|
Leptopelis Bequaerti
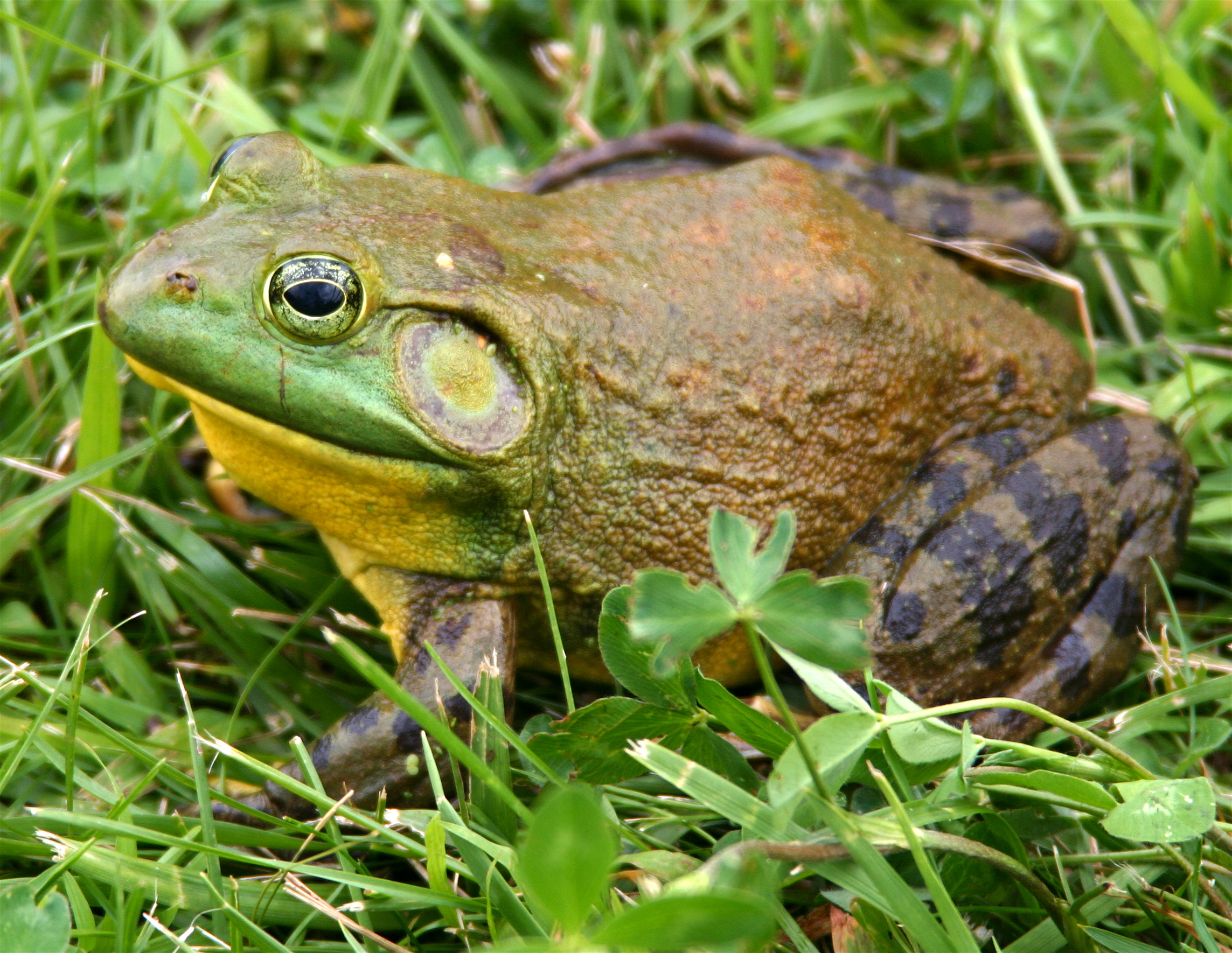
''Leptopelis bequaerti'' is a species of frog in the family Arthroleptidae. It is endemic to Liberia and only known from its type locality, Gbarnga, and from Mount Coffee. Common name Gbanga forest treefrog has been coined for it. It is a poorly known species with uncertain taxonomic validity. Etymology The specific name ''bequaerti'' honours Joseph Charles Bequaert, a Belgian botanist, entomologist, and malacologist who collected the holotype. Description Adult females measure and a single adult male in snout–vent length. A newly metamorphosed juvenile measured . The snout is rounded. The tympanum is visible. The fingers are relatively long and bear large discs but only rudimentary webbing. The toes bear discs that are slightly smaller than the finger ones. The toes are two-thirds webbed. Skin of the dorsum is shagreened and bears small scattered warts. Colouration is pale brown above with a dark triangular interorbital marking. There is often a connected hourglass like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Loveridge
Arthur Loveridge (28 May 1891 – 16 February 1980) was a British biologist and herpetologist who wrote about animals in East Africa, particularly Tanzania, and New Guinea. He gave scientific names to several gecko species in the region. Arthur Loveridge was born in Penarth, and was interested in natural history from childhood. He gained experience with the National Museum of Wales and Manchester Museum before becoming the curator of the Nairobi Museum (now the National Museum of Kenya) in 1914. During WW1, he joined the East African Mounted Rifles, later returning to the museum to build up the collections. He then became an assistant game warden in Tanganyika. In 1924, he joined the Museum of Comparative Zoology in the grounds of Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts, where he was the curator of herpetology. He returned to East Africa on several field trips and wrote many scientific papers before retiring from Harvard in 1957. He married Mary Victoria Sloan in 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tympanum (anatomy)
The tympanum is an external hearing structure in animals such as mammals, birds, some reptiles, some amphibians and some insects. Using sound, vertebrates and many insects are capable of sensing their prey, identifying and locating their predators, warning other individuals, and locating potential mates and rivals by hearing the intentional or unintentional sounds they make. In general, any animal that reacts to sounds or communicates by means of sound, needs to have an auditory mechanism. This typically consists of a membrane capable of vibration known as the tympanum, an air-filled chamber and sensory organs to detect the auditory stimuli. Anurans In frogs and toads, the tympanum is a large external oval shape membrane made up of nonglandular skin. It is located just behind the eye. It does not process sound waves; it simply transmits them to the inner parts of the amphibian's ear, which is protected from the entry of water and other foreign objects. A frog's ear drum works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Arthur Loveridge
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Fauna Of Liberia
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example ''Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibians Of West Africa
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frogs Of Africa
The fauna of Africa, in its broader sense, is all the animals living in Africa and its surrounding seas and islands. The more characteristic African fauna is found in the Afrotropical realm. Lying almost entirely within the tropics, and equally to north and south of the equator creates favourable conditions for rich wildlife. Africa is home to many of the world's most famous fauna in human culture such as lions‚ rhinos‚ cheetahs‚ giraffes‚ antelope, hippos, leopards, zebras‚ and African elephants among many others. Origins and history of African fauna Whereas the earliest traces of life in fossil record of Africa date back to the earliest times, the formation of African fauna as we know it today, began with the splitting up of the Gondwana supercontinent in the mid-Mesozoic era. After that, four to six faunal assemblages, the so-called African Faunal Strata (AFSs) can be distinguished. The isolation of Africa was broken intermittently by discontinuous "filter routes" tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptopelis
''Leptopelis'' is a genus of frogs in the family Arthroleptidae. They are found throughout Sub-Saharan Africa, excluding Madagascar. It is placed in monotypic subfamily Leptopelinae, although this subfamily is not always recognized. They have a number of common names, including forest treefrogs, tree frogs, leaf-frogs, and big-eyed frogs. Description ''Leptopelis'' are mostly medium-sized frogs (snout–vent length ), but ''Leptopelis palmatus'' can reach . Tympanum is present. Most species have expended digit tips. Ecology ''Leptopelis'' are mainly arboreal, but some species, especially in more arid areas, are terrestrial or even subfossorial. Breeding typically starts with the heavy rains in the beginning of the wet season. Eggs may be deposited either in water or in/on the ground. Development includes a free-living tadpole stage, with a possible exception of '' Leptopelis brevirostris'', whose large eggs suggest that development could be direct. Males typically call in bushe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadpole
A tadpole is the larval stage in the biological life cycle of an amphibian. Most tadpoles are fully aquatic, though some species of amphibians have tadpoles that are terrestrial. Tadpoles have some fish-like features that may not be found in adult amphibians such as a lateral line, gills and swimming tails. As they undergo metamorphosis, they start to develop functional lungs for breathing air, and the diet of tadpoles changes drastically. A few amphibians, such as some members of the frog family Brevicipitidae, undergo direct development i.e., they do not undergo a free-living larval stage as tadpoles instead emerging from eggs as fully formed "froglet" miniatures of the adult morphology. Some other species hatch into tadpoles underneath the skin of the female adult or are kept in a pouch until after metamorphosis. Having no hard skeletons, it might be expected that tadpole fossils would not exist. However, traces of biofilms have been preserved and fossil tadpoles have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsum (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessarily "typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely Carnivore, carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order (biology), order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is known from the Early Triassic of Madagascar, but molecular clock, molecular clock dating suggests their split from other amphibians may extend further back to the Permian, 265 Myr, million years ago. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics to subarctic regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity is in tropical rainforest. Frogs account for around 88% of extant amphibian species. They are also one of the five most diverse vertebrate orders. Warty frog species tend to be called toads, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal, not from Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy or evolutionary history. An adult frog has a stout body, protruding eyes, anteriorly-attached tongue, limb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Charles Bequaert
Joseph Charles Bequaert was an American naturalist of Belgian origin, born 24 May 1886 in Torhout (Belgium) and died on 12 January 1982 in Amherst, Massachusetts. Clench WJ (1982). "Joseph Charles Bequaert". '' The Nautilus'' 96(2)page 35 Career Bequaert obtained a doctorate in botany at the University of Ghent in 1908. He was an entomologist, and from 1910 to 1912 he was part of ''la commission Belge sur la maladie du sommeil'' (Belgian Committee on sleeping sickness). From 1913 to 1915 he worked as a botanist in the Belgian Congo and also collected mollusks. In 1916 he emigrated to the United States and was an associate researcher from 1917 to 1922 at the American Museum of Natural History. He became an American citizen in 1921, and taught Entomology at the Harvard Medical School. From 1929 to 1956 he was Curator of Insects at the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard, and was Professor of Zoology from 1951 to 1956 within the same institution. Bequaert became president ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.png)
_(7073641407).jpg)

_Ranomafana.jpg)