|
List Of Interurban Railways In North America
This is a list of interurban railways in North America. Elsewhere, the term was not used or did not have the same meaning. The vast majority of these systems are defunct. All were opened primarily as passenger carriers, although many survived as freight railways after passenger service ceased. Canada Provinces not listed did not have interurban systems, which were commonly called radial railways in Canada. Alberta British Columbia Manitoba Nova Scotia Ontario Quebec Cuba Mexico United States Alabama Arizona Arkansas California Colorado Connecticut Delaware District of Columbia Georgia Idaho Illinois Indiana Iowa Kansas Kentucky Louisiana Maine Maryland Massachusetts Michigan Michigan had of interurban. Minnesota Mississippi Missouri Montana Nebraska New Hampshire New Jersey New York North Carolina ;North Dakota Ohio Oklahoma Oregon Pennsylvania Puerto Rico Rhode Island South Carolina South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interurban
The Interurban (or radial railway in Europe and Canada) is a type of electric railway, with streetcar-like electric self-propelled rail cars which run within and between cities or towns. They were very prevalent in North America between 1900 and 1925 and were used primarily for passenger travel between cities and their surrounding suburban and rural communities. The concept spread to countries such as Japan, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Belgium, Italy and Poland. Interurban as a term encompassed the companies, their infrastructure, their cars that ran on the rails, and their service. In the United States, the early 1900s interurban was a valuable economic institution. Most roads between towns and many town streets were unpaved. Transportation and haulage was by horse-drawn carriages and carts. The interurban provided reliable transportation, particularly in winter weather, between the town and countryside. In 1915, of interurban railways were operating in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
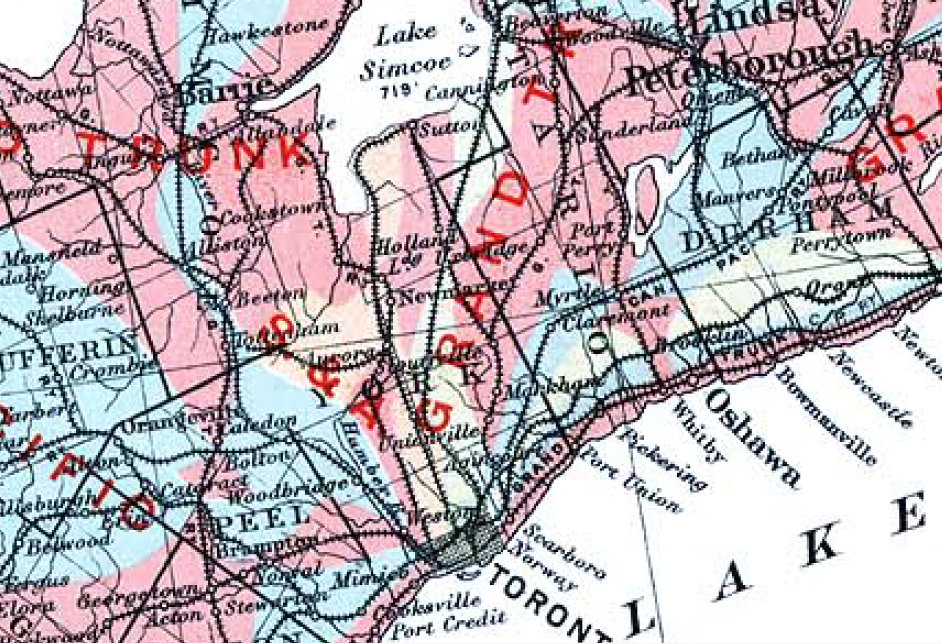
Grand Valley Railway
The Denver & Rio Grande Western Railroad , often shortened to ''Rio Grande'', D&RG or D&RGW, formerly the Denver & Rio Grande Railroad, was an American Class I railroad company. The railroad started as a narrow-gauge line running south from Denver, Colorado, in 1870. It served mainly as a transcontinental bridge line between Denver, and Salt Lake City, Utah. The Rio Grande was also a major origin of coal and mineral traffic. The Rio Grande was the epitome of mountain railroading, with a motto of ''Through the Rockies, not around them'' and later ''Main line through the Rockies'', both referring to the Rocky Mountains. The D&RGW operated the highest mainline rail line in the United States, over the Tennessee Pass in Colorado, and the famed routes through the Moffat Tunnel and the Royal Gorge. At its height, in 1889, the D&RGW had the largest narrow-gauge railroad network in North America with of track interconnecting the states of Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah. Known for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Western Traction Company
The London and Lake Erie Railway and Transportation Company is a defunct Interurban railway that operated in Ontario, Canada from 1902 to 1918. Originally chartered as the South Western Traction Company, the line was renamed the London and Lake Erie Railway in 1909. Throughout its short life, the line was always referred to locally as "The Traction Line". The South Western Traction Company In 1902, a group of London, Ontario residents led by Thomas Purdom and Alfred E. Welch chartered an electric railway based in London. Unlike the municipally-owned London and Port Stanley Railway, the South Western Traction Company was chartered primarily as a passenger hauling line. Lines were planned to several other municipalities in the area, but ultimately, the line was a 28-mile meandering route between London and Port Stanley. The line began construction in 1903 southward from London to Lambeth. Construction stopped in 1904 when the company ran out of funds but resumed after additiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schomberg And Aurora Railway
The Schomberg and Aurora Railway (S&AR, also nicknamed the "Annie Rooney") was a 36 km long railway in Ontario, Canada, running from the town of Schomberg to Oak Ridges, just south of Aurora. It connected Schomberg to the Metropolitan Line of the Toronto and York Radial Railway (T&YRR) tram service running along Yonge Street, and from there into the Toronto city proper. The service ran for 25 years between 1902 and 1927; the rails were pulled up shortly thereafter. In 1902, the Schomberg and Aurora Railway was acquired by the Metropolitan Street Railway which in turn was acquired by the Toronto and York Radial Railway in 1904. History The S&AR started at the request of a Schomberg businessman who wanted to open the local produce markets to day-trippers from Toronto. The T&YRR had greatly increased visitors to similar markets in Newmarket and they were hoping to do the same for Schomberg. The company was chartered in 1896, and construction started out from the Bond Lake a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Yonge Railways
The North Yonge Railways was a radial railway line operated by the Toronto Transportation Commission from 1930 to 1948 between Glen Echo (Toronto) and Richmond Hill. The line was created by reopening the southern portion of the TTC's Lake Simcoe radial line that had closed in 1930. Operations The North Yonge Railways ran along Yonge Street from Glen Echo Terminal at the then-Toronto city limits through the municipalities of North York, Vaughan, Markham and Richmond Hill. The line was single-track with passing loops and ran almost entirely on the side of the road, with an off-street terminal at Glen Echo and some centre-of-street track in Richmond Hill. The TTC used the Nachod block signal system on the line. The line had a 550-volt substation in Willowdale, which replaced older substations that had been used on the Lake Simcoe line closed in 1930. Service was hourly from Glen Echo to Richmond Hill, every 30 minutes to Steeles Avenue with more frequent service during rush hours. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipissing Central Railway
The Nipissing Central Railway (NCR), sometimes known as the Temiskaming Streetcar Line, is a former interurban streetcar system connecting New Liskeard, Haileybury and Cobalt on the western bank of Lake Temiskaming in northern Ontario from 1910 to 1935. As the line had a federal charter, the operating company continues to be used to operate the Ontario Northland Railway freight spur line between Swastika, Ontario and Rouyn-Noranda, Quebec, avoiding the need to re-charter either end in its respective provinces. History In 1902 the Ontario government chartered the Temiskaming & Northern Ontario Railway (T&NO) to connect the towns of New Liskeard and Haileybury on Lake Temiskaming to North Bay on Lake Nipissing. During construction, silver ore was discovered near the Mile 103 post, just southwest of Haileybury. The Cobalt Silver Rush followed, leading to the incorporation of the town of Cobalt in 1906, and a swelling population reaching 10 to 15,000 by 1911. As the populati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niagara Falls Park And River Railway
Niagara may refer to: Geography Niagara Falls and nearby places In both the United States and Canada *Niagara Falls, the famous waterfalls in the Niagara River * Niagara River, part of the U.S.–Canada border * Niagara Escarpment, the cliff over which the river forms the falls *Niagara Whirlpool, a natural whirlpool downstream from the falls *Niagara Gorge, formed by the recession of the falls United States * Niagara Falls, New York, the U.S. city adjacent to the falls * Niagara County, New York **Niagara Falls State Park, the oldest state park in the US ** Niagara Escarpment AVA, New York wine region * Niagara, New York, a town * Fort Niagara, near Youngstown, New York * Niagara Frontier, a region south of Lakes Ontario and Erie * Buffalo–Niagara Falls metropolitan area * Buffalo Niagara Region, an economic region Canada * Niagara Falls, Ontario, the Canadian city adjacent to the falls * Niagara-on-the-Lake * Niagara Peninsula, between Lakes Ontario and Erie * Niagara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount McKay And Kakabeka Falls Railway
Mount is often used as part of the name of specific mountains, e.g. Mount Everest. Mount or Mounts may also refer to: Places * Mount, Cornwall, a village in Warleggan parish, England * Mount, Perranzabuloe, a hamlet in Perranzabuloe parish, Cornwall, England * Mounts, Indiana, a community in Gibson County, Indiana, United States People * Mount (surname) * William L. Mounts (1862–1929), American lawyer and politician Computing and software * Mount (computing), the process of making a file system accessible * Mount (Unix), the utility in Unix-like operating systems which mounts file systems Displays and equipment * Mount, a fixed point for attaching equipment, such as a hardpoint on an airframe * Mounting board, in picture framing * Mount, a hanging scroll for mounting paintings * Mount, to display an item on a heavy backing such as foamcore, e.g.: ** To pin a biological specimen, on a heavy backing in a stretched stable position for ease of dissection or display ** To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And Port Stanley Railway
The London and Port Stanley Railway (L&PS or L&PSR) was a Canadian railway located in southwestern Ontario. It linked the city of London with Port Stanley on the northern shore of Lake Erie, a distance of approximately . History The L&PS was one of the first railways to be built in Ontario, with construction starting in 1856. It provided connections between London, St. Thomas and Port Stanley. It was built primarily to facilitate trade with the United States, particularly of wood and coal. As a result of its rail connection, a substantial investment was made in the port facilities of Port Stanley, which in turn attracted American and Canadian shipping. Until 1932, coal from Conneaut, Ohio was transported via railway car ferries to Port Stanley. The railway also proved popular with local residents, particularly in the summer when many commuters utilized the system to travel to Port Stanley's beach and resort facilities. However, the railway's service was not always impeccable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamilton Radial Electric Railway
The Hamilton Radial Electric Railway (HRER) was an interurban electric railway which at its maximum extent operated between Hamilton and Oakville in Ontario, Canada. Route Between March 3, 1906 and August 3, 1925, the Hamilton Radial Electric Railway was at its maximum length of , extending from Hamilton Terminal Station to Randall Street in Oakville. From Hamilton Terminal at King and Catherine Streets, the line went via street trackage east along King Street East, north on Sanford Street and east on Wilson Street to Birch Avenue. On a private right-of-way, the line continued north on Birch Avenue and west Burlington Street to Kennilworth Avenue. At this point, the HRER left the tracks it shared with the Hamilton Street Railway. After crossing Kennilworth Avenue, the HRER curved north on a double-track private right-of-way to cross the isthmus that separates Hamilton Harbour from Lake Ontario. The Burlington Canal Bridge crosses its namesake canal which splits the isthmu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |