|
Ligases
In biochemistry, a ligase is an enzyme that can catalyze the joining (ligation) of two large molecules by forming a new chemical bond. This is typically via hydrolysis of a small pendant chemical group on one of the larger molecules or the enzyme catalyzing the linking together of two compounds, e.g., enzymes that catalyze joining of C-O, C-S, C-N, etc. In general, a ligase catalyzes the following reaction: :Ab + C → A–C + b or sometimes :Ab + cD → A–D + b + c + d + e + f where the lowercase letters can signify the small, dependent groups. Ligase can join two complementary fragments of nucleic acid and repair single stranded breaks that arise in double stranded DNA during replication. Nomenclature The common names of ligases often include the word "ligase", such as DNA ligase, an enzyme commonly used in molecular biology laboratories to join together DNA fragments. Other common names for ligases include the word "synthetase", because they are used to synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
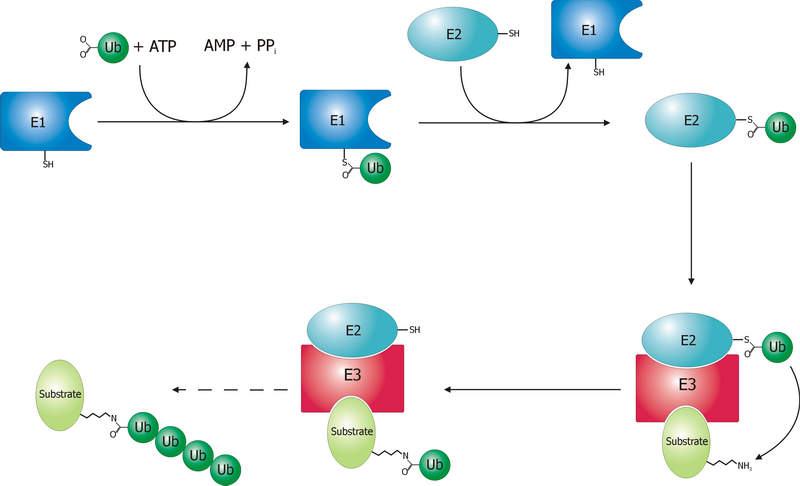
Ubiquitin Ligase
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to the protein substrate. In simple and more general terms, the ligase enables movement of ubiquitin from a ubiquitin carrier to another thing (the substrate) by some mechanism. The ubiquitin, once it reaches its destination, ends up being attached by an isopeptide bond to a lysine residue, which is part of the target protein. E3 ligases interact with both the target protein and the E2 enzyme, and so impart substrate specificity to the E2. Commonly, E3s polyubiquitinate their substrate with Lys48-linked chains of ubiquitin, targeting the substrate for destruction by the proteasome. However, many other types of linkages are possible and alter a protein's activity, interactions, or localization. Ubiquitination by E3 ligases reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Ligase
DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, () that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA). Single-strand breaks are repaired by DNA ligase using the complementary strand of the double helix as a template, with DNA ligase creating the final phosphodiester bond to fully repair the DNA. DNA ligase is used in both DNA repair and DNA replication (see '' Mammalian ligases''). In addition, DNA ligase has extensive use in molecular biology laboratories for recombinant DNA experiments (see '' Research applications''). Purified DNA ligase is used in gene cloning to join DNA molecules together to form recombinant DNA. Enzymatic mechanism The mechanism of DNA ligase is to form two covalent phos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argininosuccinate Synthetase
Argininosuccinate synthase or synthetase (ASS; ) is an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of argininosuccinic acid, argininosuccinate from citrulline and aspartic acid, aspartate. In humans, argininosuccinate synthase is encoded by the ''ASS (gene), ASS gene'' located on chromosome 9 (human), chromosome 9. ASS is responsible for the third step of the urea cycle and one of the reactions of the citrulline-NO cycle. Expression The expressed ASS gene is at least 65 kb in length, including at least 12 introns. In humans, ''ASS'' is expressed mostly in the cells of the liver and kidney. Mechanism In the first step of the catalyzed reaction, citrulline attacks the α-phosphate of Adenosine triphosphate, ATP to form citrulline adenylate, a reactive intermediate. The attachment of Adenosine monophosphate, AMP to the ureido (urea-like) group on citrulline activates the carbonyl center for subsequent nucleophilic attack. This activation facilitates the second step, in which the � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelatase
In biochemistry, chelatases are enzymes that catalyze the insertion ("metalation") of naturally occurring tetrapyrroles. Many tetrapyrrole-based cofactors exist in nature including hemes, chlorophylls, and vitamin B12. These metallo cofactors are derived by the reaction of metal cations with tetrapyrroles, which are not ligands ''per se'', but the conjugate acids thereof. In the case of ferrochelatases, the reaction that chelatases catalyze is: :Fe2+ + H2P → FeP + 2 H+ In the above equation H2P represents a sirohydrochlorin or a porphyrin, such as protoporphyrin IX. Chelatases are required because porphyrins and related macrocyclic ligands are extremely slow to metalate, despite favorable thermodynamics. These low rates are attributed to the tight fit of the metal into the rigid 18- or 17-membered tetrapyrrole macrocycle. Several families of chelatase are known including cobalt chelatase, magnesium chelatase, and ferrochelatase. Nickel insertion into a sirohydrochlori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research. Voet (2005), p. 3. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis which allows biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living cells and between cells,Karp (2009), p. 2. in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissues and organs, as well as organism structure and function.Miller (2012). p. 62. Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, which is the study of the molecular mechanisms of biological phenomena.As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks bonds. Proteases are involved in many biological functions, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism (breakdown of old proteins), and cell signaling. In the absence of functional accelerants, proteolysis would be very slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteases can be found in all forms of life and viruses. They have independently evolved multiple times, and different classes of protease can perform the same reaction by completely different catalytic mechanisms. Hierarchy of proteases Based on catalytic residue Proteases can be classified into seven broad groups: * Serine protease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclease
A nuclease (also archaically known as nucleodepolymerase or polynucleotidase) is an enzyme capable of cleaving the phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides of nucleic acids. Nucleases variously effect single and double stranded breaks in their target molecules. In living organisms, they are essential machinery for many aspects of DNA repair. Defects in certain nucleases can cause genetic instability or immunodeficiency. Nucleases are also extensively used in molecular cloning. There are two primary classifications based on the locus of activity. Exonucleases digest nucleic acids from the ends. Endonucleases act on regions in the ''middle'' of target molecules. They are further subcategorized as deoxyribonucleases and ribonucleases. The former acts on DNA, the latter on RNA. History In the late 1960s, scientists Stuart Linn and Werner Arber isolated examples of the two types of enzymes responsible for phage growth restriction in Escherichia coli ( E. coli) bacteria. One of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
-ase
The suffix -ase is used in biochemistry to form names of enzymes. The most common way to name enzymes is to add this suffix onto the end of the substrate, ''e.g.'' an enzyme that breaks down peroxides may be called peroxidase; the enzyme that produces telomeres is called telomerase. Sometimes enzymes are named for the function they perform, rather than substrate, e.g. the enzyme that polymerizes (assembles) DNA into strands is called polymerase; see also reverse transcriptase. The ''-ase'' suffix is a libfix derived from "diastase", the first recognized enzyme. Its usage in subsequently discovered enzymes was proposed by Émile Duclaux, with the intention of honoring the first scientists to isolate diastase. See also *Amylase *DNA polymerase References {{Orgchemsuffixes ase Biological nomenclature ase Ase may refer to: * Ase, Nigeria, a town in Delta State, Nigeria * -ase, a suffix used for the names of enzymes * Aṣẹ, a West African philosophical concept * American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Language
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italy (geographical region), Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a fusional language, highly inflected language, with three distinct grammatical gender, genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Compound
Neoclassical compounds are compound words composed from combining forms (which act as affixes or stems) derived from classical Latin or ancient Greek roots. New Latin comprises many such words and is a substantial component of the technical and scientific lexicon of English and other languages, via international scientific vocabulary (ISV). For example, '' bio-'' combines with '' -graphy'' to form ''biography'' ("life" + "writing/recording"). Source of international technical vocabulary Neoclassical compounds represent a significant source of Neo-Latin vocabulary. Moreover, since these words are composed from classical languages whose prestige is or was respected throughout the Western European culture, these words typically appear in many different languages. Their widespread use makes technical writing generally accessible to readers who may only have a smattering of the language in which it appears. Not all European languages have been equally receptive to neoclassical tech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membranome Database
Membranome database provides structural and functional information about more than 6000 single-pass (bitopic) transmembrane proteins from ''Homo sapiens'', ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', ''Dictyostelium discoideum'', ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', ''Escherichia coli'' and ''Methanocaldococcus jannaschii''. Bitopic membrane proteins consist of a single transmembrane alpha-helix connecting water-soluble domains of the protein situated at the opposite sides of a biological membrane. These proteins are frequently involved in the signal transduction and communication between cells in multicellular organisms. The database provides information about the individual proteins including computationally generated three-dimensional models of their transmembrane alpha-helices spatially arranged in the membrane, topology, intracellular localizations, amino acid sequences, domain architecture, functional annotation and available experimental structures from the Protein Data Bank. It also provides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |