|
Lethe Callipteris
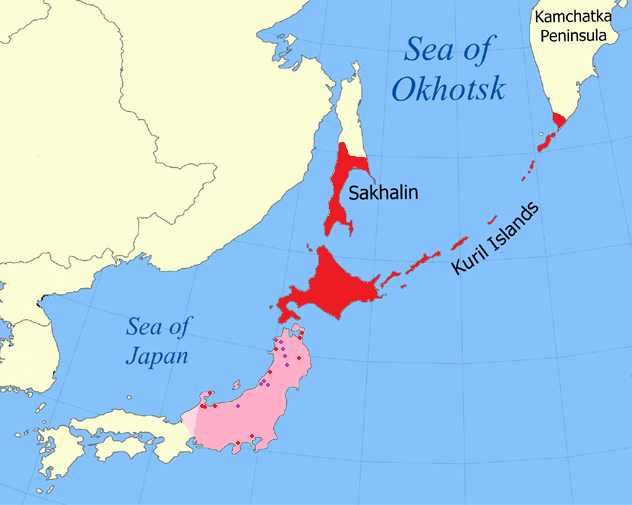
''Lethe callipteris'' is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae (Satyrinae). It is found in the East Palearctic where it is endemic to Japan, Sakhalin (''L. c. karafutonis'' Matsumura, 1925) and the Kuriles (''L. c. obscura'' Nakahara, 1926). The larva feeds on ''Sasa Sasa may refer to: People * Saša, a given name * Genjū Sasa (1900–1959), Japanese film director and critic * Sa'sa'a bin Sohan (598–666), a companion of Imam Ali revered by Shia Muslims * Sasa (politician), special envoy to the United Nation ...'' and '' Pleioblastus'', etc. (Graminae). It has single generation and hibernates as a larva.Taro Iwase, 1954 Synopsis of the known life-histories of Japanese butterflies ''The Lepidopterists' News'' 1954: 95-10pdf/ref> Subspecies *''Lethe callipteris callipteris'' (Japan) *''Lethe callipteris karafutonis'' Matsumura, 1925 (Sakhalin) *''Lethe callipteris obscura'' Nakahara, 1926 (Kuriles) References callipteris Butterflies described in 1877 Butterflies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Gardiner Butler
Arthur Gardiner Butler F.L.S., F.Z.S. (27 June 1844 – 28 May 1925) was an English entomologist, arachnologist and ornithologist. He worked at the British Museum on the taxonomy of birds, insects, and spiders. Biography Arthur Gardiner Butler was born at Cheyne Walk, Chelsea, London. He was the son of Thomas Butler (1809–1908), assistant-secretary to the British Museum.Thomas Butler: He was educated at St. Paul's School,He was admitted 15-03-1854, according to: later receiving a year's tuition in drawing at the Art School of South Kensington. At the British Museum, he was appointed as an officer with two roles, as an assistant-keeper in zoology and as an assistant-librarian in 1879. Work He also published articles on spiders of Australia, the Galápagos, Madagascar, and other places. In 1859, he described the Deana moth. Bibliography Entomology *"Monograph of the species of ''Charaxes'', a genus of diurnal Lepidoptera". ''Proceedings of the Zoological Socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterfly
Butterflies are insects in the macrolepidopteran clade Rhopalocera from the Order (biology), order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths. Adult butterflies have large, often brightly coloured wings, and conspicuous, fluttering flight. The group comprises the large superfamily (zoology), superfamily Papilionoidea, which contains at least one former group, the skippers (formerly the superfamily "Hesperioidea"), and the most recent analyses suggest it also contains the moth-butterflies (formerly the superfamily "Hedyloidea"). Butterfly fossils date to the Paleocene, about 56 million years ago. Butterflies have a four-stage life cycle, as like most insects they undergo Holometabolism, complete metamorphosis. Winged adults lay eggs on the food plant on which their larvae, known as caterpillars, will feed. The caterpillars grow, sometimes very rapidly, and when fully developed, pupate in a chrysalis. When metamorphosis is complete, the pupal skin splits, the adult insect climbs o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nymphalidae
The Nymphalidae are the largest family of butterflies, with more than 6,000 species distributed throughout most of the world. Belonging to the superfamily Papilionoidea, they are usually medium-sized to large butterflies. Most species have a reduced pair of forelegs and many hold their colourful wings flat when resting. They are also called brush-footed butterflies or four-footed butterflies, because they are known to stand on only four legs while the other two are curled up; in some species, these forelegs have a brush-like set of hairs, which gives this family its other common name. Many species are brightly coloured and include popular species such as the emperors, monarch butterfly, admirals, tortoiseshells, and fritillaries. However, the under wings are, in contrast, often dull and in some species look remarkably like dead leaves, or are much paler, producing a cryptic effect that helps the butterflies blend into their surroundings. Nomenclature Rafinesque introduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satyrinae
The Satyrinae, the satyrines or satyrids, commonly known as the browns, are a subfamily of the Nymphalidae (brush-footed butterflies). They were formerly considered a distinct family, Satyridae. This group contains nearly half of the known diversity of brush-footed butterflies. The true number of the Satyrinae species is estimated to exceed 2,400. Overview They are generally weak fliers and often shun bright sunlight, preferring moist and semishaded habitats. The caterpillars feed chiefly on monocotyledonous plants such as palms, grasses, and bamboos. The Morphinae are sometimes united with this group. The taxonomy and systematics of the subfamily are under heavy revision. Much of the early pioneering work of L. D. Miller has helped significantly by creating some sort of order. '' Dyndirus'' (Capronnier, 1874) is a satyrid ''incertae sedis''. Other than this genus, according to the latest studies on the classification of Nymphalidae, all satyrines have been assigned to one of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palearctic
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa. The realm consists of several bioregions: the Euro-Siberian region; the Mediterranean Basin; the Sahara and Arabian Deserts; and Western, Central and East Asia. The Palaearctic realm also has numerous rivers and lakes, forming several freshwater ecoregions. The term 'Palearctic' was first used in the 19th century, and is still in use as the basis for zoogeographic classification. History In an 1858 paper for the ''Proceedings of the Linnean Society'', British zoologist Philip Sclater first identified six terrestrial zoogeographic realms of the world: Palaearctic, Aethiopian/Afrotropic, Indian/Indomalayan, Australasian, Nearctic, and Neotropical. The six indicated general groupings of fauna, based on shared biogeography and large-scale geographic barriers to migration. Alfred Wallace a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Species
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Japan
Japan is an archipelagic country comprising a stratovolcanic archipelago over along the Pacific coast of East Asia. It consists of 6,852 islands. The five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu, Kyushu, Shikoku and Okinawa. There are 6,847 remote islands. The Ryukyu Islands and Nanpō Islands are south and east of the main islands. The territory covers . It is the fourth largest island country in the world and the largest island country in East Asia. The country has the 6th longest coastline at and the 8th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of in the world. The terrain is mostly rugged and mountainous with 66% forest. The population is clustered in urban areas on the coast, plains and valleys. Japan is located in the northwestern Ring of Fire on multiple tectonic plates. East of the Japanese archipelago are three oceanic trenches. The Japan Trench is created as the oceanic Pacific Plate subducts beneath the continental Okhotsk Plate. The continuous subduction process causes freq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: Yh-mif) is the largest island of Russia. It is north of the Japanese archipelago, and is administered as part of the Sakhalin Oblast. Sakhalin is situated in the Pacific Ocean, sandwiched between the Sea of Okhotsk to the east and the Sea of Japan to the west. It is located just off Khabarovsk Krai, and is north of Hokkaido in Japan. The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of which are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The Island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ). Sakhalin was once part of China during the Qing dynasty, although Chinese control was relaxed at times. Sakhalin was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuriles
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the Russian Far East. It stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaido in Japan to Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the north Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many minor rocks. The Kuril Islands consist of the Greater Kuril Chain and the Lesser Kuril Chain. They cover an area of around , with a population of roughly 20,000. The islands have been under Russian administration since their 1945 invasion as the Soviet Union towards the end of World War II. Japan claims the four southernmost islands, including two of the three largest (Iturup and Kunashir), as part of its territory, as well as Shikotan and the Habomai islets, which has led to the ongoing Kuril Islands dispute. The disputed islands are know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasa (plant)
''Sasa'' (Japanese: or ), also called broad-leaf bamboo, is a genus of running bamboo. These species have at most one branch per node. Selected species * ''Sasa borealis'' (Hack.) Makino & Shibata – northern bamboo, Jirisan bamboo * ''Sasa kagamiana'' * ''Sasa kurilensis'' (Rupr.) Makino & Shibata – chishimazasa, Kuril bamboo, Korean bamboo * ''Sasa nagimontana'' – muroi * '' Sasa nipponica'' (Makino) Makino & Shibata * ''Sasa oshidensis'' * '' Sasa palmata'' (Burb.) E.G.Camus – broad-leaf bamboo * ''Sasa senanensis'' * '' Sasa tsuboiana'' * ''Sasa veitchii'' – kumazasa Fossil record Fossil leaves of †''Sasa kodorica'' are described from the Pliocene of Kodori Valley in Abkazia.Acta Palaeobotanica – Supplementum No. 3 – New Fossil Floras from Neogene Deposits in the Belchatow Lignite Mine by Grzegor Worobiec – Polish Academy of Sciences W. Szafer Institute of Botany, Krakow 2003 See also *''Pseudosasa ''Pseudosasa'' is a genus of East Asian bamboo in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleioblastus
''Pleioblastus'' is an East Asian genus of monopodial bamboos in the grass family Poaceae. They are native to China and Japan, and naturalized in scattered places in Korea, Europe, New Zealand, and the Western Hemisphere. The plant spreads by vigorous underground rhizomes which run along just beneath the soil surface, producing plantlets at the nodes. These can be used to propagate new plants, but if not removed they can become invasive. The species ''Pleioblastus variegatus'' (green and cream stripes), and ''P. viridistriatus'' (green and yellow stripes) have gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit. Genetic research suggests that this genus may properly be part of the genus ''Arundinaria''. ;Species ;formerly included see ''Acidosasa Ampelocalamus Chimonocalamus Drepanostachyum Oligostachyum Pseudosasa Sasaella Sinobambusa Yushania ''Yushania'' is a genus of bamboo in the grass family. Recent classification systems place ''Yushania'' in the trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lethe (butterfly)
''Lethe'' is a butterfly genus from the subfamily Satyrinae in the family Nymphalidae. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1819. It includes the treebrowns, woodbrowns, foresters and their relatives. The species in the genus ''Lethe'' occur in temperate-tropical southern and eastern Asia, up to Indonesia and in North America. ''Lethe anthedon'', northern pearly-eye ''Lethe'' Selected species These 108 species belong to the genus ''Lethe''. * '' Lethe albolineata'' Poujade, 1884 * '' Lethe andersoni'' Atkinson, 1871 * '' Lethe anthedon'' (A. Clark, 1936) (northern pearly-eye) * '' Lethe appalachia'' R. Chermock, 1947 (Appalachian brown) * '' Lethe arete'' Cramer, 1780 * '' Lethe argentata'' Leech, 1891 * '' Lethe armandina'' Oberthür, 1881 (Chinese labyrinth ) * '' Lethe atkinsonia'' Hewitson, 1876 (small goldenfork ) * '' Lethe baileyi'' South, 1913 * '' Lethe baladeva'' Moore, 1865 (treble silverstripe ) * '' Lethe baucis'' Leech, 1891 * '' Lethe bhairava'' Moore, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_male_in_flight.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)