|
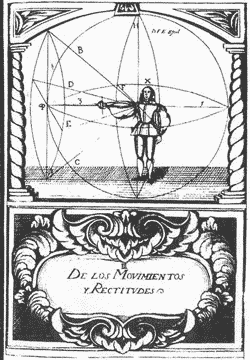
Libro De Las Grandezas De La Espada
(lit. ''Book of the Greatness of the Sword'') is a 16th-century Spanish treatise on fencing written by Don Luis Pacheco de Narváez, who is considered one of the founding fathers of Spanish fencing (''destreza'') and the disciple of Jerónimo Sánchez de Carranza. About the treatise The treatise dedicates numerous pages to the differentiation between two forms of fencing ('' destrezas''), ('true fencing') and ('vulgar or common fencing'). It must be noted that the treatise was not officially translated into English. The treatise consists of five chapters and starts with the title page which states: "Book of the Greatness of the Sword, in which many secrets which the Commander Jerónimo de Carranza composed, are declared. One may study the book without a ''maestro'' (teacher). Dedicated to Don Philip III King of Spain, and of the greater part of the world, our lord." The treatise was published in Madrid, Spain, on June 17, 1599. The preface includes text on official taxatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luis Pacheco De Narváez
Don Luis Pacheco de Narváez (1570–1640) was a Spanish writer on ''destreza'', the Spanish art of fencing. He was a follower of Don Jerónimo Sánchez de Carranza. Some of his earlier works were compendia of Carranza's work while his later works were less derivative. He served as fencing master to King Philip IV of Spain. Nevertheless, it is not known exactly when Pacheco met his teacher, the greatest master of Spanish fencing, Jerónimo Sanchez de Carranza. Biography Until recently, there has been no information on the exact date of birth of Pacheco de Narváez. Born in the city of Baeza, his life was devoted to working with weapons and becoming a sergeant major in the Canary Islands, namely on the island of Fuerteventura and Lanzarote. According to documents from the legacy of Pacheco de Narváez in the Canary Islands, it is known that he was the son of Rodrigo Marin de Narváez and Magdalena Pacheco Cameras. He married Beatriz Fernandez de Cordoba, the daughter of Mich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destreza
is the conventional term for the Spanish tradition of fencing of the early modern period. The word literally translates to 'dexterity' or 'skill, ability', and thus to 'the true skill' or 'the true art'. While is primarily a system of swordsmanship, it is intended to be a universal method of fighting, applicable to all weapons in principle, but in practice dedicated to the rapier specifically, or the rapier combined with a defensive weapon such as a cloak, a buckler or a parrying dagger, besides other weapons such as the late-renaissance two-handed '' montante''; the flail; and polearms such as the pike and halberd. Its precepts are based on reason, geometry, and tied to intellectual, philosophical, and moral ideals, incorporating various aspects of a well-rounded Renaissance humanist education, with a special focus on the writings of classical authors such as Aristotle, Euclid, and Plato. The tradition is documented in scores of fencing manuals, but centers on the works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerónimo Sánchez De Carranza
Don Jerónimo Sánchez de Carranza, ( es, link=no, Jerónimo Sánchez de Carranza), Jerónimo de Carranza, pt, Hieronimo de Carança; c. 1539 – c. 1600 or 1608) was a Spanish nobleman, humanist, scientist, one of the most famous fencers, and the creator of the Spanish school of fencing, ''destreza''. He was the author of the treatise on fencing ('The Philosophy of Arms') from 1569, published in 1582. Carranza created the ideal of a poet and a warrior, which became the main guide to life for noblemen. His work on fencing is the beginning of the fighting style in Spain, which lasted almost 300 years. Jerónimo de Carranza, as the founder of destreza, is also called "the pioneer of the science of handling weapons." His work was continued by his followers pupil Luis Pacheco de Narváez, and Dutch master of fencing Gérard Thibault d'Anvers. It was they who put philosophical, intellectual and moral ideals into the system of combat and continued to develop the school of Spanish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destreza
is the conventional term for the Spanish tradition of fencing of the early modern period. The word literally translates to 'dexterity' or 'skill, ability', and thus to 'the true skill' or 'the true art'. While is primarily a system of swordsmanship, it is intended to be a universal method of fighting, applicable to all weapons in principle, but in practice dedicated to the rapier specifically, or the rapier combined with a defensive weapon such as a cloak, a buckler or a parrying dagger, besides other weapons such as the late-renaissance two-handed '' montante''; the flail; and polearms such as the pike and halberd. Its precepts are based on reason, geometry, and tied to intellectual, philosophical, and moral ideals, incorporating various aspects of a well-rounded Renaissance humanist education, with a special focus on the writings of classical authors such as Aristotle, Euclid, and Plato. The tradition is documented in scores of fencing manuals, but centers on the works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maestro
Maestro (; from the Italian ''wikt:maestro#Italian, maestro'' , meaning "wikt:master, master" or "teacher") is an honorific title of respect (plural: maestros or maestri). The term is most commonly used in the context of Western classical music and opera, in line with the ubiquitous use of List of Italian musical terms used in English#Musical direction, Italian musical terms. In music The word ''maestro'' is most often used in addressing or referring to conducting, conductors. Less frequently, one might refer to respected composers, Performing arts#Music, performers, impresarios, musicologists, and music education, music teachers. In the world of Italian opera, the title is also used to designate a number of positions within the orchestra and company that have specific duties during rehearsal and performance. These include: * Maestro sostituto or maestro collaboratore: musicians who act as ''répétiteurs'' and assistant conductors during performances. * Maestro concertatore, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip III Of Spain
Philip III ( es, Felipe III; 14 April 1578 – 31 March 1621) was King of Spain. As Philip II, he was also King of Portugal, Naples, Sicily and Sardinia and Duke of Milan from 1598 until his death in 1621. A member of the House of Habsburg, Philip III was born in Madrid to King Philip II of Spain and his fourth wife and niece Anna, the daughter of Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian II and Maria of Spain. Philip III later married his cousin Margaret of Austria, sister of Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor. Although also known in Spain as Philip the Pious, Philip's political reputation abroad has been largely negative. Historians C. V. Wedgwood, R. Stradling and J. H. Elliott have described him, respectively, as an "undistinguished and insignificant man," a "miserable monarch," and a "pallid, anonymous creature, whose only virtue appeared to reside in a total absence of vice." In particular, Philip's reliance on his corrupt chief minister, the Duke of Lerma, drew much criticism at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Spain
, coatofarms = File:Coat_of_Arms_of_Spanish_Monarch.svg , coatofarms_article = Coat of arms of the King of Spain , image = Felipe_VI_in_2020_(cropped).jpg , incumbent = Felipe VI , incumbentsince = 19 June 2014 , his/her = His , heir_presumptive = Leonor, Princess of Asturias , first_monarch = Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon (Catholic Monarchs of Spain) , date = , appointer = Hereditary , residence = Royal Palace of Madrid (official)Palace of Zarzuela (private) , website The Spanish Monarchy The monarchy of Spain or Spanish monarchy ( es, Monarquía Española), constitutionally referred to as The Crown ( es, La Corona), is a constitutional political institution, institution and the highest office of Spain. The monarchy comprises the reigning List of Spanish monarchs, monarch, his or her family, and the Royal Household of Spain, royal household organizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and its monocentric metropolitan area is the third-largest in the EU.United Nations Department of Economic and Social AffairWorld Urbanization Prospects (2007 revision), (United Nations, 2008), Table A.12. Data for 2007. The municipality covers geographical area. Madrid lies on the River Manzanares in the central part of the Iberian Peninsula. Capital city of both Spain (almost without interruption since 1561) and the surrounding autonomous community of Madrid (since 1983), it is also the political, economic and cultural centre of the country. The city is situated on an elevated plain about from the closest seaside location. The climate of Madrid features hot summers and cool winters. The Madrid urban agglomeration has the second-large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feint
Feint is a French term that entered English via the discipline of swordsmanship and fencing. Feints are maneuvers designed to distract or mislead, done by giving the impression that a certain maneuver will take place, while in fact another, or even none, will. In military tactics and many types of combat, there are two types of feints: feint attacks and feint retreats. Attacks A feint attack is designed to draw defensive action towards the point under assault. It is usually used as a diversion to force the enemy to concentrate more manpower in a given area, to weaken the opposing force in another area. Unlike a related diversionary maneuver, the demonstration, a feint involves actual contact with the enemy. Retreats A feint retreat, or feigned retreat, is performed by briefly engaging the enemy, then retreating. It is intended to draw the enemy pursuit into a prepared ambush, or to cause disarray. For example, the Battle of Hastings was lost when Saxons pursued the Norman cav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egerton Castle
__NOTOC__ Egerton Castle M.A., F.S.A. (12 March 1858 – 16 September 1920) was an author, antiquarian, and swordsman, and an early practitioner of reconstructed historical fencing, frequently in collaboration with his colleague Captain Alfred Hutton. Castle was the captain of the British épée and sabre teams at the 1908 Summer Olympics. He was born in London into a wealthy family; his maternal grandfather was the publishing magnate and philanthropist Egerton Smith. He was a lieutenant of the Second West India Regiment and afterwards a captain of the Royal Engineers Militia. He was also an expert on bookplates and a keen collector. Egerton Castle co-authored several novels with his wife, Agnes (née Sweetman). Selected works *''Schools and Masters of Fencing : From the Middle Ages to the Eighteenth Century'', (2005), (2006). (The first edition: G. Bell & Sons, London 1885)"The Baron's Quarry"(short story) *Consequences. London: Richard Bentley and Son. 1891. 3 volume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Books
Spanish might refer to: * Items from or related to Spain: **Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain **Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries **Spanish cuisine Other places * Spanish, Ontario, Canada * Spanish River (other), the name of several rivers * Spanish Town, Jamaica Other uses * John J. Spanish (1922–2019), American politician * "Spanish" (song), a single by Craig David, 2003 See also * * * Español (other) * Spain (other) * España (other) * Espanola (other) * Hispania, the Roman and Greek name for the Iberian Peninsula * Hispanic, the people, nations, and cultures that have a historical link to Spain * Hispanic (other) * Hispanism * Spain (other) * National and regional identity in Spain * Culture of Spain * Spanish Fort (other) Spanish Fort or Old Spanish Fort may refer to: United States * Spanish Fort, Alabama, a city * Spanish Fort (Colorado ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Treatises
Combat (French for ''fight'') is a purposeful violent conflict meant to physically harm or kill the opposition. Combat may be armed (using weapons) or unarmed ( not using weapons). Combat is sometimes resorted to as a method of self-defense, or can be used as a tool to impose one's will on others. An instance of combat can be a stand-alone confrontation or a small part of a much larger violent conflict. Instances of combat may also be benign and recreational, as in the cases of combat sports and mock combat. Combat may comply with, or be in violation of local or international laws regarding conflict. Examples of rules include the Geneva Conventions (covering the treatment of people in war), medieval chivalry, the Marquess of Queensberry rules (covering boxing) and several forms of combat sports. Hand-to-hand combat Hand-to-hand combat (melee) is combat at very close range, attacking the opponent with the body ( striking, kicking, strangling, etc.) and/or with a melee weapo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |