|
Limelight
Limelight (also known as Drummond light or calcium light)James R. Smith (2004). ''San Francisco's Lost Landmarks'', Quill Driver Books. is a type of stage lighting once used in theatres and music halls. An intense illumination is created when a flame fed by oxygen and hydrogen is directed at a cylinder of quicklime ( calcium oxide), which can be heated to before melting. The light is produced by a combination of incandescence and candoluminescence. Although it has long since been replaced by electric lighting, the term has nonetheless survived, as someone in the public eye is still said to be "in the limelight". The actual lamps are called "limes", a term which has been transferred to electrical equivalents. History Discovery and invention The limelight effect was discovered in the 1820s by Goldsworthy Gurney, based on his work with the "oxy-hydrogen blowpipe", credit for which is normally given to Robert Hare. In 1825, a Scottish engineer, Thomas Drummond (1797� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limelight Diagram
Limelight (also known as Drummond light or calcium light)James R. Smith (2004). ''San Francisco's Lost Landmarks'', Quill Driver Books. is a type of stage lighting once used in Theater (structure), theatres and music halls. An intense illumination is created when a flame fed by Oxyhydrogen, oxygen and hydrogen is directed at a cylinder of quicklime (calcium oxide), which can be heated to before melting. The light is produced by a combination of incandescence and candoluminescence. Although it has long since been replaced by electric lighting, the term has nonetheless survived, as someone in the public eye is still said to be "in the limelight". The actual lamps are called "limes", a term which has been transferred to electrical equivalents. History Discovery and invention The limelight effect was discovered in the 1820s by Goldsworthy Gurney, based on his work with the "oxy-hydrogen blowpipe (tool), blowpipe", credit for which is normally given to Robert Hare (chemist), Robe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ching Lau Lauro
Ching Lau Lauro and Professor Ching were the stage names of a juggler and magician (1806?–1840; flourished 1827–1839) who performed outdoors and in theatres in London and the provinces. His real name is unknown; he was possibly Cornish and he was popularly known as Ching. He was the first magician in Europe to perform the aerial suspension illusion, and possibly the first to use limelight,See image of playbill where he is advertised to be using koniaphostic light (limelight): :File:Herne Bay Museum 090.jpg and one of the earliest Western magicians to perform in Chinese costume. In 1834 he played at The Theatre, Leeds.Playbill for Theatre, Leeds, Monday 22 September 1834. See :File:Ching Lau Lauro 1834.jpg Background Origins and identity Little is known about the early life of the performer known as Ching Lau Lauro. His real name is unknown. He was possibly born around 1806 or even a little later, although his short career spanned 1827 to 1839. The evidence which suggests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Drummond
Captain Thomas Drummond (10 October 1797 – 15 April 1840), from Edinburgh was a Scottish army officer, civil engineer and senior public official. He used the Drummond light which was employed in the trigonometrical survey of Great Britain and Ireland. He is sometimes mistakenly given credit for the invention of limelight, at the expense of Sir Goldsworthy Gurney. It was Drummond, however, who realised its value in surveying. Early life Drummond was the second of three sons. Despite his father dying when he was young, he credited his mother with getting him through his education at Edinburgh High School and then on to be a Royal Engineer cadet at Woolwich Academy in 1813. He showed an early gift for mathematics. After Woolwich he was stationed in Edinburgh and was involved with public works. He was bored with this and had enrolled at Lincoln's Inn when he was recruited to use his trigonometry to help conduct a survey in the Highlands. This new work was done in the summer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxyhydrogen
Oxyhydrogen is a mixture of hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) gases. This gaseous mixture is used for torches to process refractory materials and was the first gaseous mixture used for welding. Theoretically, a ratio of 2:1 hydrogen:oxygen is enough to achieve maximum efficiency; in practice a ratio 4:1 or 5:1 is needed to avoid an oxidizing flame. This mixture may also be referred to as ' (Scandinavian and German Knallgas: "bang-gas"), although some authors define knallgas to be a generic term for the mixture of fuel with the precise amount of oxygen required for complete combustion, thus 2:1 oxyhydrogen would be called "hydrogen-knallgas". "Brown's gas" and HHO are terms for oxyhydrogen mainly encountered in fringe science. Properties Oxyhydrogen will combust when brought to its autoignition temperature. For the stoichiometric mixture, 2:1 hydrogen:oxygen, at normal atmospheric pressure, autoignition occurs at about 570 °C (1065 °F). The minimum energy require ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candoluminescence
Candoluminescence is the light given off by certain materials at elevated temperatures (usually when exposed to a flame) that has an intensity at some wavelengths which can, through chemical action in flames, be higher than the blackbody emission expected from incandescence at the same temperature.H.F. Ivey, "Candoluminescence and radical-excited luminescence," ''Journal of Luminescence'' 8:4, pp. 271–307 (1974) The phenomenon is notable in certain transition-metal and rare-earth oxide materials (ceramics) such as zinc oxide, cerium(IV) oxide and thorium dioxide. History The existence of the candoluminescence phenomenon and the underlying mechanism have been the subject of extensive research and debate since the first reports of it in the 1800s. The topic was of particular interest before the introduction of electric lighting, when most artificial light was produced by fuel combustion. The main alternative explanation for candoluminescence is that it is simply "selective" thermal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goldsworthy Gurney
Sir Goldsworthy Gurney (14 February 1793 – 28 February 1875) was an English surgeon, chemist, architect, builder, lecturer and consultant. He was a prototypical British gentleman scientist and inventor of the Victorian era. Amongst many accomplishments, he developed the oxy-hydrogen blowpipe, and later applied its principles to a novel form of illumination, the Bude-Light; developed a series of early steam-powered road vehicles; and laid claim—still discussed and disputed today—to the blastpipe, a key component in the success of steam locomotives, engines, and other coal-fired systems. Events surrounding the failure of his steam vehicle enterprise gave rise to controversy in his time, with considerable polarisation of opinion. His daughter Anna Jane Gurney (1816–1895) was devoted to him. During her lifetime, she engaged in a campaign to ensure the blastpipe was seen as his invention. Biography Gurney was born in St Merryn, Cornwall, England on 14 February 1793. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Hydrogen Technologies
This is a timeline of the history of hydrogen technology. Timeline 16th century * c. 1520 – First recorded observation of hydrogen by Paracelsus through dissolution of metals (iron, zinc, and tin) in sulfuric acid. 17th century * 1625 – First description of hydrogen by Johann Baptista van Helmont. First to use the word "gas". * 1650 – Turquet de Mayerne obtained a gas or "inflammable air" by the action of dilute sulphuric acid on iron. * 1662 – Boyle's law (gas law relating pressure and volume) * 1670 – Robert Boyle produced hydrogen by reacting metals with acid. * 1672 – "New Experiments touching the Relation between Flame and Air" by Robert Boyle. * 1679 – Denis Papin – safety valve * 1700 – Nicolas Lemery showed that the gas produced in the sulfuric acid/iron reaction was explosive in air 18th century * 1755 – Joseph Black confirmed that different gases exist. / Latent heat * 1766 – Henry Cavendish published in "On Factitious Airs" a descript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nineteenth-century Theatrical Scenery
Nineteenth-century theatre, Theatre in the nineteenth century was noted for its changing philosophy from the Romanticism and Neoclassicism that dominated Europe since the late 18th century to Realism (theatre), Realism and Naturalism (theatre), Naturalism in the latter half of the 19th century before it eventually gave way to the rise of Modernism in the 20th century. Scenery in theater at the time closely mirrored these changes, and with the onset of the Industrial Revolution and technological advancement throughout the century, dramatically changed the aesthetics of the theater. Realism Theatrical realism was a general movement in 19th-century theatre from the time period of 1870-1960 that developed a set of dramatic and theatrical conventions with the aim of bringing a greater fidelity of real life to texts and performances. Part of a broader artistic movement, it included a focus on everyday middle-class drama, ordinary speech, and simple settings. This idea of representing subje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Opera House
The Royal Opera House (ROH) is an opera house and major performing arts venue in Covent Garden, central London. The large building is often referred to as simply Covent Garden, after a previous use of the site. It is the home of The Royal Opera, The Royal Ballet, and the Orchestra of the Royal Opera House. The first theatre on the site, the Theatre Royal (1732), served primarily as a playhouse for the first hundred years of its history. In 1734, the first ballet was presented. A year later, the first season of operas, by George Frideric Handel, began. Many of his operas and oratorios were specifically written for Covent Garden and had their premieres there. The current building is the third theatre on the site, following disastrous fires in 1808 and 1856 to previous buildings. The façade, foyer, and auditorium date from 1858, but almost every other element of the present complex dates from an extensive reconstruction in the 1990s. The main auditorium seats 2,256 people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zirconia Light
A zirconia light is an intensely brilliant chemical light produced by incandescent zirconia. It is similar in design to the Drummond light (limelight), but uses a block of zirconia instead of quicklime Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term "'' lime''" connotes calcium-containing inorganic .... Both have been replaced by the electric light. Source * Types of lamp Zirconium References *no author listed (1870"New Zirconia Light" The Pharmaceutical Journal and Transactions. 29:81-82 {{tech-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Oxide
Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term "'' lime''" connotes calcium-containing inorganic materials, in which carbonates, oxides and hydroxides of calcium, silicon, magnesium, aluminium, and iron predominate. By contrast, ''quicklime'' specifically applies to the single chemical compound calcium oxide. Calcium oxide that survives processing without reacting in building products such as cement is called free lime. Quicklime is relatively inexpensive. Both it and a chemical derivative (calcium hydroxide, of which quicklime is the base anhydride) are important commodity chemicals. Preparation Calcium oxide is usually made by the thermal decomposition of materials, such as limestone or seashells, that contain calcium carbonate (CaCO3; mineral calcite) in a lime kiln. This is accomplished by heating the material to above ,Merck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
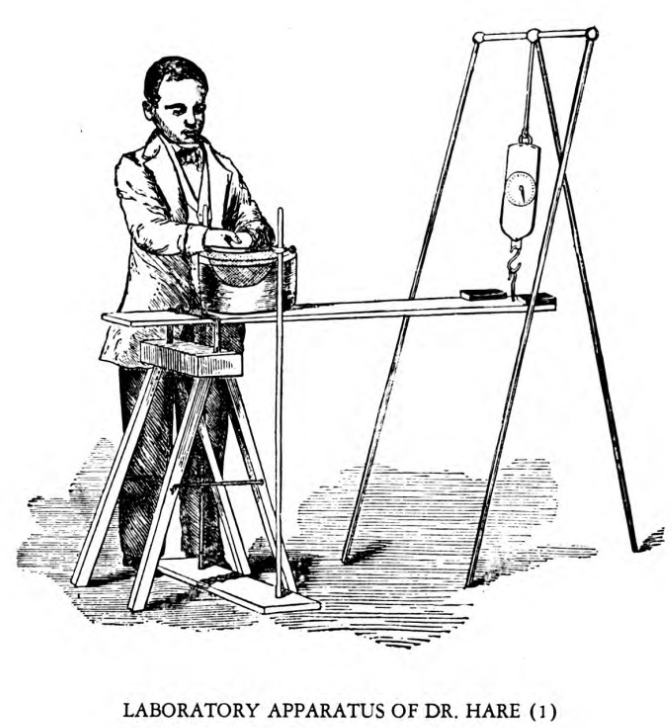
Robert Hare (chemist)
Robert Hare (January 17, 1781 – May 15, 1858) was an early American chemist and professor. Biography Hare was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, on January 17, 1781. He developed and experimented with the oxy-hydrogen blowpipe, with Edward Daniel Clarke of Oxford, shortly after 1800. He married Harriett Clark and had six children. In 1802, Hare was elected a member of the American Philosophical Society. He was a professor at the University of Pennsylvania between 1810 and 1812 and between 1818 and 1847. By the 1820s, Hare had developed the "galvanic deflagrator", a type of voltaic battery having large plates used for producing rapid and powerful combustion.Kneeland, Timothy W. (2008). ''Robert Hare: Politics, Science, and Spiritualism in the Early Republic''. The Pennsylvania Magazine of History and Biography. Vol. 132, No. 3. pp. 245-260. He was elected an Associate Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1824. Hare died in Philadelphia on May 15, 1858. Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)