|
List Of AMD Turion Microprocessors
Turion 64 is the name of a family of CPUs designed by AMD for the mobile computing market. Features overview CPU features table Single-core mobile processors Turion 64 "Lancaster" (90 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit, AMD64, PowerNow!'' "Richmond" (90 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit, AMD64, PowerNow!, AMD-V'' Sempron (Turion 64-based) "Sable" (65 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit, AMD64, PowerNow!'' Athlon (Turion 64-based) "Sable" (65 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit, AMD64, PowerNow!, AMD-V'' Sempron (Turion X2-based) "Huron" (65 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit, AMD64 Sempron (Turion II-based) "Caspian" ( 45 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSE4a, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit, AMD64, PowerNow!, AMD-V'' Dual-core mobile process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
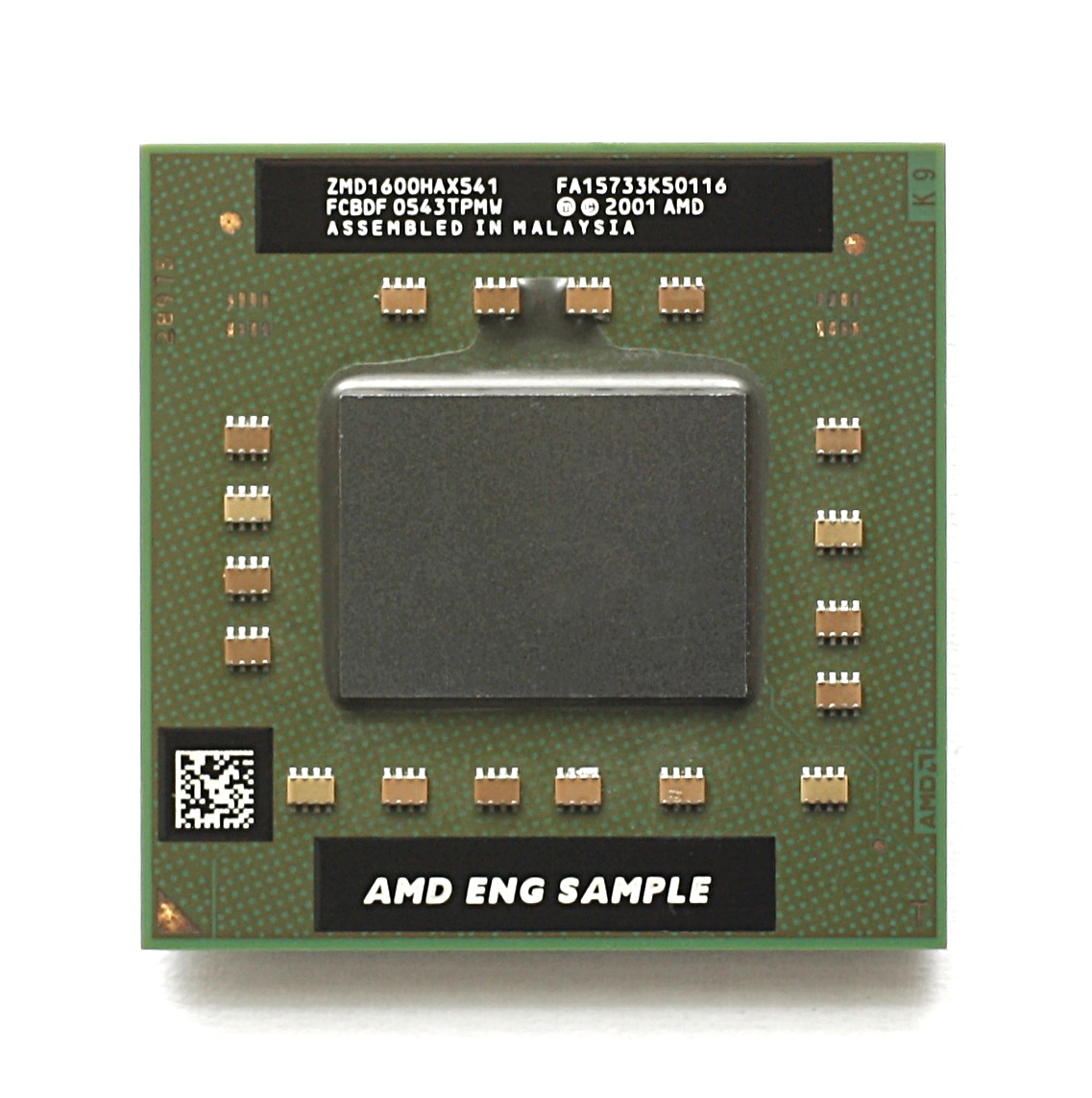
Turion 64
AMD Turion is the brand name AMD applies to its x86-64 low-power consumption (''mobile'') processors codenamed ''K8L''. The Turion 64 and Turion 64 X2/Ultra processors compete with Intel's mobile processors, initially the ''Pentium M'' and the Intel Core and Intel Core 2 processors. Features Turion 64 Earliest Turion 64 processors are plugged into AMD's Socket 754. They are equipped with 512 or 1024 KiB of L2 cache, a 64-bit single channel on-die DDR-400 memory controller, and an 800 MHz HyperTransport bus. Battery saving features, like ''PowerNow!'', are central to the marketing and usefulness of these CPUs. The newer "Richmond" models are designed for AMD's Socket S1 and have a double-channel DDR2 controller. Turion 64 X2 Turion 64 X2 is AMD's 64-bit dual-core mobile CPU, intended to compete with Intel's Core and Core 2 CPUs. The Turion 64 X2 was launched on May 17, 2006, after several delays. These processors use Socket S1 and feature DDR2 memory. They also include AMD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 754
Socket 754 is a CPU socket originally developed by AMD to supersede its Athlon XP platform (Socket 462, also referred to as Socket A). Socket 754 was the first socket developed by AMD to support their new consumer version of the 64 bit microprocessor family known as AMD64. Technical specifications Socket 754 was the original socket for AMD's Athlon 64 desktop processors. Due to the introduction of newer socket layouts (i.e. Socket 939, Socket 940 and Socket AM2), Socket 754 became the more "budget-minded" socket for use with AMD Athlon 64 or Sempron processors. It differs from Socket 939 in several areas: * support for a single channel memory controller (64 bits wide) with a maximum of three unbuffered DIMMs, or four registered DIMMs * no dual channel support * lower HyperTransport speed (800 MHz Bi-Directional, 16 bit data path, up and downstream) * lower effective data bandwidth (9.6 GB/s) * lower motherboard manufacturing costs Although AMD promoted Socket 754 as a bud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table Of AMD Processors
References See also * List of AMD microprocessors * List of AMD CPU microarchitectures * List of AMD mobile microprocessors * List of AMD Athlon microprocessors * List of AMD Athlon XP microprocessors * List of AMD Athlon 64 microprocessors * List of AMD Athlon X2 microprocessors * List of AMD Duron microprocessors * List of AMD Sempron microprocessors * List of AMD Turion microprocessors * List of AMD Opteron microprocessors * List of AMD Epyc microprocessors * List of AMD Phenom microprocessors * List of AMD FX microprocessors * List of AMD Ryzen microprocessors The AMD Ryzen family is an x86-64 microprocessor family from AMD, based on the Zen microarchitecture. The Ryzen lineup includes Ryzen 3, Ryzen 5, Ryzen 7, Ryzen 9, and Ryzen Threadripper with up to 64 cores. All consumer Ryzens have an unlocked mul ... * List of AMD Accelerated Processing Unit microprocessors * List of Intel microprocessors * List of Intel CPU microarchitectures * Comparison of Intel pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of AMD Mobile Microprocessors
Features overview CPUs CPU features table APUs APU features table Initial platform (2003) Launched in 2003, the initial platform for mobile AMD processors consists of: Mobile Sempron "Dublin" (Socket 754, CG, 130 nm, Desktop replacement) '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit'' "Dublin" (Socket 754, CG, 130 nm, Low power) ''MMX, SSE, SSE2, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit'' "Georgetown" (Socket 754, D0, 90 nm, Desktop replacement) ''MMX, SSE, SSE2, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit'' "Sonora" (Socket 754, D0, 90 nm, Low power) ''MMX, SSE, SSE2, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit'' "Albany" (Socket 754, E6, 90 nm, Desktop replacement) ''MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit'' "Roma" (Socket 754, E6, 90 nm, Low power) ''MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit'' Mobile Athlon 64 "ClawHammer" (C0 & CG, 130 nm, Desktop replacement) ''MMX, SSE, SSE2, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit, AMD64 (AMD's x86-64 implementation), PowerNow!'' "ClawHammer" (C0 & CG, 130 nm, 62 W TDP) ''M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMD Mobile Platform
The AMD mobile platform is an open platform for laptops from AMD. Though little marketing was done on this platform, it has been competing with the Centrino platform in the segment to gain more marketshare. Each platform has its own specification, catching up the latest technology developments. Since the acquisition of ATI, AMD began to include Mobility Radeon GPUs and AMD chipsets as part of the requirements of the mobile platform; the first of such platforms is the ''Puma'' platform. Open platform approach In February 2007, AMD had announced the "Better by Design" initiative to continue the success of the open platform approach for desktop back in early 2003 after the launch of Athlon 64 processors with a lack of chipset being developed by AMD, and open the platform to chipset vendors such as VIA, SiS, NVIDIA and from AMD subsidiary ATI. The initiative also includes platforms succeeding the ''Kite Refresh'' mobile platform. Under the "Better by Design" initiative, AMD introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front-side Bus
A front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the central processing unit (CPU) and a memory controller hub, known as the northbridge. Depending on the implementation, some computers may also have a back-side bus that connects the CPU to the cache. This bus and the cache connected to it are faster than accessing the system memory (or RAM) via the front-side bus. The speed of the front side bus is often used as an important measure of the performance of a computer. The original front-side bus architecture has been replaced by HyperTransport, Intel QuickPath Interconnect or Direct Media Interface in modern volume CPUs. History The term came into use by Intel Corporation about the time the Pentium Pro and Pentium II products were announced, in the 1990s. "Front side" refers to the extern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DDR3 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth (" double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-speed successor to DDR and DDR2 and predecessor to DDR4 synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) chips. DDR3 SDRAM is neither forward nor backward compatible with any earlier type of random-access memory (RAM) because of different signaling voltages, timings, and other factors. DDR3 is a DRAM interface specification. The actual DRAM arrays that store the data are similar to earlier types, with similar performance. The primary benefit of DDR3 SDRAM over its immediate predecessor DDR2 SDRAM, is its ability to transfer data at twice the rate (eight times the speed of its internal memory arrays), enabling higher bandwidth or peak data rates. The DDR3 standard permits DRAM chip capacities of up to 8 gigabits (Gbit), and up to four ranks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
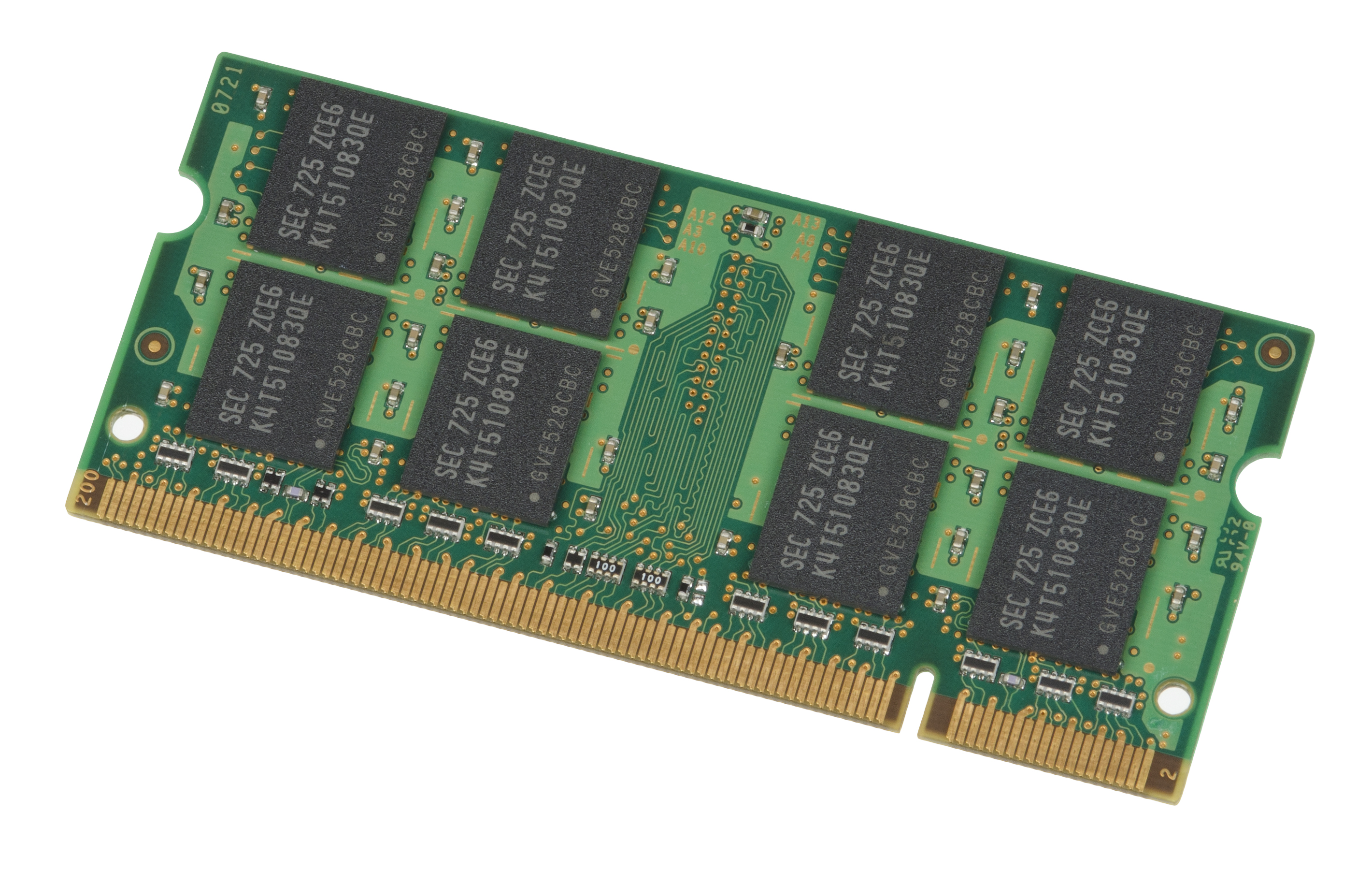
DDR2 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It superseded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself superseded by DDR3 SDRAM (launched in 2007). DDR2 DIMMs are neither forward compatible with DDR3 nor backward compatible with DDR. In addition to double pumping the data bus as in DDR SDRAM (transferring data on the rising and falling edges of the bus clock signal), DDR2 allows higher bus speed and requires lower power by running the internal clock at half the speed of the data bus. The two factors combine to produce a total of four data transfers per internal clock cycle. Since the DDR2 internal clock runs at half the DDR external clock rate, DDR2 memory operating at the same external data bus clock rate as DDR results in DDR2 being able to provide the same bandwidth but with better latency. Alternatively, DDR2 memory operating at twice the external data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating-point Unit
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can be represented as a base-ten floating-point number: 12.345 = \underbrace_\text \times \underbrace_\text\!\!\!\!\!\!^ In practice, most floating-point systems use base two, though base ten (decimal floating point) is also common. The term ''floating point'' refers to the fact that the number's radix point can "float" anywhere to the left, right, or between the significant digits of the number. This position is indicated by the exponent, so floating point can be considered a form of scientific notation. A floating-point system can be used to represent, with a fixed number of digits, numbers of very different orders of magnitude — such as the number of meters between galaxies or between protons in an atom. For this reason, floating-poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSE4a
SSE4 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 4) is a SIMD CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 (K8L). It was announced on September 27, 2006, at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper; more precise details of 47 instructions became available at the Spring 2007 Intel Developer Forum in Beijing, in the presentation. SSE4 is fully compatible with software written for previous generations of Intel 64 and IA-32 architecture microprocessors. All existing software continues to run correctly without modification on microprocessors that incorporate SSE4, as well as in the presence of existing and new applications that incorporate SSE4. SSE4 subsets Intel SSE4 consists of 54 instructions. A subset consisting of 47 instructions, referred to as ''SSE4.1'' in some Intel documentation, is available in Penryn. Additionally, ''SSE4.2'', a second subset consisting of the 7 remaining instructions, is first available in Nehalem-based Core i7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
45 Nm
Per the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors, the 45 nm process is a MOSFET technology node referring to the average half-pitch of a memory cell manufactured at around the 2007–2008 time frame. Matsushita and Intel started mass-producing 45 nm chips in late 2007, and AMD started production of 45 nm chips in late 2008, while IBM, Infineon, Samsung, and Chartered Semiconductor have already completed a common 45 nm process platform. At the end of 2008, SMIC was the first China-based semiconductor company to move to 45 nm, having licensed the bulk 45 nm process from IBM. In 2008, TSMC moved on to a 40nm process. Many critical feature sizes are smaller than the wavelength of light used for lithography (i.e., 193 nm and 248 nm). A variety of techniques, such as larger lenses, are used to make sub-wavelength features. Double patterning has also been introduced to assist in shrinking distances between features, especially if dry lith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket ASB1
Socket may refer to: Mechanics * Socket wrench, a type of wrench that uses separate, removable sockets to fit different sizes of nuts and bolts * Socket head screw, a screw (or bolt) with a cylindrical head containing a socket into which the hexagonal ends of an Allen wrench will fit * Socket termination, a termination used at the ends of wire rope * Socket, the receptacle into which a tapered tool is inserted * Socket, an opening in any fitting that matches the outside diameter of a pipe or tube Biology * Eye socket, a region in the skull where the eyes are positioned * Tooth socket, a cavity containing a tooth, in those bones that bear teeth * Dry socket, an opening as a result of the blood not clotting after a tooth is pulled * Ball and socket joint The ball-and-socket joint (or spheroid joint) is a type of synovial joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |