|
Left Gastric
In human anatomy, the left gastric artery arises from the celiac artery and runs along the superior portion of the lesser curvature of the stomach. Branches also supply the lower esophagus. The left gastric artery anastomoses with the right gastric artery, which runs right to left. Important to note is that the esophageal branch of the left gastric artery ascends and passes through the esophageal hiatus. Clinical significance In terms of disease, the left gastric artery may be involved in peptic ulcer disease: if an ulcer erodes through the stomach mucosa into a branch of the artery, this can cause massive blood loss into the stomach, which may result in such symptoms as hematemesis or melaena. Additional images File:Stomach blood supply.svg, Blood supply to the stomach: left and right gastric artery, left and right gastro-omental artery and short gastric artery The short gastric arteries consist of from five to seven small branches, which arise from the end of the splenic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celiac Artery
The celiac () artery (also spelled ''coeliac''), also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in humans, it is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta (the others are the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries). Structure The celiac artery is the first major branch of the descending abdominal aorta, branching at a 90° angle. This occurs just below the crus of the diaphragm. This is around the first lumbar vertebra. There are three main divisions of the celiac artery, and each in turn has its own named branches: The celiac artery may also give rise to the inferior phrenic arteries. Function The celiac artery supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, stomach, abdominal esophagus, spleen, and the superior half of both the duodenum and the pancreas. These structures correspond to the embryonic foregut. (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Gastrointestinal Bleed
Upper gastrointestinal bleeding is gastrointestinal bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract, commonly defined as bleeding arising from the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum. Blood may be observed in vomit or in altered form as black stool. Depending on the amount of the blood loss, symptoms may include shock. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding can be caused by peptic ulcers, gastric erosions, esophageal varices, and rarer causes such as gastric cancer. The initial assessment includes measurement of the blood pressure and heart rate, as well as blood tests to determine the hemoglobin. Significant upper gastrointestinal bleeding is considered a medical emergency. Fluid replacement, as well as blood transfusion, may be required. Endoscopy is recommended within 24 hours and bleeding can be stopped by various techniques. Proton pump inhibitors are often used. Tranexamic acid may also be useful. Procedures (such as TIPS for variceal bleeding) may be used. Recurrent or refractory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Gastric Artery
The short gastric arteries consist of from five to seven small branches, which arise from the end of the splenic artery, and from its terminal divisions. They pass from left to right, between the layers of the gastrolienal ligament, and are distributed to the greater curvature of the stomach, anastomosing with branches of the left gastric and left gastroepiploic arteries. Unlike the gastroepiploics and the left and right gastric arteries, the short gastric arteries have poor anastomoses if the splenic artery is blocked. Structure The short gastric arteries arise from the splenic artery. They run along part of the greater curvature of the stomach. Function The short gastric arteries supply the fundus of the stomach on the side of the greater curvature of the stomach The curvatures of the stomach refer to the greater and lesser curvatures. The greater curvature of the stomach is four or five times as long as the lesser curvature. Greater curvature The greater curva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Gastro-omental Artery
The right gastroepiploic artery (or right gastro-omental artery) is one of the two terminal branches of the gastroduodenal artery. It runs from right to left along the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, anastomosing with the left gastroepiploic artery, a branch of the splenic artery. Except at the pylorus where it is in contact with the stomach, it lies about a finger's breadth from the greater curvature. Branches This vessel gives off numerous branches: * "gastric branches": ascend to supply both surfaces of the stomach. * "omental branches": descend to supply the greater omentum and anastomose with branches of the middle colic. Use in coronary artery surgery The right gastroepiploic artery was first used as a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) in 1984 by John Pym and colleagues at Queen's University. It has become an accepted alternative conduit, and is particularly useful in patients who do not have suitable saphenous veins to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Gastro-omental Artery
The left gastroepiploic artery (or left gastro-omental artery), the largest branch of the splenic artery, runs from left to right about a finger's breadth or more from the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, and anastomoses with the right gastroepiploic (a branch of the right gastro-duodenal artery originating from the hepatic branch of the coeliac trunk). In its course it distributes: * "Gastric branches": several ascending branches to both surfaces of the stomach; * "Omental branches": descend to supply the greater omentum and anastomose with branches of the middle colic. Additional images File:Gray533.png, Branches of the celiac artery The celiac () artery (also spelled ''coeliac''), also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in .... References External links * - "Stomach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melaena
Melena or melaena refers to the dark black, tarry feces that are associated with upper gastrointestinal bleeding. The black color and characteristic strong odor are caused by hemoglobin in the blood being altered by digestive enzymes and intestinal bacteria. Iron supplements may cause a grayish-black stool that should be distinguished from melena, as should black coloration caused by a number of medications, such as bismuth subsalicylate (the active ingredient in Pepto-Bismol), or by foods such as beetroot, black liquorice, or blueberries. Causes The most common cause of melena is peptic ulcer disease. However, any bleeding within the upper gastrointestinal tract or the ascending colon can lead to melena. Melena may also be a complication of anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin. Causes of upper gastrointestinal bleeding that may result in melena include malignant tumors affecting the esophagus, stomach or small intestine, hemorrhagic blood diseases, such as thrombocytop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematemesis
Hematemesis is the vomiting of blood. It is always an important sign. It can be confused with hemoptysis (coughing up blood) or epistaxis (nosebleed), which are more common. The source is generally the upper gastrointestinal tract, typically above the suspensory muscle of duodenum. It may be caused by ulcers, tumors of the stomach or esophagus, varices, prolonged and vigorous retching, gastroenteritis, ingested blood (from bleeding in the mouth, nose, or throat), or certain drugs. Hematemesis is treated as a medical emergency, with treatments based on the amount of blood loss. Investigations include endoscopy. Any blood loss may be corrected with intravenous fluids and blood transfusions. Patients may need to avoid taking anything by mouth. Definition Hematemesis is the vomiting of blood. This is usually vomit that contains bright red blood. Coffee ground vomiting is similar to hematemesis, but is distinct in not involving bright red blood. Hematemesis is always an import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pain or pains in the body. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or abnormal physiological state that may be detected during a physical examination, examining the patient history, or diagnostic procedure. These signs are visible or otherwise detectable such as a rash or bruise. Medical signs, along with symptoms, assist in formulating diagnostic hypothesis. Examples of signs include elevated blood pressure, nail clubbing of the fingernails or toenails, staggering gait, and arcus senilis and arcus juvenilis of the eyes. Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Situ
''In situ'' (; often not italicized in English) is a Latin phrase that translates literally to "on site" or "in position." It can mean "locally", "on site", "on the premises", or "in place" to describe where an event takes place and is used in many different contexts. For example, in fields such as physics, geology, chemistry, or biology, ''in situ'' may describe the way a measurement is taken, that is, in the same place the phenomenon is occurring without isolating it from other systems or altering the original conditions of the test. The opposite of ''in situ'' is ''ex situ''. Aerospace In the aerospace industry, equipment on-board aircraft must be tested ''in situ'', or in place, to confirm everything functions properly as a system. Individually, each piece may work but interference from nearby equipment may create unanticipated problems. Special test equipment is available for this ''in situ'' testing. It can also refer to repairs made to the aircraft structure or flight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
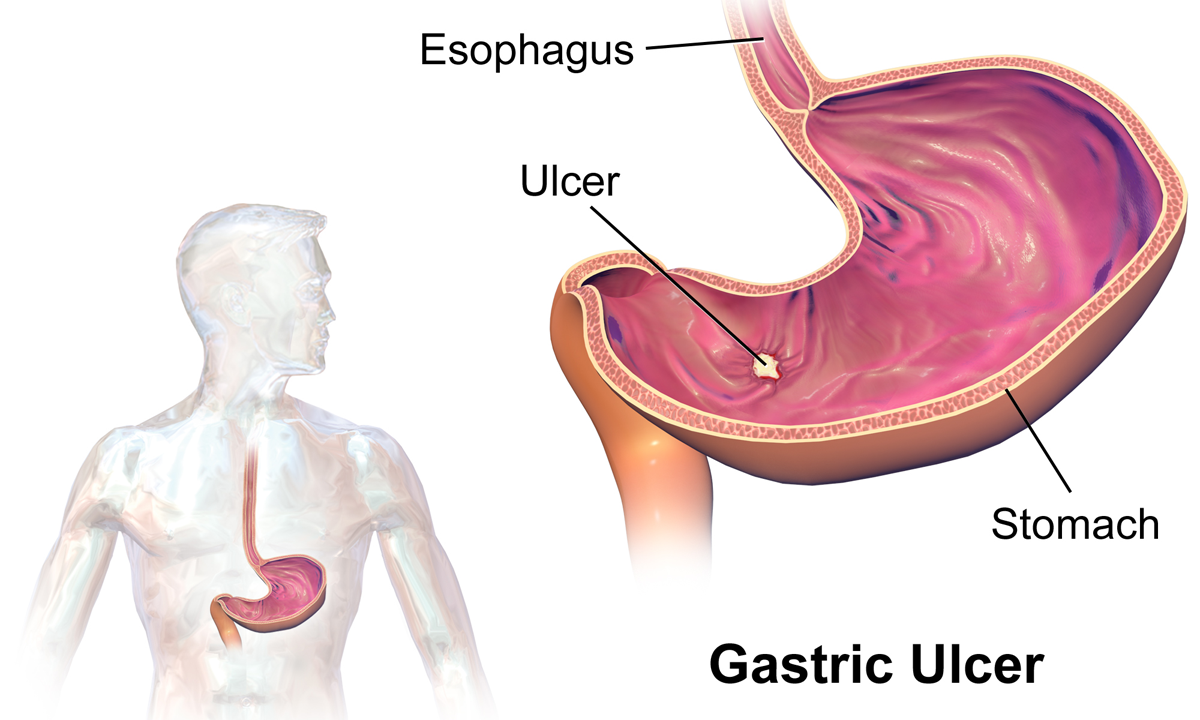
Peptic Ulcer Disease
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases. Common causes include the bacteria ''Helicobacter pylori'' and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Other, less common causes include tobacco smoking, stress as a result of other serious health conditions, Behçet's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Hiatus
In human anatomy, the esophageal hiatus is an opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus and the vagus nerve pass. Structure It is located in the right crus, one of the two tendinous structures that connect the diaphragm to the spine. Fibers of the right crus cross one another below the hiatus. It is located approximately at level of the tenth thoracic vertebra (T10) and the 8th or 9th intercostal spaces. The esophageal hiatus is situated in the muscular part of the diaphragm at the level of the tenth thoracic vertebra, and is elliptical in shape. It is placed superior, anterior, and slightly left of the aortic hiatus, and transmits the esophagus, the vagus nerve, the left inferior phrenic vessels, and some small esophageal arteries from left gastric vessels. The right crus of the diaphragm loops around forming a sling around the esophagus. Upon inspiration, this sling would constrict the esophagus, forming a functional (not anatomical) sphincter that prevents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |