|
Levi F. Noble
Levi Fatzinger Noble (November 11, 1882 – August 4, 1965) was an American geologist. His entire career was spent as a member of the United States Geological Survey (USGS). Noble is largely known for his work in the American southwest, particularly as a pioneer geologist in the Death Valley region. Early life Noble was born in 1882 into a prominent and wealthy family of Auburn, New York. He received his bachelor's degree from Yale University in 1905 and his PhD in geology in 1909, also from Yale. Shortly after receiving his doctorate he was appointed to the USGS; being independently wealthy, he received only a token salary, and was largely permitted to select his own projects. In 1910, Noble married Dorothy Evans of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. As a wedding gift, Dorothy's parents gave them a fruit ranch near Valyermo, California, at the foot of the north slope of the San Gabriel Mountains and athwart the San Andreas Fault zone. The ranch was their principal residence for the rest o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auburn, New York
Auburn is a city in Cayuga County, New York, United States. Located at the north end of Owasco Lake, one of the Finger Lakes in Central New York, the city had a population of 26,866 at the 2020 census. It is the largest city of Cayuga County, the county seat, and the site of the maximum-security Auburn Correctional Facility, as well as the William H. Seward House Museum and the house of abolitionist Harriet Tubman. History The region around Auburn had been Haudenosaunee territory for centuries before European contact and historical records. Auburn was founded in 1793, during the post-Revolutionary period of settlement of western New York. The founder, John L. Hardenbergh, was a veteran of the Sullivan-Clinton campaign against the Iroquois during the American Revolution. Hardenbergh settled in the vicinity of the Owasco River with his infant daughter and two African-American indentured servants, Harry and Kate Freeman. After his death in 1806, Hardenbergh was buried in Aub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinumo Quartzite
The Shinumo Quartzite also known as the Shinumo Sandstone, is a Mesoproterozoic rock formation, which outcrops in the eastern Grand Canyon, Coconino County, Arizona, (Northern Arizona). It is the 3rd member of the 5-unit Unkar Group. The Shinumo Quartzite consists of a series of massive, cliff-forming sandstones and sedimentary quartzites. Its cliffs contrast sharply with the stair-stepped topography of typically brightly-colored (orange, red, yellow, etc) strata of the underlying slope-forming Hakatai Shale. Overlying the Shinumo, dark green to black, fissile, slope-forming shales of the Dox Formation create a well-defined notch. It and other formations of the Unkar Group occur as isolated fault-bound remnants along the main stem of the Colorado River and its tributaries in Grand Canyon. Typically, the Shinumo Quartzite and associated strata of the Unkar Group dip northeast (10°–30°) toward normal faults that dip 60+° toward the southwest. This can be seen at the Palisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Grand Canyon Area
The geology of the Grand Canyon area includes one of the most complete and studied sequences of rock (geology), rock on Earth. The nearly 40 major sedimentary rock layers exposed in the Grand Canyon and in the Grand Canyon National Park area range in age from about 200 million to nearly 2 billion years old. Most were deposited in warm, shallow seas and near ancient, long-gone sea shores in western North America. Both marine and terrestrial sediments are represented, including lithified sand dunes from an extinct desert. There are at least 14 known Unconformity, unconformities in the geologic record found in the Grand Canyon. Uplift of the region started about 75 million years ago during the Laramide orogeny; a mountain-building event that is largely responsible for creating the Rocky Mountains to the east. In total, the Colorado Plateau was uplifted an estimated . The adjacent Basin and Range Province to the west started to form about 18 million years ago as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Death Valley Area
The exposed geology of the Death Valley area presents a diverse and complex set of at least 23 formations of sedimentary units, two major gaps in the geologic record called unconformities, and at least one distinct set of related formations geologists call a group. The oldest rocks in the area that now includes Death Valley National Park are extensively metamorphosed by intense heat and pressure and are at least 1700 million years old. These rocks were intruded by a mass of granite 1400 Ma (million years ago) and later uplifted and exposed to nearly 500 million years of erosion. Marine deposition occurred 1200 to 800 Ma, creating thick sequences of conglomerate, mudstone, and carbonate rock topped by stromatolites, and possibly glacial deposits from the hypothesized Snowball Earth event. Rifting thinned huge roughly linear parts of the supercontinent Rodinia enough to allow sea water to invade and divide its landmass into component continents separated by narrow straits. A pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobleite
Nobleite is a rare borate mineral with the chemical formula CaB6O9(OH)2·3H2O. It was discovered in 1961, in Death Valley, California, and is named for Levi F. Noble, a USGS geologist, in honor of his contributions to the geology of the Death Valley region. Nobleite has also been identified at two localities in Chile and Argentina Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th .... References Webmineral Phylloborates Monoclinic minerals [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly through California. It forms the tectonics, tectonic boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, and its motion is Fault (geology)#Strike-slip faults, right-lateral strike-slip (horizontal). The fault divides into three segments, each with different characteristics and a different degree of earthquake risk. The slip rate along the fault ranges from /yr. It was formed by a transform boundary. The fault was identified in 1895 by Professor Andrew Lawson of University of California, Berkeley, UC Berkeley, who discovered the northern zone. It is often described as having been named after San Andreas Lake, a small body of water that was formed in a valley between the two plates. However, according to some of his reports from 1895 and 1908, Lawson actually named it after the surrounding San Andreas Valley. Following the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, Lawson concluded that the fault extende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Geology Unit
The Military Geology Unit was a unit in the United States military during World War II. It was established on June 24, 1942, six months after Pearl Harbor.Terman, Maurice, 1998, ''Military Geology Unit of the U.S. Geological Survey during World War II''. Military Geology in War and Peace. Geological Society of America. p. 49-54. People in the US Geological Survey wanted to get involved in the war effort, either for patriotism or prestige or both, and provided a geological intelligence report for a randomly chosen country, Sierra Leone. The Sierra Leone report described the terrain, locations of water supplies and road-building materials, and other facts useful for military operations. The US military bought the idea and so the Military Geological Unit was formed, starting out with six people but quickly expanding. The US Geological Survey, USGS continued to operate a Military Geology Unit through 1975, providing the US Department of Defense with research and documentation nece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
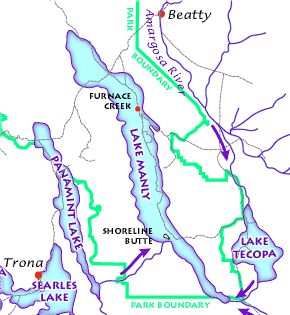
Lake Manly
Lake Manly was a pluvial lake in Death Valley, California, covering much of Death Valley with a surface area of during the so-called "Blackwelder stand". Water levels varied through its history, and the chronology is further complicated by active tectonic processes that have modified the elevations of the various shorelines of Lake Manly; during the Blackwelder stage they reached above sea level. The lake received water mainly from the Amargosa River and at various points from the Mojave River and Owens River. The lake and its substantial catchment favoured the spread of a number of aquatic species, including some lizards, pupfish and springsnails. The lake probably supported a substantial ecosystem, and a number of diatoms developed there. In Death Valley, lakes existed during different times in the geological past. After some poorly defined lake stages during the Miocene, Pliocene and early Pleistocene, the first large lake stage occurred about 185,000–128,000 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoshone
The Shoshone or Shoshoni ( or ) are a Native American tribe with four large cultural/linguistic divisions: * Eastern Shoshone: Wyoming * Northern Shoshone: southern Idaho * Western Shoshone: Nevada, northern Utah * Goshute: western Utah, eastern Nevada They traditionally speak the Shoshoni language, part of the Numic languages branch of the large Uto-Aztecan language family. The Shoshone were sometimes called the Snake Indians by neighboring tribes and early American explorers. Their peoples have become members of federally recognized tribes throughout their traditional areas of settlement, often co-located with the Northern Paiute people of the Great Basin. Etymology The name "Shoshone" comes from ''Sosoni'', a Shoshone word for high-growing grasses. Some neighboring tribes call the Shoshone "Grass House People," based on their traditional homes made from ''sosoni''. Shoshones call themselves ''Newe'', meaning "People".Loether, Christopher"Shoshones."''Encyclopedia of the Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borate
A borate is any of several boron oxyanions, negative ions consisting of boron and oxygen, such as orthoborate , metaborate , or tetraborate ; or any salt with such anions, such as sodium metaborate, and disodium tetraborate . The name also refers to certain functional groups in molecules consisting of boron and oxygen, and esters with such groups, such as triethyl orthoborate . Natural occurrence Borate ions occur, alone or with other anions, in many borate and borosilicate minerals such as borax, boracite, ulexite (boronatrocalcite) and colemanite. Borates also occur in seawater, where they make an important contribution to the absorption of low frequency sound in seawater. Borates also occur in plants, including almost all fruits. Anions The main borate anions are: * tetrahydroxyborate , found in sodium tetrahydroxyborate . * orthoborate , found in trisodium orthoborate * perborate , as in sodium perborate * metaborate or , found in sodium metaborate * diborate , f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colemanite
Colemanite (Ca2B6O11·5H2O) or (CaB3O4(OH)3·H2O) is a borate mineral found in evaporite deposits of alkaline lacustrine environments. Colemanite is a secondary mineral that forms by alteration of borax and ulexite. It was first described in 1884 for an occurrence near Furnace Creek in Death Valley and was named after William Tell Coleman (1824–1893), owner of the mine "Harmony Borax Works" where it was first found. At the time, Coleman had alternatively proposed the name "smithite" instead after his business associate Francis Marion Smith. Uses Colemanite is an important ore of boron, and was the most important boron ore until the discovery of kernite Kernite, also known as rasorite, is a hydrated sodium borate hydroxide mineral with formula . It is a colorless to white mineral crystallizing in the monoclinic crystal system typically occurring as prismatic to acicular crystals or granular ... in 1926. It has many industrial uses, like the manufacturing of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)