|
Light Map
A lightmap is a data structure used in lightmapping, a form of surface caching in which the brightness of surfaces in a virtual scene is pre-calculated and stored in texture maps for later use. Lightmaps are most commonly applied to static objects in applications that use real-time 3D computer graphics, such as video games, in order to provide lighting effects such as global illumination at a relatively low computational cost. History John Carmack's Quake was the first computer game to use lightmaps to augment rendering. Before lightmaps were invented, realtime applications relied purely on Gouraud shading to interpolate vertex lighting for surfaces. This only allowed low frequency lighting information, and could create clipping artifacts close to the camera without perspective-correct interpolation. Discontinuity meshing was sometimes used especially with radiosity solutions to adaptively improve the resolution of vertex lighting information, however the additional co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightmap Cube Sample
A lightmap is a data structure used in lightmapping, a form of surface caching in which the brightness of surfaces in a virtual scene is pre-calculated and stored in texture maps for later use. Lightmaps are most commonly applied to static objects in applications that use real-time 3D computer graphics, such as video games, in order to provide lighting effects such as global illumination at a relatively low computational cost. History John Carmack's Quake was the first computer game to use lightmaps to augment rendering. Before lightmaps were invented, realtime applications relied purely on Gouraud shading to interpolate vertex lighting for surfaces. This only allowed low frequency lighting information, and could create clipping artifacts close to the camera without perspective-correct interpolation. Discontinuity meshing was sometimes used especially with radiosity solutions to adaptively improve the resolution of vertex lighting information, however the additional co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blend Modes
A blend is a mixture of two or more different things or substances; e.g., a product of a Blender, mixer or blender. Blend Blend may also refer to: * Blend word, a word formed from parts of other words * Blend (album), ''Blend'' (album), a 1996 album by BoDeans * Blend (cigarette), a Swedish brand * Blend (textile), Textile product made out of a mixture of two or more fibers * .blend (file format), a file format used by the open-source 3D application Blender * Consonant blend, a group of consonants which have no intervening vowel * Polymer blend, a member of a class of materials analogous to metal alloys * Microsoft Blend, Microsoft Blend for Visual Studio (formerly Microsoft Expression Blend), a user interface design tool for WPF and Silverlight * Blend modes in digital image editing, used to determine how two layers are blended into each other * The Blend (Sirius XM), a satellite radio channel * Mashup (music) Blended Blended may refer to: * Blended (film), ''Blended'' (film), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture Filtering
In computer graphics, texture filtering or texture smoothing is the method used to determine the texture color for a texture mapped pixel, using the colors of nearby texels (pixels of the texture). There are two main categories of texture filtering, magnification filtering and minification filtering. Depending on the situation texture filtering is either a type of reconstruction filter where sparse data is interpolated to fill gaps (magnification), or a type of anti-aliasing (AA), where texture samples exist at a higher frequency than required for the sample frequency needed for texture fill (minification). Put simply, filtering describes how a texture is applied at many different shapes, size, angles and scales. Depending on the chosen filter algorithm the result will show varying degrees of blurriness, detail, spatial aliasing, temporal aliasing and blocking. Depending on the circumstances filtering can be performed in software (such as a software rendering package) or in hardware ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pixelation
In computer graphics, pixelation (or pixellation in British English) is caused by displaying a bitmap or a section of a bitmap at such a large size that individual pixels, small single-colored square display elements that comprise the bitmap, are visible. Such an image is said to be pixelated (pixellated in the UK). Early graphical applications such as video games ran at very low resolutions with a small number of colors, resulting in easily visible pixels. The resulting sharp edges gave curved objects and diagonal lines an unnatural appearance. However, when the number of available colors increased to 256, it was possible to gainfully employ anti-aliasing to smooth the appearance of low-resolution objects, not eliminating pixelation but making it less jarring to the eye. Higher resolutions would soon make this type of pixelation all but invisible on the screen, but pixelation is still visible if a low-resolution image is printed on paper. In the realm of real-time 3D compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray Tracing (graphics)
In 3D computer graphics, ray tracing is a technique for modeling light transport for use in a wide variety of rendering algorithms for generating digital images. On a spectrum of computational cost and visual fidelity, ray tracing-based rendering techniques, such as ray casting, recursive ray tracing, distribution ray tracing, photon mapping and path tracing, are generally slower and higher fidelity than scanline rendering methods. Thus, ray tracing was first deployed in applications where taking a relatively long time to render could be tolerated, such as in still computer-generated images, and film and television visual effects (VFX), but was less suited to real-time applications such as video games, where speed is critical in rendering each frame. Since 2018, however, hardware acceleration for real-time ray tracing has become standard on new commercial graphics cards, and graphics APIs have followed suit, allowing developers to use hybrid ray tracing and rasterization- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
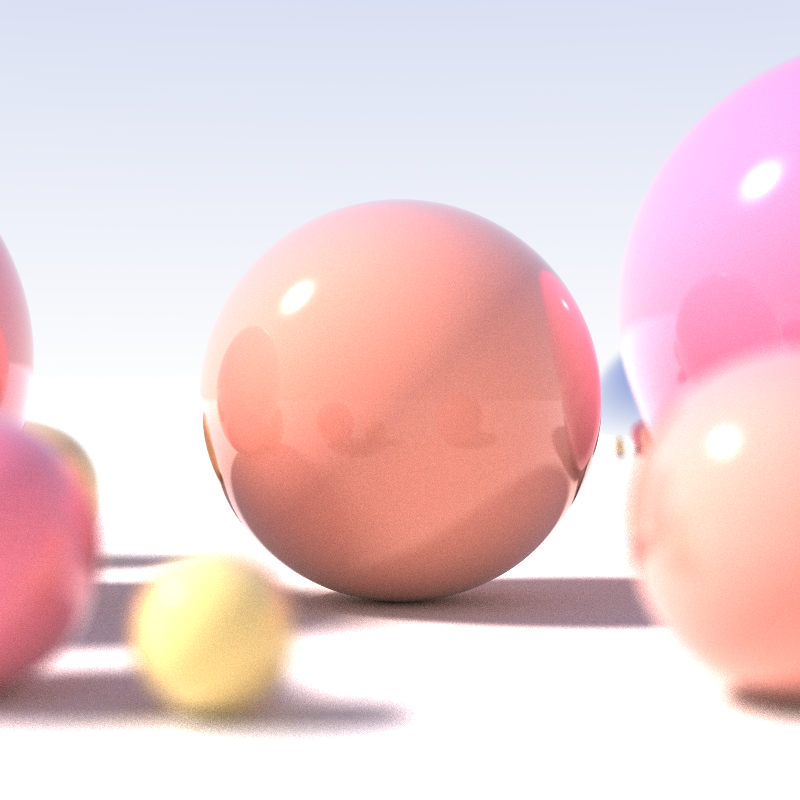
Soft Shadows
The umbra, penumbra and antumbra are three distinct parts of a shadow, created by any light source after impinging on an opaque object. Assuming no diffraction, for a collimated beam (such as a point source) of light, only the umbra is cast. These names are most often used for the shadows cast by celestial bodies, though they are sometimes used to describe levels, such as in sunspots. Umbra The umbra (Latin for "shadow") is the innermost and darkest part of a shadow, where the light source is completely blocked by the occluding body. An observer within the umbra experiences a total eclipse. The umbra of a round body occluding a round light source forms a right circular cone. When viewed from the cone's apex, the two bodies appear the same size. The distance from the Moon to the apex of its umbra is roughly equal to that between the Moon and Earth: . Since Earth's diameter is 3.7 times the Moon's, its umbra extends correspondingly farther: roughly . Penumbra The penum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S3 Texture Compression
S3 Texture Compression (S3TC) (sometimes also called DXTn, DXTC, or BCn) is a group of related lossy texture compression algorithms originally developed by Iourcha et al. of S3 Graphics, Ltd. for use in their Savage 3D computer graphics accelerator. The method of compression is strikingly similar to the previously published Color Cell Compression, which is in turn an adaptation of Block Truncation Coding published in the late 1970s. Unlike some image compression algorithms (e.g. JPEG), S3TC's fixed-rate data compression coupled with the single memory access (cf. Color Cell Compression and some VQ-based schemes) made it well-suited for use in compressing textures in hardware-accelerated 3D computer graphics. Its subsequent inclusion in Microsoft's DirectX 6.0 and OpenGL 1.3 (via the GL_EXT_texture_compression_s3tc extension) led to widespread adoption of the technology among hardware and software makers. While S3 Graphics is no longer a competitor in the graphics accelerator market ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambient Occlusion
In 3D computer graphics, modeling, and animation, ambient occlusion is a shading and rendering technique used to calculate how exposed each point in a scene is to ambient lighting. For example, the interior of a tube is typically more occluded (and hence darker) than the exposed outer surfaces, and becomes darker the deeper inside the tube one goes. Ambient occlusion can be seen as an accessibility value that is calculated for each surface point. In scenes with open sky, this is done by estimating the amount of visible sky for each point, while in indoor environments, only objects within a certain radius are taken into account and the walls are assumed to be the origin of the ambient light. The result is a diffuse, non-directional shading effect that casts no clear shadows, but that darkens enclosed and sheltered areas and can affect the rendered image's overall tone. It is often used as a post-processing effect. Unlike local methods such as Phong shading, ambient occlusion i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Engine
A game engine is a software framework primarily designed for the development of video games and generally includes relevant libraries and support programs. The "engine" terminology is similar to the term "software engine" used in the software industry. The game engine can also refer to the development software utilizing this framework, typically offering a suite of tools and features for developing games. Developers can use game engines to construct games for video game consoles and other types of computers. The core functionality typically provided by a game engine may include a rendering engine ("renderer") for 2D or 3D graphics, a physics engine or collision detection (and collision response), sound, scripting, animation, artificial intelligence, networking, streaming, memory management, threading, localization support, scene graph, and video support for cinematics. Game engine implementers often economize on the process of game development by reusing/adapting, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NVIDIA
Nvidia CorporationOfficially written as NVIDIA and stylized in its logo as VIDIA with the lowercase "n" the same height as the uppercase "VIDIA"; formerly stylized as VIDIA with a large italicized lowercase "n" on products from the mid 1990s to early-mid 2000s. Though unofficial, second letter capitalization of NVIDIA, i.e. nVidia, may be found within enthusiast communities and publications. ( ) is an American multinational technology company incorporated in Delaware and based in Santa Clara, California. It is a software and fabless company which designs graphics processing units (GPUs), application programming interface (APIs) for data science and high-performance computing as well as system on a chip units (SoCs) for the mobile computing and automotive market. Nvidia is a global leader in artificial intelligence hardware and software. Its professional line of GPUs are used in workstations for applications in such fields as architecture, engineering and construction, media ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Artist
In 3D computer graphics, 3D modeling is the process of developing a mathematical coordinate-based representation of any surface of an object (inanimate or living) in three dimensions via specialized software by manipulating edges, vertices, and polygons in a simulated 3D space. Three-dimensional (3D) models represent a physical body using a collection of points in 3D space, connected by various geometric entities such as triangles, lines, curved surfaces, etc. Being a collection of data ( points and other information), 3D models can be created manually, algorithmically (procedural modeling), or by scanning. Their surfaces may be further defined with texture mapping. Outline The product is called a 3D model. Someone who works with 3D models may be referred to as a 3D artist or a 3D modeler. A 3D Model can also be displayed as a two-dimensional image through a process called 3D rendering or used in a computer simulation of physical phenomena. 3D Models may be created autom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Level Design
In video games, a level (also referred to as a map, stage, or round in some older games) is any space available to the player during the course of completion of an objective. Video game levels generally have progressively-increasing difficulty to appeal to players with different skill levels. Each level may present new concepts and challenges to keep a player's interest high. In games with linear progression, levels are areas of a larger world, such as Green Hill Zone. Games may also feature interconnected levels, representing locations. Although the challenge in a game is often to defeat some sort of character, levels are sometimes designed with a movement challenge, such as a jumping puzzle, a form of obstacle course. Players must judge the distance between platforms or ledges and safely jump between them to reach the next area. These puzzles can slow the momentum down for players of fast action games; the first ''Half-Life'''s penultimate chapter, "Interloper", featured multi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |