|
Leptochilichthyidae
''Leptochilichthys'' is a genus of marine smelts containing four species. ''Leptochilichthys'' is the only genus in the former family Leptochilichthyidae but is now included within the broader family Alepocephalidae.R. Betancur-Rodriguez, E. Wiley, N. Bailly, A. Acero, M. Miya, G. Lecointre, G. Ortí''Phylogenetic Classification of Bony Fishes – Version 4''(2016) Its name derives from the Greek λεπτός (''leptos'', "small"); χεῖλος (''cheilos'', "lip"); and ἰχθύς (''ichthys'', "fish"). Species The currently recognized species in this genus are: * ''Leptochilichthys agassizii'' (Garman, 1899) (Agassiz' smooth-head) * '' Leptochilichthys microlepis'' ( Machida & Shiogaki, 1988) (smallscale smooth-head) * '' Leptochilichthys pinguis'' ( Vaillant, 1886) (Vaillant's smooth-head) Description Species in genus ''Leptochilichthys'' have toothless maxillae. The maxillae are considered especially long There are teeth on the palate and dentary. Many long gill rakers a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptochilichthys Microlepis
''Leptochilichthys'' is a genus of marine smelts containing four species. ''Leptochilichthys'' is the only genus in the former family Leptochilichthyidae but is now included within the broader family Alepocephalidae.R. Betancur-Rodriguez, E. Wiley, N. Bailly, A. Acero, M. Miya, G. Lecointre, G. Ortí''Phylogenetic Classification of Bony Fishes – Version 4''(2016) Its name derives from the Greek λεπτός (''leptos'', "small"); χεῖλος (''cheilos'', "lip"); and ἰχθύς (''ichthys'', "fish"). Species The currently recognized species in this genus are: * ''Leptochilichthys agassizii'' (Garman, 1899) (Agassiz' smooth-head) * '' Leptochilichthys microlepis'' ( Machida & Shiogaki, 1988) (smallscale smooth-head) * '' Leptochilichthys pinguis'' ( Vaillant, 1886) (Vaillant's smooth-head) Description Species in genus ''Leptochilichthys'' have toothless maxillae. The maxillae are considered especially long There are teeth on the palate and dentary. Many long gill rakers a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptochilichthys Pinguis
''Leptochilichthys'' is a genus of marine smelts containing four species. ''Leptochilichthys'' is the only genus in the former family Leptochilichthyidae but is now included within the broader family Alepocephalidae.R. Betancur-Rodriguez, E. Wiley, N. Bailly, A. Acero, M. Miya, G. Lecointre, G. Ortí''Phylogenetic Classification of Bony Fishes – Version 4''(2016) Its name derives from the Greek λεπτός (''leptos'', "small"); χεῖλος (''cheilos'', "lip"); and ἰχθύς (''ichthys'', "fish"). Species The currently recognized species in this genus are: * ''Leptochilichthys agassizii'' (Garman, 1899) (Agassiz' smooth-head) * ''Leptochilichthys microlepis'' ( Machida & Shiogaki, 1988) (smallscale smooth-head) * '' Leptochilichthys pinguis'' ( Vaillant, 1886) (Vaillant's smooth-head) Description Species in genus ''Leptochilichthys'' have toothless maxillae. The maxillae are considered especially long There are teeth on the palate and dentary. Many long gill rakers ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alepocephaliformes
Alepocephaliformes is an order of ray-finned fish. It was previously classified as the suborder Alepocephaloidei of the order Argentiniformes The Argentiniformes are an order of ray-finned fish whose distinctness was recognized only fairly recently. In former times, they were included in the Osmeriformes (typical smelt and allies) as suborder Argentinoidei. That term refers only to .... Subdivisions * Family Alepocephalidae (typical slickheads) (includes former families Bathylaconidae; Leptochilichthyidae) * Family Platytroctidae (including Searsiidae) References Ray-finned fish orders {{Rayfinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alepocephalidae
Slickheads, also known as nakedheads or smoothheads, are deep water fishes that belong to the family Alepocephalidae. They are most commonly found in the bathypelagic layer, which is approximately 3000m below the surface. They get their name from the lack of scales on their heads. Similarly, the scientific name is from the Greek ᾰ̓- (''a''-, "not"); λέπος (''lepos'', "scale"); and κεφαλή (''kephalē'', "head"). It has about 22 genera with ca. 96 species. In Japanese they are known as . Description The following characteristics are generally shared by the Alepocephalidae family: Their mouths consist of 80 to 100 razor-sharp teeth, being rather small and feeble. They are shaped in an eel-like elongation, with large eyes, gill rakers that range from moderate to long and numerous, and spineless fins. The single dorsal fin is located posterior to the midpoint of the body and there is no adipose dorsal fin present, there is a pectoral fin ranging from small to rudimenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Smelt
The Argentiniformes are an order of ray-finned fish whose distinctness was recognized only fairly recently. In former times, they were included in the Osmeriformes (typical smelt and allies) as suborder Argentinoidei. That term refers only to the suborder of marine smelts and barreleyes in the classification used here, with the slickheads and allies being the Alepocephaloidei. These suborders were treated as superfamilies Argentinoidea and Alepocephaloidea, respectively, when the present group was still included in the Osmeriformes. They contain six or seven families with almost 60 genera and at least 228 species. A common name for the group is marine smelts and allies, but this is rather misleading since the " freshwater" smelts of the Osmeridae also live predominantly in the ocean. FishBase (2006)Order Osmeriformes Version of 2006-OCT-09. Retrieved 2009-SEP-28. pp. 190-194 Description and ecology The Argentiniformes are smallish silvery or dark and generally bathypelagic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after Indian subcontinent, India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' (Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic) before the Pacific Ocean, Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Ming treasure voyages, Chinese explorers in the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the Atlanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
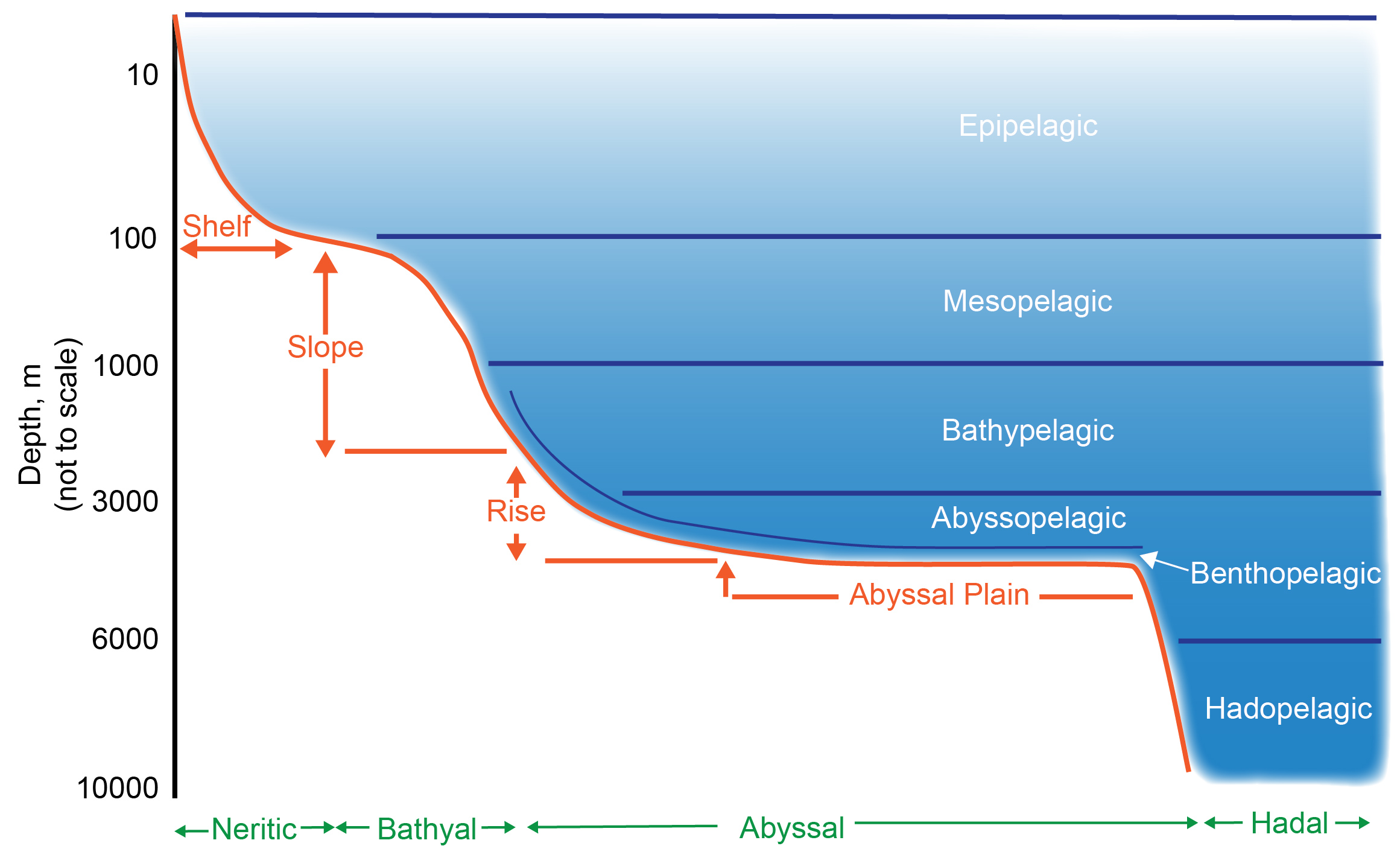
Deep Sea
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of 200 metres (656 feet) or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combination of low temperatures, darkness and high pressure The deep sea is considered the least explored Earth biome, with the extreme conditions making the environment difficult to access and explore. Organisms living within the deep sea have a variety of adaptations to survive in these conditions. Organisms can survive in the deep sea through a number of feeding methods including scavenging, predation and filtration, with a number of organisms surviving by feeding on marine snow. Marine snow is organic material that has fallen from upper waters into the deep sea. In 1960, the bathyscaphe ''Trieste'' descended to the bottom of the Mariana Trench near Guam, at , the deepest known spot in any ocean. If Mount Everest () were submerged there, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelial cells, known as hair cells, which respond to displacement caused by motion and transduce these signals into electrical impulses via excitatory synapses. Lateral lines serve an important role in schooling behavior, predation, and orientation. Fish can use their lateral line system to follow the vortices produced by fleeing prey. Lateral lines are usually visible as faint lines of pores running lengthwise down each side, from the vicinity of the gill covers to the base of the tail. In some species, the receptive organs of the lateral line have been modified to function as electroreceptors, which are organs used to detect electrical impulses, and as such, these systems remain closely linked. Most amphibian larvae and some fully aquatic adult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gill Raker
Gill rakers in fish are bony or cartilaginous processes that project from the branchial arch (gill arch) and are involved with suspension feeding tiny prey. They are not to be confused with the gill filaments that compose the fleshy part of the gill used for gas exchange. Rakers are usually present in two rows, projecting from both the anterior and posterior side of each gill arch. Rakers are widely varied in number, spacing, and form. By preventing food particles from exiting the spaces between the gill arches, they enable the retention of food particles in filter feeders. The structure and spacing of gill rakers in fish determines the size of food particles trapped, and correlates with feeding behavior. Fish with densely spaced, elongated, comb-like gill rakers are efficient at filtering tiny prey, whereas carnivores and omnivores often have more widely spaced gill rakers with secondary projections. Because gill raker characters often vary between closely related taxa, they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)