|
List Of COVID-19 Vaccine Authorizations
National regulatory authorities have granted full or emergency use authorizations for 40 COVID-19 vaccines. Ten vaccines have been approved for emergency or full use by at least one stringent regulatory authority recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO): Pfizer–BioNTech, Oxford–AstraZeneca, Sinopharm BIBP, Moderna, Janssen, CoronaVac, Covaxin, Novavax, Convidecia, and Sanofi–GSK. Seven others are under assessment by the WHO: Sputnik V, Sinopharm WIBP, Abdala, Zifivax, Corbevax, COVIran Barekat, and SCB-2019. Of the 40 vaccines, 16 have a full or emergency authorization in only one country, 12 in ten or fewer countries, and 12 in more than ten countries. Note that in some countries, vaccines may be authorized solely for travel purposes. They may not be approved for the general population. For example, the CoronaVac, Covishield, BBIBP-CorV and Covaxin vaccines are not part of Australia's national vaccination program; however, they are recognized for the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulation Of Therapeutic Goods
The regulation of therapeutic goods, defined as drugs and therapeutic devices, varies by jurisdiction. In some countries, such as the United States, they are regulated at the national level by a single agency. In other jurisdictions they are regulated at the state level, or at both state and national levels by various bodies, as in Australia. The role of therapeutic goods regulation is designed mainly to protect the health and safety of the population. Regulation is aimed at ensuring the safety, quality, and efficacy of the therapeutic goods which are covered under the scope of the regulation. In most jurisdictions, therapeutic goods must be registered before they are allowed to be sold. There is usually some degree of restriction on the availability of certain therapeutic goods, depending on their risk to consumers. History Modern drug regulation has historical roots in the response to the proliferation of universal antidotes which appeared in the wake of Mithridates' death. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZF2001
ZF2001, trade-named Zifivax or ZF-UZ-VAC-2001, is an adjuvanted protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine developed by Anhui Zhifei Longcom in collaboration with the Institute of Microbiology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The vaccine candidate is in Phase III trials with 29,000 participants in China, Ecuador, Malaysia, Pakistan, and Uzbekistan. ZF2001 employs technology similar to other protein-based vaccines in Phase III trials from Novavax, Vector Institute, and Medicago. ZF2001 was first approved for use in Uzbekistan and later China. Production capacity is expected to be one billion doses a year in China and 200 million in Uzbekistan. By July, 100 million doses had been administered in China and Uzbekistan. Medical uses It is administered in three doses over a period of two months. Efficacy In August 2021, preliminary data from a phase III study with 28,500 participants indicated an overall efficacy of 82% against disease of any severity. Efficacy was 93% against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valneva COVID-19 Vaccine
Valneva COVID-19 vaccine is a COVID-19 vaccine developed by French biotechnology company Valneva SE in collaboration with the American biopharmaceutical company Dynavax Technologies. In April 2022, the United Kingdom Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) approved the vaccine, being the first in the world to do so. It was approved for medical use in the European Union in June 2022. Technology It is a whole inactivated virus vaccine, grown in culture using the Vero cell line and inactivated with BPL. It also contains two adjuvants: alum and CpG 1018. It uses the same manufacturing technology as Valneva's Ixiaro vaccine for Japanese encephalitis. History Clinical trials Valneva COVID-19 vaccine completed phase I/II trial with 153 participants in the United Kingdom. The trials were supported by the UK National Institute for Health Research and four British universities. In April 2021, Valneva COVID-19 vaccine commenced phase III trials with approxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inactivated Vaccine
An inactivated vaccine (or killed vaccine) is a vaccine consisting of virus particles, bacteria, or other pathogens that have been grown in culture and then killed to destroy disease-producing capacity. In contrast, live vaccines use pathogens that are still alive (but are almost always attenuated, that is, weakened). Pathogens for inactivated vaccines are grown under controlled conditions and are killed as a means to reduce infectivity and thus prevent infection from the vaccine. Inactivated vaccines were first developed in the late 1800s and early 1900s for cholera, plague, and typhoid. Today, inactivated vaccines exist for many pathogens, including influenza, polio (IPV), rabies, hepatitis A and pertussis. Because inactivated pathogens tend to produce a weaker response by the immune system than live pathogens, immunologic adjuvants and multiple "booster" injections may be required in some vaccines to provide an effective immune response against the pathogen. Attenuated vacci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BBV154
iNCOVACC (codenamed BBV154) is an intranasal COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Bharat Biotech, American company Precision Virologics and the Washington University School of Medicine in St Louis, Missouri, United States. History Clinical trials Phase I trials On recommendation by the Subject Expert Committee (SEC) under the Indian drug regulator, the company is going to conduct phase 1 clinical trials using 75 volunteers and submit safety and immunogenicity data for the committee's consideration before it proceeds to the second phase of the trial. Phase II and III trials On 12 August 2021, after evaluating the results of phase I trial data, the drug regulator approved for phase II/III randomized trials that involves evaluation of the immunogenicity and safety of Covaxin Covaxin (codenamed as BBV152) is a whole inactivated virus-based COVID-19 vaccine developed by Bharat Biotech in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research - National Institute of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sputnik Light
Sputnik Light (russian: Спутник Лайт, Sputnik Layt or Lajt) is a single dose COVID-19 vaccine developed by the Gamaleya Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology. It consists of the first dose of the Sputnik V vaccine, which is based on the Ad26 vector, and it can be stored at a normal refrigerator temperature of . The institute says this version would be ideally suited for areas with acute outbreaks, allowing more people to be vaccinated quickly. It will also be used as a third (booster) dose for those who received Sputnik V at least 6 months earlier. Effectiveness A vaccine is generally considered effective if the estimate is ≥50% with a >30% lower limit of the 95% confidence interval. As of September 2021, no study on Sputnik Light reported confidence intervals, so it is not possible to know the accuracy of the estimates. Effectiveness is generally expected to slowly decrease over time. A real-world study with participants aged 60–79 years in Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Vector Vaccine
A viral vector vaccine is a vaccine that uses a viral vector to deliver genetic material ( DNA), which can be transcribed by the recipient's host cells as mRNA coding for a desired protein (or: antigen) to elicit an immune response. , six viral vector vaccines have been authorized for use in humans in at least one country: four COVID-19 vaccines and two Ebola vaccines. Technology Viral vector vaccines use a modified version of one virus as a vector to deliver to a cell a nucleic acid coding for an antigen for another infectious agent. Viral vector vaccines do not cause infection with either the virus used as the vector, or the source of the antigen. The genetic material it delivers does not integrate into a person's genome. Viral vector vaccines enable antigen expression within cells and induce a robust cytotoxic T cell response, unlike subunit vaccines which only confer humoral immunity. Most viral vectors are designed to be incapable of replication because the necessary gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Vaccine
A DNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that transfects a specific antigen-coding DNA sequence into the cells of an organism as a mechanism to induce an immune response. DNA vaccines work by injecting genetically engineered plasmid containing the DNA sequence encoding the antigen(s) against which an immune response is sought, so the cells directly produce the antigen, thus causing a protective immunological response. DNA vaccines have theoretical advantages over conventional vaccines, including the "ability to induce a wider range of types of immune response". Several DNA vaccines have been tested for veterinary use. In some cases, protection from disease in animals has been obtained, in others not. Research is ongoing over the approach for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases in humans, as well as for cancers. In August 2021, Indian authorities gave emergency approval to ZyCoV-D. Developed by Cadila Healthcare, it is the first DNA vaccine approved for humans. History Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Vaccine
An mRNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that uses a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) to produce an immune response. The vaccine delivers molecules of antigen-encoding mRNA into immune cells, which use the designed mRNA as a blueprint to build foreign protein that would normally be produced by a pathogen (such as a virus) or by a cancer cell. These protein molecules stimulate an adaptive immune response that teaches the body to identify and destroy the corresponding pathogen or cancer cells. The mRNA is delivered by a co-formulation of the RNA encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles that protect the RNA strands and help their absorption into the cells. Reactogenicity, the tendency of a vaccine to produce adverse reactions, is similar to that of conventional non-RNA vaccines. People susceptible to an autoimmune response may have an adverse reaction to messenger RNA vaccines. The advantages of mRNA vaccines over traditional vaccines are ease of design, speed and lower cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19 Vaccination In Australia
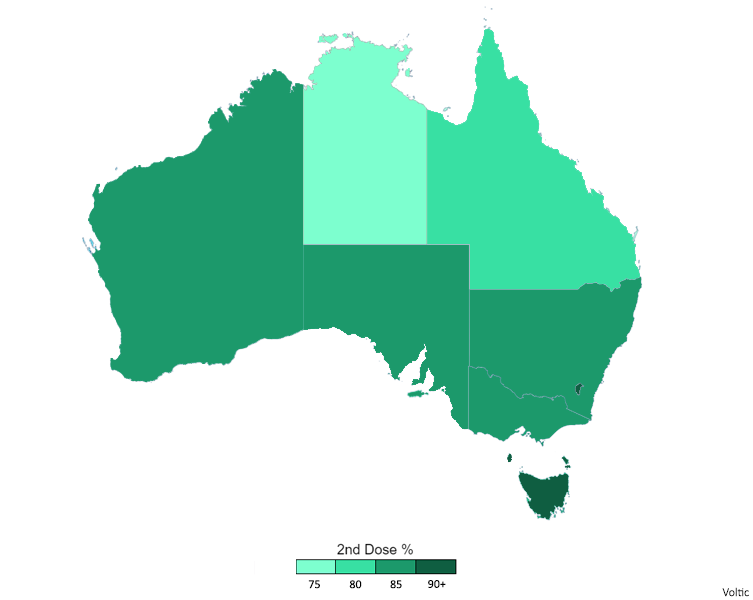
The general COVID-19 vaccination in Australia program began on 22 February 2021 in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, with the goal of vaccinating all willing people in Australia before 2022. Front-line workers and aged care staff and residents had priority for being inoculated, before a gradual phased release to less-vulnerable and lower-risk population groups throughout 2021. The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) approved four vaccines for Australian use in 2021: the Pfizer–BioNTech vaccine on 25 January, the Oxford–AstraZeneca vaccine on 16 February, Janssen vaccine on 25 June and the Moderna vaccine on 9 August. Although approved for use, the Janssen vaccine was not included in the Australian vaccination program . As of 3 August 2022, Australia had administered 62,492,656 vaccine doses across the country.(The data on this site changes daily)( The data on this site changes daily.)( The data on this site changes daily) The country's vaccination rollout initia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BBIBP-CorV
The Sinopharm BIBP COVID-19 vaccine, also known as BBIBP-CorV, the Sinopharm COVID-19 vaccine, or BIBP vaccine, is one of two Inactivated vaccine, whole inactivated virus COVID-19 vaccines developed by Sinopharm's Beijing Institute of Biological Products (sometimes written as Beijing Bio-Institute of Biological Products, resulting in the two different acronyms BBIBP and BIBP for the same vaccine). It completed Phases of clinical research#Phase III, Phase III trials in Argentina, Bahrain, Egypt, Morocco, Pakistan, Peru, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) with over 60,000 participants. BBIBP-CorV shares similar technology with CoronaVac and Covaxin, other inactivated virus vaccines for COVID-19. Its product name is SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine (Vero Cell), not to be confused with the similar product name of CoronaVac. Peer-reviewed results published in ''JAMA'' of Phase III trials in United Arab Emirates and Bahrain showed that the vaccine is 78.1% effective against symptomatic cases and 100% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |