|
Lisa Steiner (model)
Lisa Steiner is a professor of immunology in the department of biology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. When she arrived at MIT in 1967, she was the first woman faculty member in the department. Her research focuses on the evolution and development of the immune system, using zebrafish as a model organism. Early life and education Steiner was born in Austria and left the country with her mother shortly before the Anschluss. She spend the rest of her childhood in Queens, New York. She won the well-known Westinghouse Science Talent Search competition as a high school student but chose to major in mathematics at Swarthmore College, where she received her bachelor's degree. Deterred from pursuing graduate school in math at Princeton University because the department did not admit women at the time, she instead attended Harvard University for a short time before deciding to change her career path by applying to medical school. She received her M.D. from Yale School of Medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous city and state. A landlocked country, Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has a population of 9 million. Austria emerged from the remnants of the Eastern and Hungarian March at the end of the first millennium. Originally a margraviate of Bavaria, it developed into a duchy of the Holy Roman Empire in 1156 and was later made an archduchy in 1453. In the 16th century, Vienna began serving as the empire's administrative capital and Austria thus became the heartland of the Habsburg monarchy. After the dissolution of the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postdoctoral Fellow
A postdoctoral fellow, postdoctoral researcher, or simply postdoc, is a person professionally conducting research after the completion of their doctoral studies (typically a PhD). The ultimate goal of a postdoctoral research position is to pursue additional research, training, or teaching in order to have better skills to pursue a career in academia, research, or any other field. Postdocs often, but not always, have a temporary academic appointment, sometimes in preparation for an academic faculty position. They continue their studies or carry out research and further increase expertise in a specialist subject, including integrating a team and acquiring novel skills and research methods. Postdoctoral research is often considered essential while advancing the scholarly mission of the host institution; it is expected to produce relevant publications in peer-reviewed academic journals or conferences. In some countries, postdoctoral research may lead to further formal qualificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Genetics
Molecular genetics is a sub-field of biology that addresses how differences in the structures or expression of DNA molecules manifests as variation among organisms. Molecular genetics often applies an "investigative approach" to determine the structure and/or function of genes in an organism's genome using genetic screens. The field of study is based on the merging of several sub-fields in biology: classical Mendelian inheritance, Cell biology, cellular biology, molecular biology, biochemistry, and biotechnology. Researchers search for mutations in a gene or induce mutations in a gene to link a gene sequence to a specific phenotype. Molecular genetics is a powerful methodology for linking mutations to genetic conditions that may aid the search for treatments/cures for various genetics diseases. History For molecular genetics to develop as a discipline, several scientific discoveries were necessary. The discovery of DNA as a means to transfer the genetic code of life f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
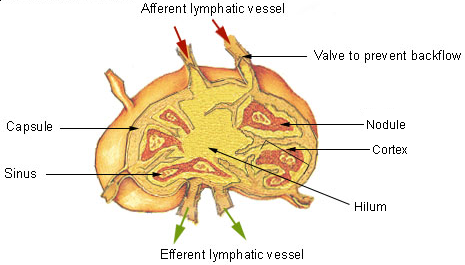
Lymphoid Organs
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the Latin word ''lympha'' refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha") back towards the heart, for re-circulation. Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres. The other main function is that of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocytic
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of gnathostomata, most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated immunity, cell-mediated, cytotoxicity, cytotoxic innate immune system, innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity), and B cells (for humoral immunity, humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte". Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cells, B cells and Natural killer cell, natural killer (NK) cells. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cells T cells (thymus cells) and B cells (bone marrow- or bursa of Fabricius, bursa-derived cells) are the major cellular components of the adaptive immune response. T cells are involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Although metabolic composition does get altered quite dramaticall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following: * jawless fish, which include hagfish and lampreys * jawed vertebrates, which include: ** cartilaginous fish (sharks, rays, and ratfish) ** bony vertebrates, which include: *** ray-fins (the majority of living bony fish) *** lobe-fins, which include: **** coelacanths and lungfish **** tetrapods (limbed vertebrates) Extant vertebrates range in size from the frog species ''Paedophryne amauensis'', at as little as , to the blue whale, at up to . Vertebrates make up less than five percent of all described animal species; the rest are invertebrates, which lack vertebral columns. The vertebrates traditionally include the hagfish, which do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helen Hay Whitney Foundation
The Helen Hay Whitney Foundation, established in New York in 1943 by Joan Whitney Payson in cooperation with the estate planning of her mother, Helen Hay Whitney (1875–1944), awards the "Helen Hay Whitney Postdoctoral Fellowship" for support postdoctoral research in the biomedical sciences. Currently the Foundation awards 20 fellowships per year. The award is one of four highly competitive postdoctoral awards in the life sciences,''JCC Fund Newsletter'', 2007. and many of North America's leading scientists and medical researchers were supported in the early stages of their career by the Whitney Foundation. Members of the Scientific Advisory Committee have included: * Barbara Meyer * Erin O'Shea * Matthew Scharff * Daniel Kahne * Thomas Jessell * Stephen C. Harrison * Julie Theriot * Jonathan Weissman * S. Lawrence Zipursky Notable fellows have included: * Eric J. Ackerman * David Agard * Ronald A. Albright * David J. Anderson * Karen M. Arndt * Cornelia Bargmann * Marga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Vest
Charles "Chuck" Marstiller Vest (September 9, 1941 – December 12, 2013) was an American educator and engineer. He served as President of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology from October 1990 until December 2004. He succeeded Paul Gray and was succeeded by Susan Hockfield. He served as president of the National Academy of Engineering from 2007 to 2013. Education and career Vest was born in Morgantown, West Virginia, in 1941. He went to Morgantown High School. He graduated from West Virginia University in Morgantown in 1963 with a bachelor of science degree in mechanical engineering, and earned a master of science in engineering degree in 1964 and a PhD in 1967, both in mechanical engineering at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, Michigan, where he later served as professor of mechanical engineering, dean of the College of Engineering, and provost of the university, prior to his appointment as MIT's president. In 2004, a selection of Vest's speeches from his time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary-Lou Pardue
Mary-Lou Pardue is an American geneticist who is an emeritus professor in the Department of Biology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, which she originally joined in 1972. Her research focused on the role of telomeres in chromosome replication, particularly in ''Drosophila'' (fruit flies). Early life and education Pardue received a bachelor's degree in biology in 1955 from the College of William and Mary. She received a master's degree in radiation biology in 1959 from the University of Tennessee, where she had been eligible for a Ph.D. but convinced the department to give her the master's degree instead, later explaining in an interview that "in the society I was in it was quite all right for a wife to be going to school, but getting a Ph.D. was a little too serious". She subsequently worked for several years as a research technician before returning to graduate school at Yale University, from which she received a Ph.D. in biology in 1970. She worked under the supervi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nancy Hopkins (scientist)
Nancy Hopkins, an American molecular biologist, (born 16 June 1943) is the Amgen, Inc. Professor of Biology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. She is a member of the United States National Academy of Sciences, National Academy of Sciences, the Institute of Medicine of the National Academy, and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. She is known for her research identifying genes required for zebrafish development, and for her earlier research on gene expression in the bacterial virus, lambda, and on mouse RNA tumor viruses. She is also known for her work promoting equality of opportunity for women scientists in academia. Early life and education Nancy Hopkins was born in 1943 in New York City. Hopkins received her BA from Radcliffe College in 1964, and earned her PhD from the Department of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry at Harvard University in 1971, where she worked with Professor Mark Ptashne. With Ptashne she identified the operator sites on DNA to which th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |