|
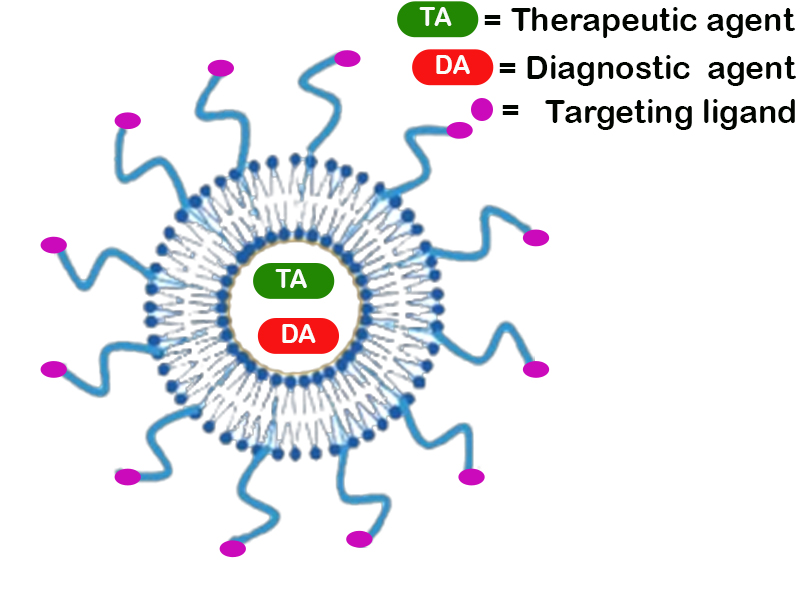
Liposomes
A liposome is a small artificial Vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicle, spherical in shape, having at least one lipid bilayer. Due to their hydrophobicity and/or hydrophilicity, biocompatibility, particle size and many other properties, liposomes can be used as drug delivery vehicles for route of administration, administration of pharmaceutical drugs and nutrients, such as solid lipid nanoparticles, lipid nanoparticles in mRNA vaccines, and DNA vaccination, DNA vaccines. Liposomes can be prepared by disrupting biological membranes (such as by sonication). Liposomes are most often composed of phospholipids, especially phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol, but may also include other lipids, such as Egg (food), egg, phosphatidylethanolamine, as long as they are compatible with lipid bilayer structure. A liposome design may employ surface ligands for attaching to unhealthy tissue. The major types of liposomes are the multilamellar vesicle (MLV, with several lamellar phase lipid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liposome Scheme-en
A liposome is a small artificial vesicle, spherical in shape, having at least one lipid bilayer. Due to their hydrophobicity and/or hydrophilicity, biocompatibility, particle size and many other properties, liposomes can be used as drug delivery vehicles for administration of pharmaceutical drugs and nutrients, such as lipid nanoparticles in mRNA vaccines, and DNA vaccines. Liposomes can be prepared by disrupting biological membranes (such as by sonication). Liposomes are most often composed of phospholipids, especially phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol, but may also include other lipids, such as egg, phosphatidylethanolamine, as long as they are compatible with lipid bilayer structure. A liposome design may employ surface ligands for attaching to unhealthy tissue. The major types of liposomes are the multilamellar vesicle (MLV, with several lamellar phase lipid bilayers), the small unilamellar liposome vesicle (SUV, with one lipid bilayer), the large unilam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liposome
A liposome is a small artificial vesicle, spherical in shape, having at least one lipid bilayer. Due to their hydrophobicity and/or hydrophilicity, biocompatibility, particle size and many other properties, liposomes can be used as drug delivery vehicles for administration of pharmaceutical drugs and nutrients, such as lipid nanoparticles in mRNA vaccines, and DNA vaccines. Liposomes can be prepared by disrupting biological membranes (such as by sonication). Liposomes are most often composed of phospholipids, especially phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol, but may also include other lipids, such as egg, phosphatidylethanolamine, as long as they are compatible with lipid bilayer structure. A liposome design may employ surface ligands for attaching to unhealthy tissue. The major types of liposomes are the multilamellar vesicle (MLV, with several lamellar phase lipid bilayers), the small unilamellar liposome vesicle (SUV, with one lipid bilayer), the large unilamellar vesicle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unilamellar Liposome
A unilamellar liposome is a spherical liposome, a vesicle, bounded by a single bilayer of an amphiphilic lipid or a mixture of such lipids, containing aqueous solution inside the chamber. Unilamellar liposomes are used to study biological systems and to mimic cell membranes, and are classified into three groups based on their size: small unilamellar liposomes/vesicles (SUVs) that with a size range of 20–100 nm, large unilamellar liposomes/vesicles (LUVs) with a size range of 100–1000 nm and giant unilamellar liposomes/vesicles (GUVs) with a size range of 1-200 µm. GUVs are mostly used as models for biological membranes in research work. Animal cells are 10–30 µm and plant cells are typically 10–100 µm. Even smaller cell organelles such as mitochondria are typically 1-2 µm. Therefore, a proper model should account for the size of the specimen being studied. In addition, the size of vesicles dictates their membrane curvature which is an impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus, and membranes of the membrane-bound organelles in the cell. The lipid bilayer is the barrier that keeps ions, proteins and other molecules where they are needed and prevents them from diffusing into areas where they should not be. Lipid bilayers are ideally suited to this role, even though they are only a few nanometers in width, because they are impermeable to most water-soluble ( hydrophilic) molecules. Bilayers are particularly impermeable to ions, which allows cells to regulate salt concentrations and pH by transporting ions across their membranes using proteins called ion pumps. Biological bilayers are usually composed of amphiphilic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerald Weissmann
Gerald Weissmann (August 7, 1930 – July 10, 2019) was an Austrian-born American physician/scientist, editor, and essayist. He was Professor Emeritus and Research Professor of Medicine (Rheumatology) at New York University School of Medicine. He was editor-in-chief (2006–16) of ''The FASEB Journal''. At the time of his death he was its book review editor. In 1965, he was one of the discoverers of liposomes and is credited with coining that term. Early life and education Weissmann was born in Vienna, Austria, on August 7, 1930, to Adolf and Greta (Lustbader) Weissmann. His family, being Jewish, fled the Nazis and immigrated to the United States in 1938, and Gerald and his family became naturalized American citizens in 1943. After the Bronx High School of Science, he received a B.A. from Columbia University in 1950 and his M.D. from New York University in 1954. He also pursued an early career in art, exhibiting at a major New York gallery. Career After clinical training at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesicle (biology And Chemistry)
In cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion ( exocytosis), uptake ( endocytosis) and transport of materials within the plasma membrane. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes (not to be confused with lysosomes). If there is only one phospholipid bilayer, the vesicles are called '' unilamellar liposomes''; otherwise they are called ''multilamellar liposomes''. The membrane enclosing the vesicle is also a lamellar phase, similar to that of the plasma membrane, and intracellular vesicles can fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell. Vesicles can also fuse with other organelles within the cell. A vesicle released from the cell is known as an extracellular vesicle. Vesicles perform a variety of functions. Because it is separated from the cytosol, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellar Phase
Lamellar phase refers generally to packing of polar-headed long chain nonpolar-tail molecules in an environment of bulk polar liquid, as sheets of bilayers separated by bulk liquid. In biophysics, polar lipids (mostly, phospholipids, and rarely, glycolipids) pack as a liquid crystalline bilayer, with hydrophobic fatty acyl long chains directed inwardly and polar headgroups of lipids aligned on the outside in contact with water, as a 2-dimensional flat sheet surface. Under transmission electron microscope (TEM), after staining with polar headgroup reactive chemical osmium tetroxide, lamellar lipid phase appears as two thin parallel dark staining lines/sheets, constituted by aligned polar headgroups of lipids. 'Sandwiched' between these two parallel lines, there exists one thicker line/sheet of non-staining closely packed layer of long lipid fatty acyl chains. This TEM-appearance became famous as Robertson's unit membrane - the basis of all biological membranes, and structure of lipi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alec Douglas Bangham
Alec Douglas Bangham FRS (10 November 1921 Manchester – 9 March 2010 Great Shelford) was a British biophysicist who first studied blood clotting mechanisms but became well known for his research on liposomes and his invention of clinically useful artificial lung surfactants. Life Bangham was the son of Donald Bangham, and Edith Kerby. He studied at the Downs School, and then Bryanston School, and proceeded to earn an MB MS in medicine from University College London. He was appointed to Addenbrooke's Hospital, where he served as a pathologist, in the Royal Army Medical Corps, becoming a captain in 1948. Bangham worked at the Babraham Institute in Cambridge from 1952 to 1982. He is best known for his research on liposomes. Family He was married to Rosalind; they had four children and eleven grandchildren. His brother was Derek Bangham. Awards *1965 doctorate of medicine from London University *1977 Fellow of the Royal Society *1981 Fellow of University College London *199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Delivery
Drug delivery refers to approaches, formulations, manufacturing techniques, storage systems, and technologies involved in transporting a pharmaceutical compound to its target site to achieve a desired therapeutic effect. Principles related to drug preparation, route of administration, site-specific targeting, metabolism, and toxicity are used to optimize efficacy and safety, and to improve patient convenience and compliance. Drug delivery is aimed at altering a drug's pharmacokinetics and specificity by formulating it with different excipients, drug carriers, and medical devices. There is additional emphasis on increasing the bioavailability and duration of action of a drug to improve therapeutic outcomes. Some research has also been focused on improving safety for the person administering the medication. For example, several types of microneedle patches have been developed for administering vaccines and other medications to reduce the risk of needlestick injury. Drug deli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Route Of Administration
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the way by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body. Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. Common examples include oral and intravenous administration. Routes can also be classified based on where the target of action is. Action may be topical (local), enteral (system-wide effect, but delivered through the gastrointestinal tract), or parenteral (systemic action, but delivered by routes other than the GI tract). Route of administration and dosage form are aspects of drug delivery. Classification Routes of administration are usually classified by application location (or exposition). The route or course the active substance takes from application location to the location where it has its target effect is usually rather a matter of pharmacokinetics (concerning the processes of uptake, distribution, and elimination of dru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmalemma
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Vaccination
A DNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that transfects a specific antigen-coding DNA sequence into the cells of an organism as a mechanism to induce an immune response. DNA vaccines work by injecting genetically engineered plasmid containing the DNA sequence encoding the antigen(s) against which an immune response is sought, so the cells directly produce the antigen, thus causing a protective immunological response. DNA vaccines have theoretical advantages over conventional vaccines, including the "ability to induce a wider range of types of immune response". Several DNA vaccines have been tested for veterinary use. In some cases, protection from disease in animals has been obtained, in others not. Research is ongoing over the approach for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases in humans, as well as for cancers. In August 2021, Indian authorities gave emergency approval to ZyCoV-D. Developed by Cadila Healthcare, it is the first DNA vaccine approved for humans. History C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)