|
Leonhard Hess Stejneger
Leonhard Hess Stejneger (30 October 1851 – 28 February 1943) was a Norwegian-born American ornithologist, herpetologist and zoologist. Stejneger specialized in vertebrate natural history studies. He gained his greatest reputation with reptiles and amphibians. Wetmore, Alexander (1945). "Leonhard Hess Stejneger (1851-1943)". ''Biographical Memoir. Nat. Acad. Sci.'' 24: 145-195PDF/ref> Early life and family Stejneger was born in Bergen, Norway. His father was Peter Stamer Steineger, a merchant and auditor; his mother was Ingeborg Catharine (née Hess). Leonhard was the eldest of seven children. His sister Agnes Steineger was a Norwegian artist. Until 1880, the Steineger family had been one of the wealthy families in Bergen; at that time business reverses led to the father declaring bankruptcy. Stejneger attended the Smith Theological School in Bergen from 1859 to 1860, and Bergen Latin School until 1869. His interests in zoology developed early. By age sixteen he had a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergen, Norway
Bergen (), historically Bjørgvin, is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Vestland county on the Western Norway, west coast of Norway. , its population is roughly 285,900. Bergen is the list of towns and cities in Norway, second-largest city in Norway. The municipality covers and is on the peninsula of Bergenshalvøyen. The city centre and northern neighbourhoods are on Byfjorden (Hordaland), Byfjorden, 'the city fjord', and the city is surrounded by mountains; Bergen is known as the "city of Seven Mountains, Bergen, seven mountains". Many of the extra-municipal suburbs are on islands. Bergen is the administrative centre of Vestland county. The city consists of eight boroughs: Arna, Norway, Arna, Bergenhus, Fana, Fyllingsdalen, Laksevåg, Ytrebygda, Årstad, Bergen, Årstad, and Åsane. Trading in Bergen may have started as early as the 1020s. According to tradition, the city was founded in 1070 by King Olaf III of Norway, Olav Kyrre and was named Bjørgvin, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Cabanis
Jean Louis Cabanis (8 March 1816 – 20 February 1906) was a German ornithologist. Cabanis was born in Berlin to an old Huguenot family who had moved from France. Little is known of his early life. He studied at the University of Berlin from 1835 to 1839, and then travelled to North America, returning in 1841 with a large natural history collection. He was assistant and later director of the Natural History Museum of Berlin (which was at the time the Berlin University Museum), taking over from Martin Lichtenstein. He founded the ''Journal für Ornithologie'' in 1853, editing it for the next forty-one years, when he was succeeded by his son-in-law Anton Reichenow. He died in Friedrichshagen. A number of birds are named after him, including Cabanis's bunting ''Emberiza cabanisi'', Cabanis's spinetail ''Synallaxis cabanisi'', Azure-rumped tanager The azure-rumped tanager or Cabanis's tanager (''Poecilostreptus cabanisi'') is a species of bird in the family Thraupidae. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Wilhelm Steller
Georg Wilhelm Steller (10 March 1709 – 14 November 1746) was a German botanist, zoologist, physician and explorer, who worked in Russia and is considered a pioneer of Alaskan natural history.Evans, Howard Ensign. Edward Osborne Wilson (col.) ''The Man who Loved Wasps: A Howard Ensign Evans Reader''. in: Evans, Mary Alice. Big Earth Publishing, 2005. pp. 169. Nuttall, Mark. ''Encyclopedia of the Arctic''. Routledge, 2012. pp. 1953. Biography Steller was born in Windsheim, near Nuremberg in Germany, son to a Lutheran cantor named Johann Jakob Stöhler (after 1715, Stöller), and studied at the University of Wittenberg. He then traveled to Russia as a physician on a troop ship returning home with the wounded. He arrived in Russia in November 1734. He met the naturalist Daniel Gottlieb Messerschmidt (1685–1735) at the Imperial Academy of Sciences. Two years after Messerschmidt's death, Steller married his widow and acquired notes from his travels in Siberia not handed over to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated territories of the United States, unincorporated territory of the United States. It is located in the northeast Caribbean Sea, approximately southeast of Miami, Florida, between the Dominican Republic and the United States Virgin Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands, and includes the eponymous main island and several smaller islands, such as Isla de Mona, Mona, Culebra, Puerto Rico, Culebra, and Vieques, Puerto Rico, Vieques. It has roughly 3.2 million residents, and its Capital city, capital and Municipalities of Puerto Rico, most populous city is San Juan, Puerto Rico, San Juan. Spanish language, Spanish and English language, English are the official languages of the executive branch of government, though Spanish predominates. Puerto Rico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpetology
Herpetology (from Greek ἑρπετόν ''herpetón'', meaning "reptile" or "creeping animal") is the branch of zoology concerned with the study of amphibians (including frogs, toads, salamanders, newts, and caecilians (gymnophiona)) and reptiles (including snakes, lizards, amphisbaenids, turtles, terrapins, tortoises, crocodilians, and the tuataras). Birds, which are cladistically included within Reptilia, are traditionally excluded here; the scientific study of birds is the subject of ornithology. Thus, the definition of herpetology can be more precisely stated as the study of ectothermic (cold-blooded) tetrapods. Under this definition "herps" (or sometimes "herptiles" or "herpetofauna") exclude fish, but it is not uncommon for herpetological and ichthyological scientific societies to collaborate. Examples include publishing joint journals and holding conferences in order to foster the exchange of ideas between the fields, as the American Society of Ichthyologists and He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibia
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramatic decl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fur Seal
Fur seals are any of nine species of pinnipeds belonging to the subfamily Arctocephalinae in the family '' Otariidae''. They are much more closely related to sea lions than true seals, and share with them external ears (pinnae), relatively long and muscular foreflippers, and the ability to walk on all fours. They are marked by their dense underfur, which made them a long-time object of commercial hunting. Eight species belong to the genus '' Arctocephalus'' and are found primarily in the Southern Hemisphere, while a ninth species also sometimes called fur seal, the Northern fur seal (''Callorhinus ursinus''), belongs to a different genus and inhabits the North Pacific. The fur seals in ''Arctocephalus'' are more closely related to sea lions than they are to the Northern fur seal, but all three groups are more closely related to each other than they are to true seals. Taxonomy Fur seals and sea lions make up the family Otariidae. Along with the Phocidae and Odobodenidae, otta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
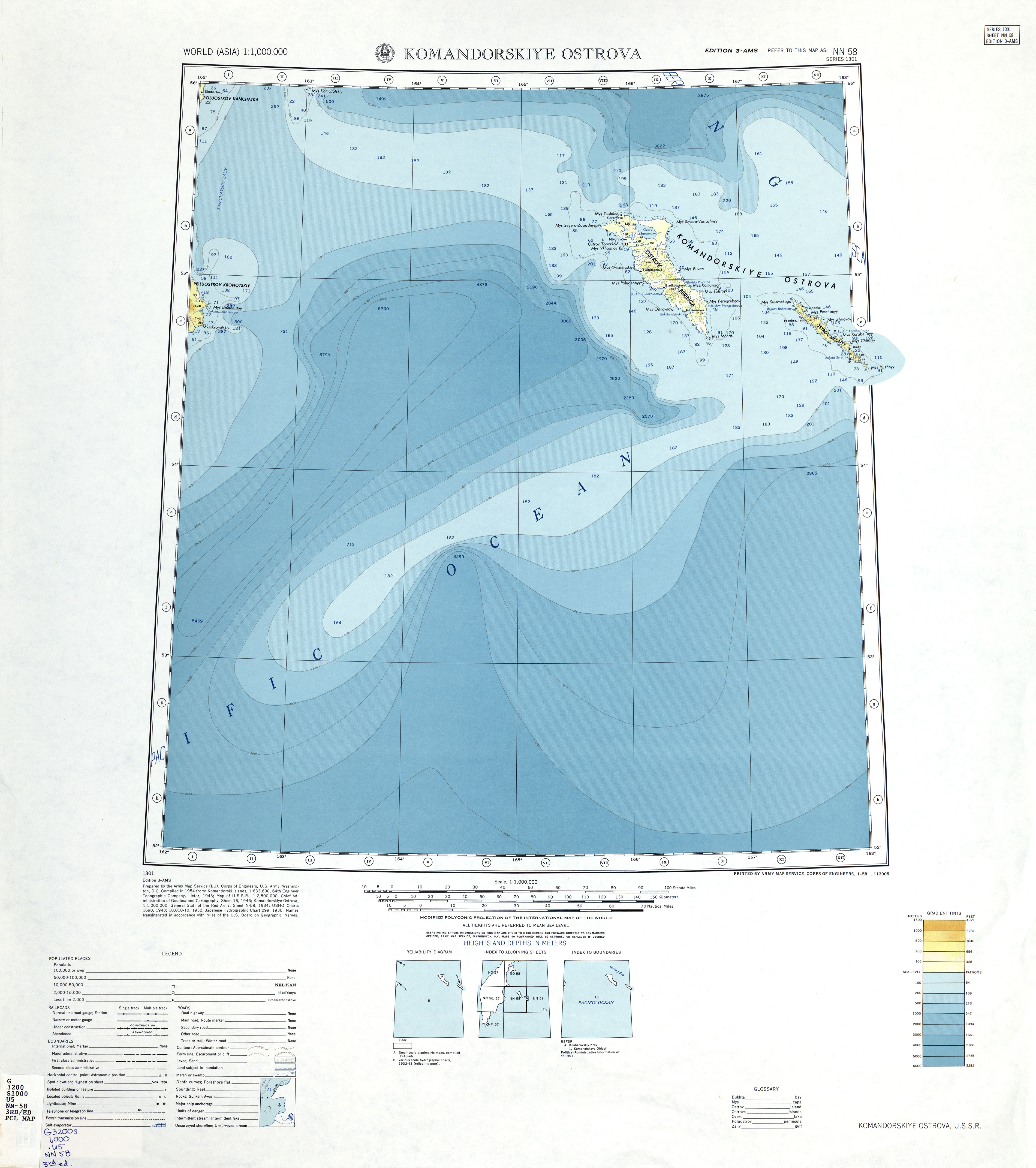
Commander Islands
The Commander Islands, Komandorski Islands, or Komandorskie Islands (russian: Командо́рские острова́, ''Komandorskiye ostrova'') are a series of treeless, sparsely populated Russian islands in the Bering Sea located about east of the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Russian Far East. The islands consist of Bering Island ( by ), Medny Island ( by ) and fifteen smaller ones (islets and rocks), the largest of which are ''Tufted Puffin Rock (Kamen Toporkov'' or ''Ostrov Toporkov)'', , and Kamen Ariy, which are between and west of the only settlement, Nikolskoye. Administratively, they compose Aleutsky District of Kamchatka Krai in Russia. Geography The Commander Islands are the westernmost of the Aleutian Islands, most of which are part of the US state of Alaska, and are separated from the closest US island, Attu Island, and the rest of the chain by . Between the two runs the International Date Line. The relief is somewhat diverse, encompassing folded-block mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively. Immediately offshore along the Pacific coast of the peninsula runs the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench. The Kamchatka Peninsula, the Commander Islands, and the Karaginsky Island, constitute the Kamchatka Krai of the Russia, Russian Federation. The vast majority of the 322,079 inhabitants are ethnic Russians, although about 13,000 are Koryaks (2014). More than half of the population lives in Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky (179,526 in 2010) and nearby Yelizovo (38,980). The Kamchatka peninsula contains the volcanoes of Kamchatka, a World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography Politically, the peninsula forms part of Kamchatka Krai. The southern tip is called Cape Lopatka. (Lopatka is Russian for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bering Island
Bering Island (russian: о́стров Бе́ринга, ''ostrov Beringa'') is located off the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Bering Sea. Description At long by wide, it is the largest and westernmost of the Commander Islands, with an area of . Most of Bering Island and several of the smaller islands in their entirety are now part of the Komandorsky Zapovednik nature preserve. Bering Island is treeless, desolate and experiences severe weather, including high winds, persistent fog and earthquakes. It had no year-round human residents until roughly 1826. Now, the village of Nikolskoye is home to 800 people, roughly three hundred of them identifying as Aleuts. The island's small population is involved mostly in fishing. off Bering Island's western shore lies small Toporkov Island (Ostrov Toporkov) . It is a round island with a diameter of . History In 1741 Commander Vitus Bering, sailing in ''Svyatoy Pyotr'' (''St. Peter'') for the Russian Navy, was shipwrecked and died o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)

.jpg)