|
Linux-based Devices
Linux-based devices or Linux devices are computer appliances that are powered by the Linux kernel and possibly parts of the GNU operating system. Device manufacturers' reasons to use Linux may be various: low cost, security, stability, scalability or customizability. Many original equipment manufacturers use free and open source software to brand their products. Community maintained Linux devices are also available. Community maintained devices These devices were not intended to run Linux at the time of their production, but a community effort made possible either full or partial Linux support. Because of the open source philosophy that free and open source software brings to the software world, many people have ported the Linux kernel to run on devices other than a typical desktop, laptop or server computer. Some ports are performed by committed individuals or groups to provide alternative software on their favorite hardware. Examples include iPods, PlayStations, Xbox, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Series 2 Tivo Front
Series may refer to: People with the name * Caroline Series (born 1951), English mathematician, daughter of George Series * George Series (1920–1995), English physicist Arts, entertainment, and media Music * Series, the ordered Set (music), sets used in serialism including tone rows * Harmonic series (music) * Serialism, including the twelve-tone technique Types of series in arts, entertainment, and media * Anime series * Book series * Comic book series * Film series * Manga series * Podcast series * Radio series * Television series * "Television series", the Australian, British, and a number of others countries' equivalent term for the North American "television season", a set of episodes produced by a television serial * Video game series * Web series Mathematics and science * Series (botany), a taxonomic rank between genus and species * Series (mathematics), the sum of a sequence of terms * Series (stratigraphy), a stratigraphic unit deposited during a certain interva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smartphone
A smartphone is a mobile phone with advanced computing capabilities. It typically has a touchscreen interface, allowing users to access a wide range of applications and services, such as web browsing, email, and social media, as well as multimedia playback and Streaming media, streaming. Smartphones have built-in cameras, GPS navigation, and support for various communication methods, including voice calls, text messaging, and internet-based messaging apps. Smartphones are distinguished from older-design feature phones by their more advanced hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, access to the internet, business applications, Mobile payment, mobile payments, and multimedia functionality, including music, video, mobile gaming, gaming, Internet radio, radio, and Mobile television, television. Smartphones typically feature MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) chips, various sensors, and support for multiple wireless communicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux-based Devices
Linux-based devices or Linux devices are computer appliances that are powered by the Linux kernel and possibly parts of the GNU operating system. Device manufacturers' reasons to use Linux may be various: low cost, security, stability, scalability or customizability. Many original equipment manufacturers use free and open source software to brand their products. Community maintained Linux devices are also available. Community maintained devices These devices were not intended to run Linux at the time of their production, but a community effort made possible either full or partial Linux support. Because of the open source philosophy that free and open source software brings to the software world, many people have ported the Linux kernel to run on devices other than a typical desktop, laptop or server computer. Some ports are performed by committed individuals or groups to provide alternative software on their favorite hardware. Examples include iPods, PlayStations, Xbox, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
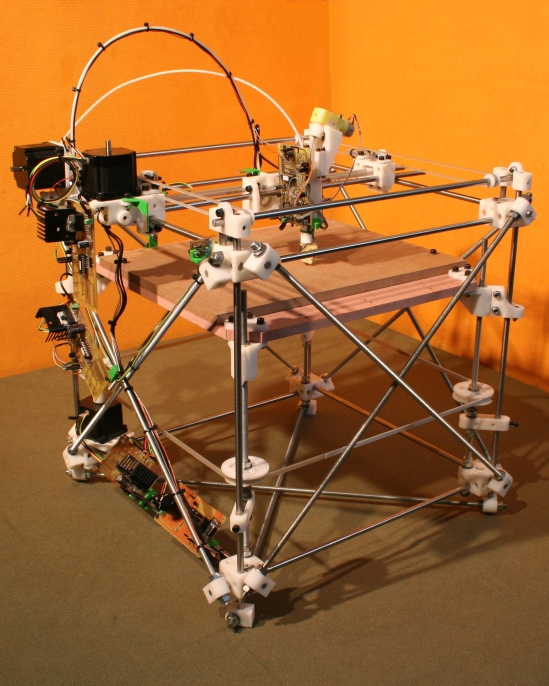
Open-source Robotics
Open-source robotics is a branch of robotics where robots are developed with open-source hardware and free and open-source software, publicly sharing blueprints, schematics, and source code. It is thus closely related to the open design movement, the maker movement and open science. Requirements Open source robotics means that information about the hardware is easily discerned, so that others can easily rebuild it. In turn, this requires design to use only easily available standard subcomponents and tools, and for the build process to be documented in detail including a bill of materials and detailed ('Ikea style') step-by-step building and testing instructions. (A CAD file alone is not sufficient, as it does not show the steps for performing or testing the build). These requirements are standard to open source hardware in general, and are formalised by various licences, certifications, especially those defined by the peer-reviewed journals Journal of Open Hardware and Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-design Movement
The open-design movement involves the development of physical products, machines and systems through use of publicly shared design information. This includes the making of both free and open-source software (FOSS) as well as open-source hardware. The process is generally facilitated by the Internet and often performed without monetary compensation. The goals and philosophy of the movement are identical to that of the open-source movement, but are implemented for the development of physical products rather than software. Open design is a form of co-creation, where the final product is designed by the users, rather than an external stakeholder such as a private company. Origin Sharing of manufacturing information can be traced back to the 18th and 19th century. Aggressive patenting put an end to that period of extensive knowledge sharing. More recently, principles of open design have been related to the free software, free and open-source software, open-source software movements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux For Mobile Devices
Linux for mobile devices, sometimes referred to as mobile Linux, is the usage of Linux-based operating systems on portable devices, whose primary or only Human interface device (HID) is a touchscreen. It mainly comprises smartphones and tablet computers, but also some mobile phones, personal digital assistants (PDAs) portable media players that come with a touchscreen separately. Mobile Linux is a relatively recent addition to the Linux range of use, with Google's Android operating system pioneering the concept. While UBPorts tried to follow suit with Ubuntu Touch, a wider development of free Linux operating systems specifically for mobile devices was only really spurred in the latter 2010s, when various smaller companies started projects to develop open source phones. Lists Operating systems This is a list of Linux distros directly targeted towards use with mobile phones, being offered preconfigured with the mobile-oriented software listed below. There are both phone produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux On Embedded Systems
The Linux, Linux Operating system is prevalent in embedded systems. As of 2024, developer surveys and industry reports find that Embedded Linux is used in 44%-46% of embedded systems. Due to its Linux range of use, versatility, its large community of developers, as well as its adaptability to devices with size and power constraints, Linux is a popular choice for devices used in Edge Computing and autonomous systems. History : additional source for this section Early Days Prior to becoming the de-facto standard for microprocessor-based devices, a linux distribution was created for the Linux Router Project, with the intent of transforming PCs to routers. Introduction of uClinux Starting in the late 1990s and the first decade of the 21st century, the introduction of uCLinux enabled ports to a large variety of microprocessors. Linux is also used as an alternative to using a Proprietary software, proprietary operating system and its associated toolchain. Introduction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Freedom Law Center
The Software Freedom Law Center (SFLC) is an organization that provides ''pro bono'' legal representation and related services to not-for-profit developers of free software/open source software. It was launched in February 2005 with Eben Moglen as chairman. Initial funding of US$4 million was pledged by Open Source Development Labs. A news article stated: GPL version 3 SFLC represented and advised the Free Software Foundation, one of its principal clients, throughout the process of drafting and public discussion of version 3 of the GNU General Public License (GPLv3) during 2005–2007. Along with FSF president Richard M. Stallman, SFLC director Eben Moglen and then-SFLC counsel Richard Fontana were principal authors of GPLv3, LGPLv3, and the GNU Affero General Public License. BusyBox litigation During 2007 and 2008, SFLC filed a series of copyright infringement lawsuits against various defendants, on behalf of Erik Andersen and Rob Landley, the principal developers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Software Foundation
The Free Software Foundation (FSF) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded by Richard Stallman on October 4, 1985. The organisation supports the free software movement, with the organization's preference for software being distributed under copyleft ("share alike") terms, such as with its own GNU General Public License. The FSF was incorporated in Boston where it is also based. From its founding until the mid-1990s, FSF's funds were mostly used to employ software developers to write free software for the GNU Project and its employees and volunteers have mostly worked on legal and structural issues for the free software movement and the free software community. Consistent with its goals, the FSF aims to use only free software on its own computers. The FSF holds the copyrights on many pieces of the GNU system, such as GNU Compiler Collection. As the holder of these copyrights, it has authority to enforce the copyleft requirements of the GNU General Public License (GPL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gpl-violations
gpl-violations.org is a not-for-profit project founded and led by Harald Welte in 2004. It works to make sure software licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL) is not used in ways prohibited by the license. Goals The goals of the project are, according to its website, to: * Raise public awareness of the infringing use of free software, and thus putting pressure on the infringers, * Give users who detect or assume GPL-licensed software is being misused a way to report them to the copyright holders, * Assist copyright holders in any action against GPL infringing organizations, and to * Distribute information on how a commercial entity using GPL licensed software in their products can comply with the license. In May 2008, gpl-violations.org and the Free Software Foundation Europe Freedom Task Force announced that they were to deepen their previous cooperation. The task force would focus on educating and informing, while gpl-violations.org would focus on enforcing the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public Licenses (GNU GPL or simply GPL) are a series of widely used free software licenses, or ''copyleft'' licenses, that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, or modify the software. The GPL was the first copyleft license available for general use. It was originally written by Richard Stallman, the founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), for the GNU Project. The license grants the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. The licenses in the GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. The GPL is more restrictive than the GNU Lesser General Public License, and even more distinct from the more widely used permissive software licenses such as BSD, MIT, and Apache. Historically, the GPL license family has been one of the most popular software licenses in the free and open-source software (FOSS) domai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Software Licenses
A free-software license is a notice that grants the recipient of a piece of software extensive rights to modify and redistribute that software. These actions are usually prohibited by copyright law, but the rights-holder (usually the author) of a piece of software can remove these restrictions by accompanying the software with a software license which grants the recipient these rights. Software using such a license is free software (or free and open-source software) as conferred by the copyright holder. Free-software licenses are applied to software in source code and also binary object-code form, as the copyright law recognizes both forms. Comparison Free-software licenses provide risk mitigation against different legal threats or behaviors that are seen as potentially harmful by developers: History Pre-1980s In the early times of software, sharing of software and source code was common in certain communities, for instance academic institutions. Before the US Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |