|
Libu Yangtze River Road-Railway Bridge
The Libu ( egy, rbw; also transcribed Rebu, Lebu, Lbou, Libou) were an Ancient Libyan tribe of Berber origin, from which the name '' Libya'' derives. Early history Their occupation of Ancient Libya is first attested in Egyptian language texts from the New Kingdom, especially from the Ramesside Period. The earliest occurrence is in a Ramesses II inscription. There were no vowels in the Egyptian script. The name Libu is written as '' rbw'' in Egyptian hieroglyphs. In the Great Karnak Inscription Merneptah describes how hostilities between Egypt and Libya broke out in his regnal year 5 (1208 BCE) and how a coalition of Libu and Sea Peoples led by the chief of the Libu Meryey was defeated. ''Libu'' appears as an ethnic name on ''the Merneptah Stele'', also known as the ''Israel Stele''. Ramesses III defeated the Libyans in the 5th year of his reign, but six years later the Libyans joined the Meshwesh and invaded the western Delta and were defeated again. This name ''Lib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypte Louvre 131 Statuette
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture, urban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and other territories. Most of these regions were officially unified only once, for 13 years, under Alexander the Great's empire from 336 to 323 BC (though this excludes a number of Greek city-states free from Alexander's jurisdiction in the western Mediterranean, around the Black Sea, Cyprus, and Cyrenaica). In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Roughly three centuries after the Late Bronze Age collapse of Mycenaean Greece, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoshenq III
King Usermaatre Setepenre Shoshenq III of the 22nd Dynasty ruled for 39 years according to contemporary historical records. Two Apis Bulls were buried in the fourth and 28th years of his reign and he celebrated his Heb Sed Jubilee in his regnal year 30. He was not a son of Osorkon II but instead a grandson through his dead father prince Takelot. As he was only a grandson, his cousin Takelot II contested his succession and Egypt was divided. He married his aunt Tjesbastperu to strengthen his claim. He outlived his first five sons and was thus succeeded by his 6th son Shoshenq IV, who later died childless as well and was succeeded by Shoshenq III's 7th son Pami. From Shoshenq III's eighth regnal year, his reign was marked by the loss of Egypt's political unity, with the appearance of Pedubast I at Thebes. Henceforth, the kings of the 22nd Dynasty only controlled Lower Egypt. The Theban High Priest Osorkon B (the future Osorkon III) did date his activities at Thebes and (Upper Egy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stele Inamunnifnebu Moscow
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), when derived from Latin, is a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected in the ancient world as a monument. The surface of the stele often has text, ornamentation, or both. These may be inscribed, carved in relief, or painted. Stelae were created for many reasons. Grave stelae were used for funerary or commemorative purposes. Stelae as slabs of stone would also be used as ancient Greek and Roman government notices or as boundary markers to mark borders or property lines. Stelae were occasionally erected as memorials to battles. For example, along with other memorials, there are more than half-a-dozen steles erected on the battlefield of Waterloo at the locations of notable actions by participants in battle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regnal Year
A regnal year is a year of the reign of a sovereign, from the Latin ''regnum'' meaning kingdom, rule. Regnal years considered the date as an ordinal, not a cardinal number. For example, a monarch could have a first year of rule, a second year of rule, a third year of rule, and so on, but not a zeroth year of rule. Applying this ancient epoch system to modern calculations of time, which include zero, is what led to the debate over when the third millennium began. Regnal years are "finite era names", contrary to "infinite era names" such as Christian era, Jimmu era, ''Juche'' era, and so on. Early use In ancient times, calendars were counted in terms of the number of years of the reign of the current monarch. Reckoning long periods of times required a king list. The oldest such reckoning is preserved in the Sumerian king list. Ancient Egyptian chronology was also dated using regnal years. The Zoroastrian calendar also operated with regnal years following the reform of Ardash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty-fourth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twenty-fourth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XXIV, alternatively 24th Dynasty or Dynasty 24) is usually classified as the fourth Dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian Third Intermediate Period. History The Twenty-Fourth Dynasty was a short-lived group of pharaohs who had their capital at Sais in the western Nile Delta. Tefnakht I Tefnakht I formed an alliance of the Delta kinglets, with whose support he attempted to conquer Upper Egypt; his campaign attracted the attention of the Nubian king, Piye, who recorded his conquest and subjection of Tefnakhte of Sais and his peers in a well-known inscription. Tefnakht is always called the "Great Chief of the West" in Piye's Victory stela and in two stelas dating to the regnal years 36 and 38 of Shoshenq V. It is uncertain if he ever adopted an official royal title. However, Olivier PerduOlivier Perdu, "La Chefferie de Sébennytos de Piankhy à Psammétique Ier", ''Revue d'Égyptology'' 55 (2004), pp. 95-111. has now argued that a cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Empire in 30 BC. However, regardless of gender, "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom. The term "pharaoh" was not used contemporaneously for a ruler until a possible reference to Merneptah, c. 1210 BC during the Nineteenth Dynasty, nor consistently used until the decline and instability that began with the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty. In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as three titles: the Horus, the Sedge and Bee ( ''nswt-bjtj''), and the Two Ladies or Nebty ( ''nbtj'') name. The Golden Horus and the nomen and prenomen titles were added later. In Egyptian society, religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sais
Sais ( grc, Σάϊς, cop, Ⲥⲁⲓ) was an ancient Egyptian city in the Western Nile Delta on the Canopic branch of the Nile,Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. "Saïs." '' Webster's Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary''. 9th ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., 1985. , (indexed), and (deluxe). known by the ancient Egyptians as Sꜣw. It was the provincial capital of Sap-Meh, the fifth nome of Lower Egypt and became the seat of power during the Twenty-fourth Dynasty of Egypt (c. 732–720 BC) and the Saite Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt (664–525 BC) during the Late Period.Ian Shaw & Paul Nicholson, The Dictionary of Ancient Egypt, British Museum Press, 1995. p.250 On its ruins today stands the town of Sa el-Hagar ( ar, صا الحجر) or Sa El Hajar. Neolithic period A Neolithic settlement has been identified at Sais recently (1999), dating to 5000 BC. Agriculture appears here during this period, as well as at another similar site, Merimde Beni Salama, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tefnakht
Shepsesre Tefnakht (in grc, Τνέφαχθος, translit=Tnephachthos) was a prince of Sais and founder of the relatively short Twenty-fourth Dynasty of Egypt; he rose to become a Chief of the Ma in his home city. He is thought to have reigned roughly 732 BCE to 725 BCE, or seven years. Tefnakht I first began his career as the "Great Chief of the West" and Prince of Sais and was a late contemporary of the last ruler of the 22nd Dynasty: Shoshenq V. Tefnakht I was actually the second ruler of Sais; he was preceded by Osorkon C, who is attested by several documents mentioning him as this city's Chief of the Ma and Army Leader, according to Kenneth Kitchen, while his predecessor as Great Chief of the West was a man named Ankhhor. A recently discovered statue, dedicated by Tefnakht I to Amun-Re, reveals important details about his personal origins. The statue's text states that Tefnakht was the son of a certain Gemnefsutkapu and the grandson of Basa, a priest of Amun near Sais. Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
22nd Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt is also known as the Bubastite Dynasty, since the pharaohs originally ruled from the city of Bubastis. It was founded by Shoshenq I. The Twenty-first, Twenty-second, Twenty-third, Twenty-fourth, and Twenty-fifth dynasties of ancient Egypt are often combined under the group designation of the Third Intermediate Period. Rulers The pharaohs of the Twenty-second Dynasty were a series of Meshwesh (ancient Libyan tribe) chieftains, who ruled from c. 943 BC until 716 BC. They had settled in Egypt since the Twentieth Dynasty and were known in Egypt as the 'Great Chiefs of the Ma' (Ma being a synonym of Meshwesh). Manetho states that this Egyptianized ancient Libyan dynasty first ruled over Bubastis, but its rulers almost certainly governed from Tanis, which was their capital and the city where their tombs have been excavated. Another pharaoh who belongs to this group is Tutkheperre Shoshenq. His period of rule within this dynasty is currently uncer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
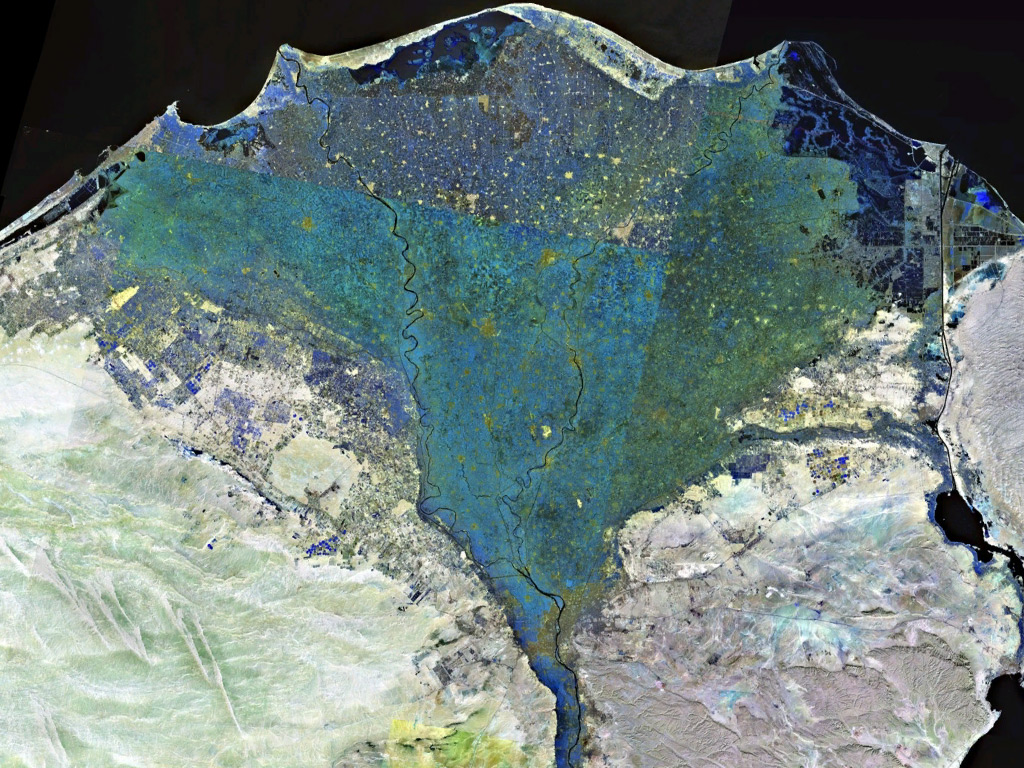
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers of Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same name. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta and enters the coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Gender
In linguistics, grammatical gender system is a specific form of noun class system, where nouns are assigned with gender categories that are often not related to their real-world qualities. In languages with grammatical gender, most or all nouns inherently carry one value of the grammatical category called ''gender''; the values present in a given language (of which there are usually two or three) are called the ''genders'' of that language. Whereas some authors use the term "grammatical gender" as a synonym of "noun class", others use different definitions for each; many authors prefer "noun classes" when none of the inflections in a language relate to sex. Gender systems are used in approximately one half of the world's languages. According to one definition: "Genders are classes of nouns reflected in the behaviour of associated words." Overview Languages with grammatical gender usually have two to four different genders, but some are attested with up to 20. #Gender contras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

_det.jpg)


.jpg)