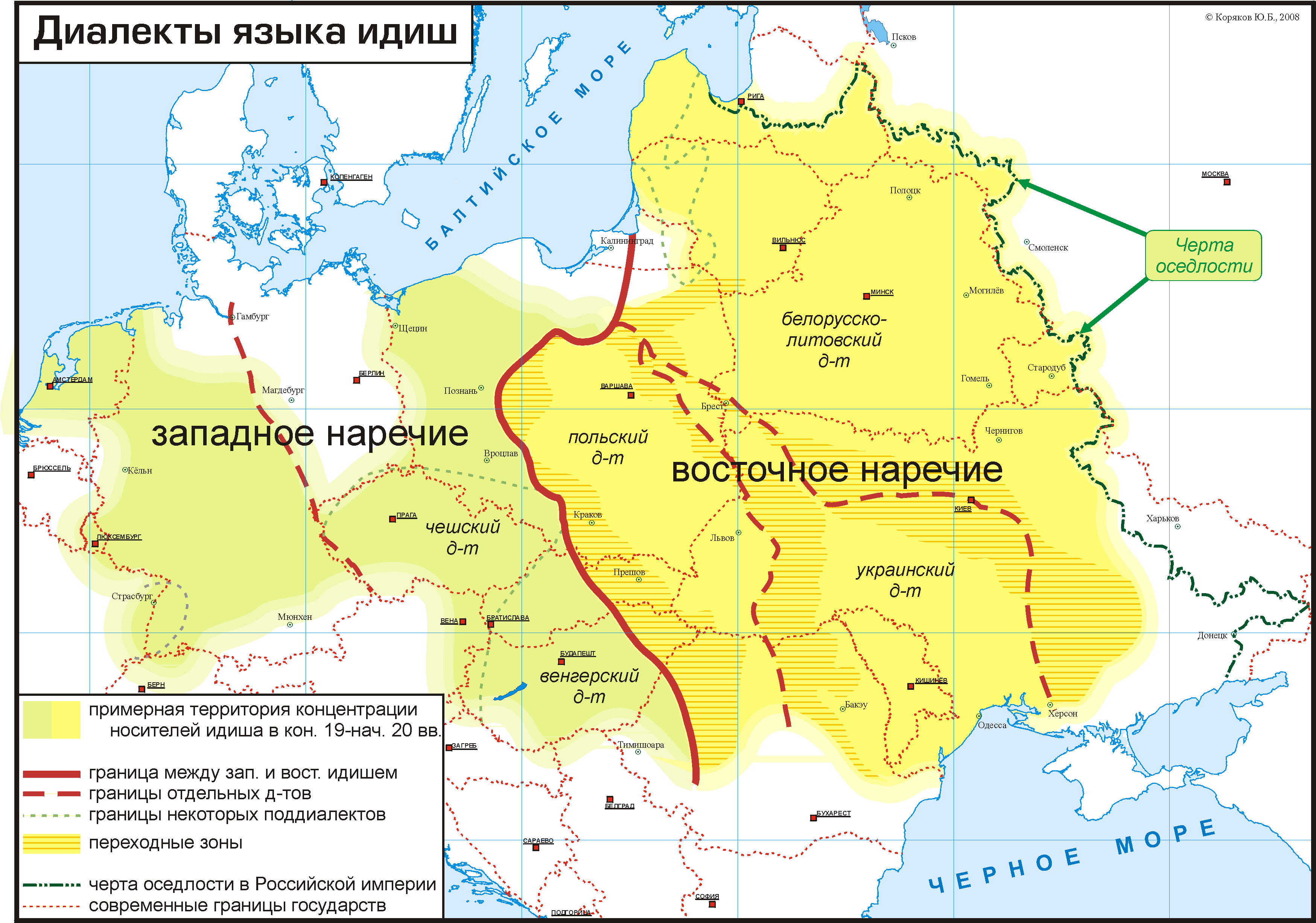
Western Yiddish
Yiddish dialects are variants of the Yiddish language and are divided according to the region in Europe where each developed its distinctiveness. Linguistically, Yiddish is divided in distinct Eastern and Western dialects. While the Western dialects mostly died out in the 19th-century due to Jewish language assimilation into mainstream culture, the Eastern dialects were very vital until most of Eastern European Jewry was wiped out by the Shoah. The Northeastern dialects of Eastern Yiddish were dominant in 20th-century Yiddish culture and academia, but in the 21st-century, since Yiddish is largely dying out everywhere due to language assimilation, the Southern dialects of Yiddish that are preserved by many Hasidic communities, have become the most commonly spoken form of Yiddish. Varieties Yiddish dialects are generally grouped into either Western Yiddish and Eastern Yiddish. Western Yiddish developed from the 9th century in Western-Central Europe, in the region which was called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Yiddish
Yiddish dialects are Variety (linguistics), variants of the Yiddish language and are divided according to the region in Europe where each developed its distinctiveness. Linguistically, Yiddish is divided in distinct Eastern and Western dialects. While the Western dialects mostly died out in the 19th-century due to Jewish language assimilation into mainstream culture, the Eastern dialects were very vital until most of Eastern European Jewry was wiped out by the Holocaust, Shoah. The Northeastern dialects of Eastern Yiddish were dominant in 20th-century Yiddish culture and academia, but in the 21st-century, since Yiddish is largely dying out everywhere due to language assimilation, the Southern dialects of Yiddish that are preserved by many Hasidic Judaism, Hasidic communities, have become the most commonly spoken form of Yiddish. Varieties Yiddish dialects are generally grouped into either Western Yiddish and Eastern Yiddish. Western Yiddish developed from the 9th century in West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yiddish Language
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with many elements taken from Hebrew (notably Mishnaic) and to some extent Aramaic. Most varieties of Yiddish include elements of Slavic languages and the vocabulary contains traces of Romance languages.Aram Yardumian"A Tale of Two Hypotheses: Genetics and the Ethnogenesis of Ashkenazi Jewry".University of Pennsylvania. 2013. Yiddish is primarily written in the Hebrew alphabet. Prior to World War II, its worldwide peak was 11 million, with the number of speakers in the United States and Canada then totaling 150,000. Eighty-five percent of the approximately six million Jews who were murdered in the Holocaust were Yiddish speakers,Solomon Birnbaum, ''Grammatik der jiddischen Sprache'' (4., erg. Aufl., Hambu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lotegorisch
Lotegorisch or ''Lottegorisch'' or ''Lekoudesch'' (older own description: ''lochne kodesch'', from the he, laschon = "tongue, language", and ''kodesch'' = "holy") is a trading language and Palatine variant of the secret language, Rotwelsch, spoken in the Leiningerland (especially in Carlsberg), where in the late 18th century many vagrants, including many Jews, were settled and where many of them worked as cattle traders, itinerant craftsmen, and peddler A peddler, in British English pedlar, also known as a chapman, packman, cheapjack, hawker, higler, huckster, (coster)monger, colporteur or solicitor, is a door-to-door and/or travelling vendor of goods. In England, the term was mostly used f ...s.Meißner (1999) References Literature *Anton Meißner: ''Die pfälzische Handelssprache Lotegorisch. Wörterbuch mit Leseproben''. Meißner Verlag, Wattenheim, 1999 (printed as a manuscript) External links www.lotegorisch.de (archived version at archive.org @ 2019-01-22 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lachoudisch
Lachoudisch was a dialect of German, containing many Hebrew and Yiddish words, native to the Bavarian town of Schopfloch. It was created in the sixteenth century. Few speakers remained after the Holocaust The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; .... See also * Lotegorisch References * German dialects Judeo-Germanic languages Jews and Judaism in Germany Yiddish culture in Germany Endangered languages of Europe {{Germanic-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish English Languages
Jewish English is a cover term for varieties of the English language spoken by Jews. They may include significant amounts of vocabulary and syntax taken from Yiddish, and both classical and modern Hebrew. These varieties can be classified into several types: Yeshivish, Yinglish, and Heblish, as well as more flexible mixtures of English and other Jewish languages, which may contain features and other elements from languages other than Yiddish and Hebrew. The classification "Jewish English" eliminates the need for concern with identifying the specific origin of the non-English components of any such variant. This offsets, for example, misperceptions that can result from failure to note the Hebrew origin of a word that may have become widely known in Anglophone contexts via Yiddish, and may be, therefore, simply regarded as Yiddish. (This problem is illustrated in the list of English words of Yiddish origin.) Variants Several terms for hybrid Jewish English are being used or have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judeo-Malayalam
Judeo-Malayalam ( ml, links=no, യെഹൂദ്യമലയാളം, '; he, links=no, מלאיאלאם יהודית, ') is the traditional language of the Cochin Jews (also called Malabar Jews), from Kerala, in southern India, spoken today by a few dozens of people in Israel and by probably fewer than 25 in India. Judeo-Malayalam is the only known Dravidian Jewish language. (There is another Dravidian language spoken regularly by a Jewish community Telugu, spoken by the small, and only very newly observant Jewish community of east-central Andhra Pradesh but because of the long period in which the people were not practicing Judaism, they did not develop any distinctly identifiable Judeo-Telugu language or the dialect. ''See main article: Telugu Jews''.) Since it does not differ substantially in grammar or syntax from other colloquial Malayalam dialects, it is not considered by many linguists to be a language in its own right, but a dialect, or simply a language variation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judeo-Berber Language
Judeo-Berber or Judeo-Amazigh ( ber, ⵜⴰⵎⴰⵣⵉⵖⵜ ⵏ ⵡⵓⴷⴰⵢⵏ ''tamazight n wudayen'', berberit yehudit) is any of several hybrid Berber varieties traditionally spoken as a second language in Berber Jewish communities of central and southern Morocco, and perhaps earlier in Algeria. Judeo-Berber is (or was) a contact language; the first language of speakers was Judeo-Arabic.Chetrit (2016) "Jewish Berber", in Kahn & Rubin (eds.) ''Handbook of Jewish Languages'', Brill (There were also Jews who spoke Berber as their first language, but not a distinct Jewish variety.) Speakers immigrated to Israel in the 1950s and 1960s. While mutually comprehensible with the Tamazight spoken by most inhabitants of the area (Galand-Pernet et al. 1970:14), these varieties are distinguished by the use of Hebrew loanwords and the pronunciation of ''š'' as ''s'' (as in many Jewish Moroccan Arabic dialects). Speaker population According to a 1936 survey, approximately 145,700 o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lishanid Noshan
Inter-Zab Jewish Neo-Aramaic, or ''Lishanid Noshan'', is a modern Jewish-Aramaic dialect, a variant of Northeastern Neo-Aramaic. It was originally spoken in Kurdistan Region of Iraq, in and around Arbil between the Great Zab and Little Zab rivers. Most speakers now live in Israel. Phonology Lishanid Noshan has 40 phonemes. 34 of them are consonants, and 6 of them are vowels. Laryngeals and pharyngeals originally found in Lishanid Noshan have not been preserved. In Aramaic, ''*ʕ'', a voiced pharyngeal fricative is prominent in words. However, it has weakened in Lishanid Noshan to /ʔ/ or zero. Regarding interdental fricatives, there has been a shift seen with ''*t'' and ''*d''. ''*h'', the original unvoiced pharyngeal fricative, has fused with the velar fricative /x/ in Northeastern Neo-Aramaic dialects. This is not the case for Lishanid Noshan. ''*h'' can still be seen in some words such as ''dbh'', which means "to slaughter." Word stress often occurs on the final syllabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lishan Didan
The Jewish Neo-Aramaic dialect of Urmia is a dialect of Northeastern Neo-Aramaic was originally spoken by Jews in Urmia and surrounding areas of Iranian Azerbaijan from Salmas to Solduz and into what is now eastern Turkey, Yüksekova and Başkale. Most speakers now live in Israel. History Various Neo-Aramaic dialects were spoken across a wide area from Lake Urmia to Lake Van (in Turkey), down to the plain of Mosul (in Iraq) and back across to Sanandaj (in Iran again). There are two major dialect clusters of Lishán Didán. The northern cluster of dialects centered on Urmia and Salmas in West Azerbaijan, and extended into the Jewish villages of the Turkish province of Van. The southern cluster of dialects was focused on the town of Mahabad and villages just south of Lake Urmia. The dialects of the two clusters are intelligible to one another, and most of the differences are due to receiving loanwords from different languages: Persian, Kurdish and Turkish languages especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |