|
Limenavis
''Limenavis'' is a prehistoric bird genus from the Late Cretaceous. It lived about 70 million years ago, around the Campanian-Maastrichtian boundary. Known from several broken bones, the remains of the only known species ''Limenavis patagonica'' were found in rocks of the "lower member" of the Allen Formation at Salitral Moreno, 20 km south of General Roca, Río Negro (Argentina).LEONA LEONARD, GARETH J. DYKE,1, AND MARCEL VAN TUINEN (2005) "A New Specimen of the Fossil Lithornis from the Lower Eocene". ''American Museum Novitates''. Number 3491, 11 pp., 4 figures AMERICAN MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORYCENTRAL PARK WEST AT 79TH STREET, NEW YORK, NY 10024 It is the closest relative, in the fossil record, of the modern birds. Of all the prehistoric birds known to date, this species is among those closest to the common ancestor of all living birds. Its generic name pays tribute to this fact: ''Limenavis'', meaning "bird of the threshold" or "limit-bird", is derived from Latin ''li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleognathae
Palaeognathae (; ) is a infraclass of birds, called paleognaths, within the class Aves of the clade Archosauria. It is one of the two extant infraclasses of birds, the other being Neognathae, both of which form Neornithes. Palaeognathae contains five extant branches of flightless lineages (plus two extinct clades), termed ratites, and one flying lineage, the Neotropic tinamous.Wetmore, A. (1960) A Classification for Birds of the World. Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collection (Washington D.C.: Smithsonian Institution) 139: 1–37. There are 47 species of tinamous, five of kiwis (''Apteryx''), three of cassowaries (''Casuarius''), one of emus ('' Dromaius'') (another became extinct in historic times), two of rheas (''Rhea'') and two of ostrich (''Struthio'').Clements, J. C. ''et al''. (2010) Recent research has indicated that paleognaths are monophyletic but the traditional taxonomic split between flightless and flighted forms is incorrect; tinamous are within the ratite radiation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allen Formation
The Allen Formation is a geological formation in Argentina whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous (middle Campanian to early Maastrichtian.Salgado et al., 2007 Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous, South America)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 600-604. . Description The stratotype of the formation was defined by Uliana and Dellapé in 1981 in the eastern area of the Bajo de Añelo, where the relation between base and top is clearly exposed. The deposits are mostly clastic, interbedded with banks of limestone and layers of anhydrite, which were defined continental and shallow marine facies associated with semiarid conditions.Armas & Sánchez, 2015, p.101 The interpreted sedimentary paleoenvironments range from purely continental such as ephemer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleognath
Palaeognathae (; ) is a infraclass of birds, called paleognaths, within the class Aves of the clade Archosauria. It is one of the two extant infraclasses of birds, the other being Neognathae, both of which form Neornithes. Palaeognathae contains five extant branches of flightless lineages (plus two extinct clades), termed ratites, and one flying lineage, the Neotropic tinamous.Wetmore, A. (1960) A Classification for Birds of the World. Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collection (Washington D.C.: Smithsonian Institution) 139: 1–37. There are 47 species of tinamous, five of kiwis (''Apteryx''), three of cassowaries (''Casuarius''), one of emus ('' Dromaius'') (another became extinct in historic times), two of rheas (''Rhea'') and two of ostrich (''Struthio'').Clements, J. C. ''et al''. (2010) Recent research has indicated that paleognaths are monophyletic but the traditional taxonomic split between flightless and flighted forms is incorrect; tinamous are within the ratite radiation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
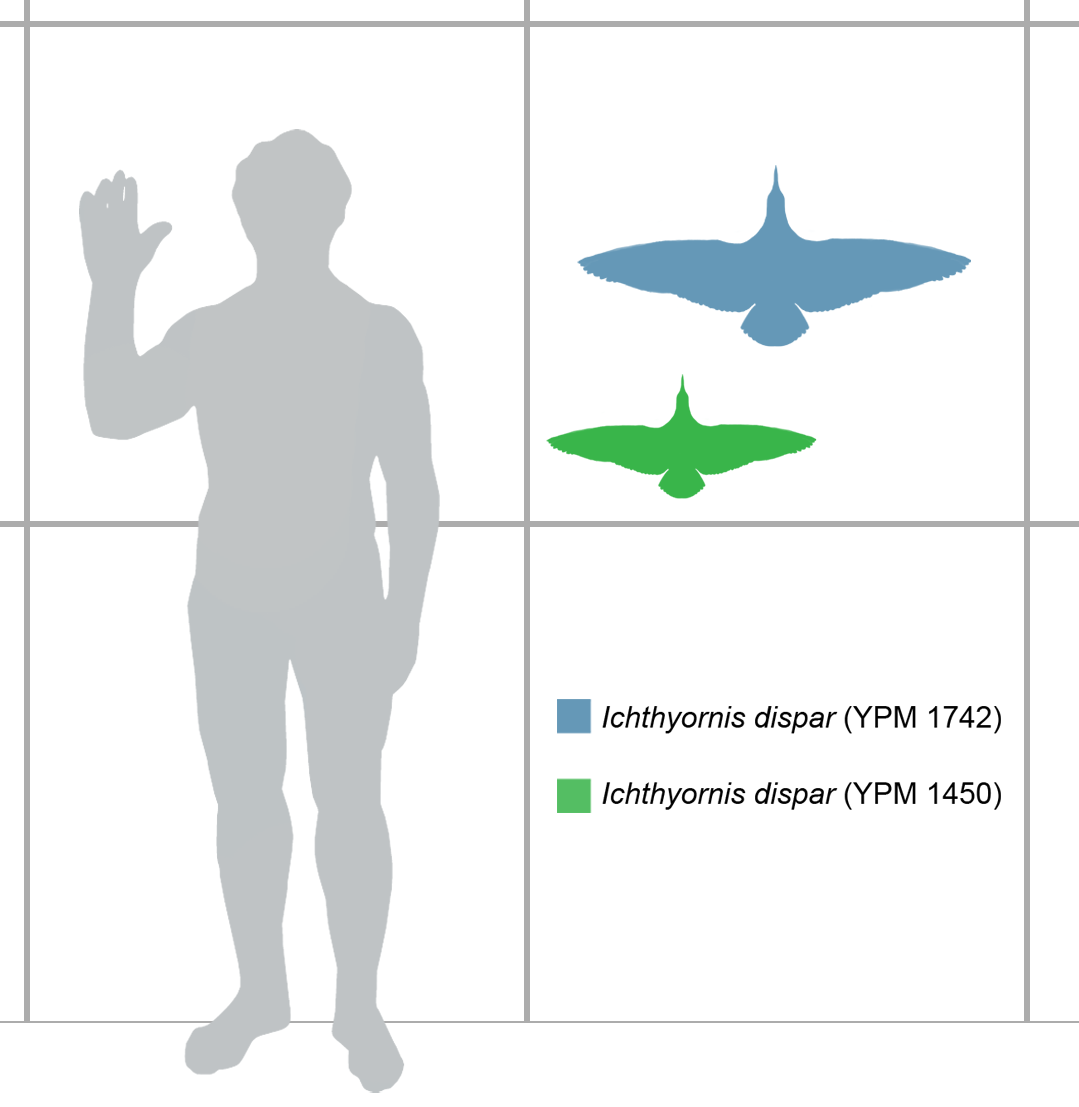
Ichthyornis
''Ichthyornis'' (meaning "fish bird", after its fish-like vertebrae) is an extinct genus of toothy seabird-like ornithuran from the late Cretaceous period of North America. Its fossil remains are known from the chalks of Alberta, Alabama, Kansas (Greenhorn Limestone), New Mexico, Saskatchewan, and Texas, in strata that were laid down in the Western Interior Seaway during the Turonian through Campanian ages, about 95–83.5 million years ago. ''Ichthyornis'' is a common component of the Niobrara Formation fauna, and numerous specimens have been found. ''Ichthyornis'' has been historically important in shedding light on bird evolution. It was the first known prehistoric bird relative preserved with teeth, and Charles Darwin noted its significance during the early years of the theory of evolution. ''Ichthyornis'' remains important today as it is one of the few Mesozoic era ornithurans known from more than a few specimens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers in the west and deserts, tablelands and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel, and the Drake Passage to the south. The Colorado and Barrancas rivers, which run from the Andes to the Atlantic, are commonly considered the northern limit of Argentine Patagonia. The archipelago of Tierra del Fuego is sometimes included as part of Patagonia. Most geographers and historians locate the northern limit of Chilean Patagonia at Huincul Fault, in Araucanía Region.Manuel Enrique Schilling; Richard WalterCarlson; AndrésTassara; Rommulo Vieira Conceição; Gustavo Walter Berto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Ornithurans
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Genera
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. Bird ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern subregion of a single continent called America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a British Overseas Territory), Bouvet Island ( dependency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal (evolution)
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa. While there must always be two or more equally "basal" clades sprouting from the root of every cladogram, those clades may differ widely in taxonomic rank, species diversity, or both. If ''C'' is a basal clade within ''D'' that has the lowest rank of all basal clades within ''D'', ''C'' may be described as ''the'' basal taxon of that rank within ''D''. The concept of a 'key innovation' implies some degree of correlation between evolutionary innovation and diversification. However, such a correlation does not make a given case predicable, so ancestral characters should not be imputed to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhea (bird)
The rheas ( ), also known as ñandus ( ) or South American ostriches, are large ratites (flightless birds without a keel on their sternum bone) in the order Rheiformes, native to South America, distantly related to the ostrich and emu. Most taxonomic authorities recognize two extant species: the greater or American rhea (''Rhea americana''), and the lesser or Darwin's rhea (''Rhea pennata''). The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classifies the puna rhea as another species instead of a subspecies of the lesser rhea. The IUCN currently rates the greater and puna rheas as near-threatened in their native ranges, while Darwin's rhea is of least concern. In addition, a feral population of the greater rhea in Germany appears to be growing, though control efforts are underway, and seem to be succeeding in controlling the birds' population growth. Etymology The name "rhea" was used in 1752 by Paul Möhring and adopted as the English common name. Möhring named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_white_background.jpg)


.jpg)


