|
Leonardian
In the geologic timescale, the Kungurian is an age or stage of the Permian. It is the latest or upper of four subdivisions of the Cisuralian Epoch or Series. The Kungurian lasted between and million years ago (Ma). It was preceded by the Artinskian and followed by the Roadian. It corresponds roughly to the Leonardian Stage, covering the span from 280 to 270.6 ± 0.7 Ma in the North American system. Stratigraphy The Kungurian is named after the Russian city of Kungur in Perm Krai. The stage was introduced into scientific literature by Russian geologist Alexandr Antonovich Stukenberg (Alexander Stuckenberg) in 1890.; 2002: ''Progress report on the base of the Artinskian and base of the Kungurian by the Cisuralian Working Group'', Permophiles 41: pp 13–16. The base of the Kungurian Stage is defined as the place in the stratigraphic record where fossils of conodont species ''Neostreptognathodus pnevi'' and ''Neostreptognathodus exculptus'' first appear. As of 2009, ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kungurian
In the geologic timescale, the Kungurian is an age or stage of the Permian. It is the latest or upper of four subdivisions of the Cisuralian Epoch or Series. The Kungurian lasted between and million years ago (Ma). It was preceded by the Artinskian and followed by the Roadian. It corresponds roughly to the Leonardian Stage, covering the span from 280 to 270.6 ± 0.7 Ma in the North American system. Stratigraphy The Kungurian is named after the Russian city of Kungur in Perm Krai. The stage was introduced into scientific literature by Russian geologist Alexandr Antonovich Stukenberg (Alexander Stuckenberg) in 1890.; 2002: ''Progress report on the base of the Artinskian and base of the Kungurian by the Cisuralian Working Group'', Permophiles 41: pp 13–16. The base of the Kungurian Stage is defined as the place in the stratigraphic record where fossils of conodont species ''Neostreptognathodus pnevi'' and ''Neostreptognathodus exculptus'' first appear. As of 2009, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian Geochronology
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids (reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their amphibian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
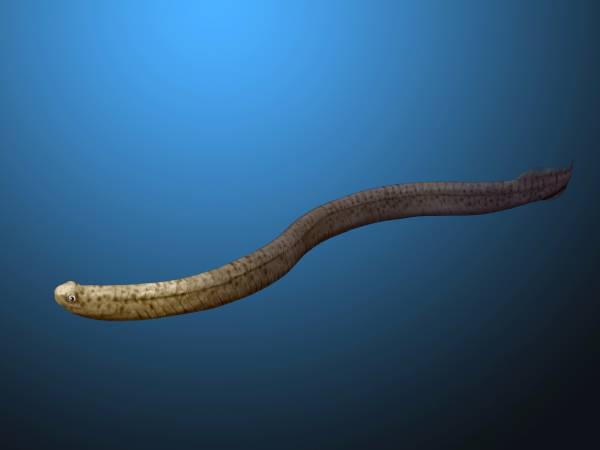
Neostreptognathodus
''Neostreptognathodus'' is an extinct genus of conodonts from the Cisuralian (Early Permian). Use in stratigraphy The top of the Artinskian (the base of the Kungurian In the geologic timescale, the Kungurian is an age or stage of the Permian. It is the latest or upper of four subdivisions of the Cisuralian Epoch or Series. The Kungurian lasted between and million years ago (Ma). It was preceded by the Artin ...) stage is defined as the place in the stratigraphic record where fossils of conodont species ''Neostreptognathodus pnevi'' and ''Neostreptognathodus exculptus'' first appear. ''Neostreptognathodus costatus'' is from the Early Permian Amushan Formation in Xiwuzhumuqin Qi, Inner Mongolia, in China. References External links * * Conodont genera Permian conodonts Cisuralian animals {{conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Series (stratigraphy)
Series are subdivisions of rock layers based on the age of the rock and formally defined by international conventions of the geological timescale. A series is therefore a sequence of strata defining a chronostratigraphic unit. Series are subdivisions of systems and are themselves divided into stages. Series is a term defining a unit of rock layers formed during a certain interval of time (a chronostratigraphic unit); it is equivalent (but not synonymous) to the term ''geological epoch'' (see epoch criteria) which defines the interval of time itself, although the two words are sometimes confused in informal literature. Series in the geological timescale The geological timescale has all systems in the Phanerozoic eonothem subdivided into series. Some of these have their own names, in other cases a system is simply divided into a Lower, Middle and Upper series. The Cretaceous system is for example divided into the Upper Cretaceous and Lower Cretaceous series; while the Carbonifero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conodont
Conodonts (Greek ''kōnos'', "cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil evidence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biozone
In biostratigraphy, biostratigraphic units or biozones are intervals of geological strata that are defined on the basis of their characteristic fossil taxa, as opposed to a lithostratigraphic unit which is defined by the lithological properties of the surrounding rock. A biostratigraphic unit is defined by the zone fossils it contains. These may be a single taxon or combinations of taxa if the taxa are relatively abundant, or variations in features related to the distribution of fossils. The same strata may be zoned differently depending on the diagnostic criteria or fossil group chosen, so there may be several, sometimes overlapping, biostratigraphic units in the same interval. Like lithostratigraphic units, biozones must have a type section designated as a stratotype. These stratotypes are named according to the typical taxon (or taxa) that are found in that particular biozone. The boundary of two distinct biostratigraphic units is called a ''biohorizon''. Biozones can be furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalupian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSSP
A Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) is an internationally agreed upon reference point on a stratigraphic section which defines the lower boundary of a stage on the geologic time scale. The effort to define GSSPs is conducted by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, a part of the International Union of Geological Sciences. Most, but not all, GSSPs are based on paleontological changes. Hence GSSPs are usually described in terms of transitions between different faunal stages, though far more faunal stages have been described than GSSPs. The GSSP definition effort commenced in 1977. As of 2022, 77 of the 101 stages that need a GSSP have a ratified GSSP. Rules A geologic section has to fulfill a set of criteria to be adapted as a GSSP by the ICS. The following list summarizes the criteria: * A GSSP has to define the lower boundary of a geologic stage. * The lower boundary has to be defined using a primary marker (usually first appearance datum of a fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conodont
Conodonts (Greek ''kōnos'', "cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil evidence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perm Krai
Perm Krai (russian: Пе́рмский край, r=Permsky kray, p=ˈpʲɛrmskʲɪj ˈkraj, ''Permsky krai'', , ''Perem lador'') is a federal subject of Russia (a krai) that came into existence on December 1, 2005 as a result of the 2004 referendum on the merger of Perm Oblast and Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug. The city of Perm is the administrative center. The population of the krai was 2,635,276 according to the ( 2010 Census). Komi-Permyak Okrug retained its autonomous status within Perm Krai during the transitional period of 2006–2008. It also retained a budget separate from that of the krai, keeping all federal transfers. Starting in 2009, Komi-Permyak Okrug's budget became subject to the budgeting law of Perm Krai. The transitional period was implemented in part because Komi-Permyak Okrug relies heavily on federal subsidies, and an abrupt cut would have been detrimental to its economy. Geography Perm Krai is located in the east of the East European Plain and the weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kungur
Kungur (russian: Кунгу́р) is a town in the southeast of Perm Krai, Russia, located in the Ural Mountains at the confluence of the rivers Iren and Shakva with the Sylva (Kama's basin). Population: 64,800 (1959); 36,000 (1939). History Kungur was founded above the Iren's mouth on the banks of the Kungurka in 1648. In 1662, it was burnt by Bashkirs. In 1663, it was rebuilt as a fortress on the place of the village of Mysovskoye. In the beginning of the 18th century, leather and footwear industries started to develop here, and in 1724, a tannery was built. By the mid-18th century, Kungur became one of the most populated areas in the Urals. In 1759, Perm administration of mining plants was moved to Kungur. By the end of the 18th century, Kungur is an important transit trade center of the Siberian road, as well as the center of leather manufacture in Perm Governorate. Kungur rope and linseed oil were widely known. In 1774, the town withstood a siege by Yemelyan Pugac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |