|
Lecithoepitheliata
The Lecithoepitheliata are an order of rhabditophoran flatworms. They are free-living worms, found in freshwater, soil, and marine environments. However, it is still poorly known their roles in the natural food web. Description Members of the order Lecithoepitheliata are distinguished from other flatworms by the presence of four nerve cords and the fact that the ovary forms a single structure that produces both the eggs (ovocytes) and nourishing yolk cells (vitellocytes). The vitellocytes form a follicle around the ovocyte, hence the name of the group, which means "with a yolk epithelium". In most other rhabditophorans, yolk cells, where present at all, are typically formed in glands derived from the ovaries, but separate from them, called vitellaria. Other diagnostic features of this order include the presence of a sharp stylet on the end of the penis, and a simple, unbranched, intestine. The penis lacks a proper pore and is protruded through the mouth. Phylogeny The order Lec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prorhynchidae
The Lecithoepitheliata are an order of rhabditophoran flatworms. They are free-living worms, found in freshwater, soil, and marine environments. However, it is still poorly known their roles in the natural food web. Description Members of the order Lecithoepitheliata are distinguished from other flatworms by the presence of four nerve cords and the fact that the ovary forms a single structure that produces both the eggs ( ovocytes) and nourishing yolk cells (vitellocytes). The vitellocytes form a follicle around the ovocyte, hence the name of the group, which means "with a yolk epithelium". In most other rhabditophorans, yolk cells, where present at all, are typically formed in glands derived from the ovaries, but separate from them, called vitellaria. Other diagnostic features of this order include the presence of a sharp stylet on the end of the penis, and a simple, unbranched, intestine. The penis lacks a proper pore and is protruded through the mouth. Phylogeny The order Lec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoophora
Neoophora is a group of rhabditophoran flatworms with ectolecithal eggs, i.e., yolk is not present in the egg as in most animals, but rather is secreted by accessory glands called vitellaria or yolk glands. These glands have the same embryonic origin as the ovaries, but usually constitute a separate organ in adult animals. The monophyly of Neoophora is disputed, since some recent molecular studies indicated that the most basal order, Lecithoepitheliata, is more closely related to Polycladida The Polycladida represents a highly diverse clade of free-living marine flatworms. They are known from the littoral to the Sublittoral zone, sublittoral zone (extending to the deep hot vents), and many species are common from coral reefs. Only a ..., a non-neoophoran order, than to other neoophorans. This would imply that the ectolecithal condition would have evolved twice. The clade formed by all other neoophorans, excluding Lecithoepitheliata, is usually called Euneoophora. Referenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euneoophora
Trepaxonemata (from ''trepa''-, spiral + axoneme) is a subclass of the Platyhelminthes or flatworms.Ehlers, U. (1985). Das Phylogenetische System der Plathelminthes. Stuttgart: G. Fischer. It includes all parasitic flatworms (clade Neodermata) and several free-living species that were previously grouped in the now obsolete class Turbellaria. Therefore, it contains the majority of species in the phylum Platyhelminthes, excluding the Catenulida, and the Macrostomorpha. Description The Trepaxonemata are characterised by: * biflagellate spermatozoa * axoneme of the spermatozoa with a special type of dense core (9+“1” pattern). The axoneme in the spermatozoa of species of Trepaxonemata, also called "trepaxoneme" or "trepaxonematan axoneme" has nine peripheral doublets of microtubules as the usual 9+2 axoneme but the two central microtubules are replaced by a central core. This central core appears as a spiral when seen in longitudinal sections in transmission electron mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geocentrophora Baltica
''Geocentrophora'' is a genus of flatworms belonging to the family Prorhynchidae The Lecithoepitheliata are an order of rhabditophoran flatworms. They are free-living worms, found in freshwater, soil, and marine environments. However, it is still poorly known their roles in the natural food web. Description Members of the ord .... The species of this genus are found in Europe and Northern America. Species: * '' Geocentrophora applanata'' (Kennel, 1888) * '' Geocentrophora baltica'' (Kennel, 1883) References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4993904 Platyhelminthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnosonesimidae
Rhabditophora (from ''rhabdito''-, rhabdite + Greek -φορος ''phoros'' bearer, i.e., "rhabdite bearers") is a class of flatworms. It includes all parasitic flatworms (clade Neodermata) and most free-living species that were previously grouped in the now obsolete class Turbellaria. Therefore, it contains the majority of the species in the phylum Platyhelminthes, excluding only the catenulids, to which they appear to be the sister group. The clade Rhabditophora was originally erected by Ulrich Ehlers in 1985Ehlers, U. (1985) ''Phylogenetic relationships within the Platyhelminthes''. ''In'' S. Conway Morris; J. D. George; R. Gibson; H. M. Platt (Eds.), ''The origins and relationships of lower invertebrates''. Oxford, Clarendon Press, p. 143-158. based on morphological analyses and its monophyly was later confirmed by molecular studies. Description Rhabditophorans are characterized by the presence of lamellated rhabdites, rodlike granules secreted in the cells of the ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhabditophora
Rhabditophora (from ''rhabdito''-, rhabdite + Greek -φορος ''phoros'' bearer, i.e., "rhabdite bearers") is a class of flatworms. It includes all parasitic flatworms (clade Neodermata) and most free-living species that were previously grouped in the now obsolete class Turbellaria. Therefore, it contains the majority of the species in the phylum Platyhelminthes, excluding only the catenulids, to which they appear to be the sister group. The clade Rhabditophora was originally erected by Ulrich Ehlers in 1985Ehlers, U. (1985) ''Phylogenetic relationships within the Platyhelminthes''. ''In'' S. Conway Morris; J. D. George; R. Gibson; H. M. Platt (Eds.), ''The origins and relationships of lower invertebrates''. Oxford, Clarendon Press, p. 143-158. based on morphological analyses and its monophyly was later confirmed by molecular studies. Description Rhabditophorans are characterized by the presence of lamellated rhabdites, rodlike granules secreted in the cells of the epidermis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platyhelminthes
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek language, Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") are a Phylum (biology), phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, Segmentation (biology), unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates (having no coelom, body cavity), and have no specialized circulatory system, circulatory and respiratory system, respiratory organ (anatomy), organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion (intake of nutrients) and egestion (removal of undigested wastes); as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously. In traditional medicinal texts, Platyhelminthes are divided into Turbellaria, which are mostly non-parasitic animals such as planarians, and three entirely p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
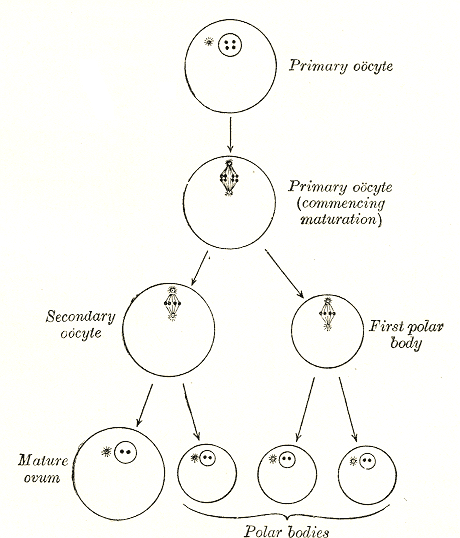
Ovocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yolk
Among animals which produce eggs, the yolk (; also known as the vitellus) is the nutrient-bearing portion of the egg whose primary function is to supply food for the development of the embryo. Some types of egg contain no yolk, for example because they are laid in situations where the food supply is sufficient (such as in the body of the host of a parasitoid) or because the embryo develops in the parent's body, which supplies the food, usually through a placenta. Reproductive systems in which the mother's body supplies the embryo directly are said to be matrotrophic; those in which the embryo is supplied by yolk are said to be lecithotrophic. In many species, such as all birds, and most reptiles and insects, the yolk takes the form of a special storage organ constructed in the reproductive tract of the mother. In many other animals, especially very small species such as some fish and invertebrates, the yolk material is not in a special organ, but inside the egg cell. As sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylet (anatomy)
A stylet is a hard, sharp, anatomical structure found in some invertebrates. For example, the word ''stylet'' or stomatostyle is used for the primitive piercing mouthparts of some nematodes and some nemerteans. In these groups the stylet is a hardened protrusible opening to the stomach. These stylets are adapted for the piercing of cell walls and usually function by providing the operative organism with access to the nutrients contained within the prey cell. The mouthparts of tardigrades, diptera and aphid Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white woolly aphids. A t ...s are also called stylets. In octopodes, the stylets are internal, needle-like bent rods within the mantle, the vestigial remnants of an external shell. References Nematode anatomy {{Animal-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycladida
The Polycladida represents a highly diverse clade of free-living marine flatworms. They are known from the littoral to the Sublittoral zone, sublittoral zone (extending to the deep hot vents), and many species are common from coral reefs. Only a few species are found in freshwater habitats. Description Polyclads range from to in length with a flattened, roughly oval, body shape and, in many cases, a pair of short tentacles on the head. They are distinguished from other related animals by the presence of a folded pharynx, an elongated intestine with numerous complex diverticulum, diverticula, and multiple ocellus, ocelli. The etymology of the order name ''Polycladida'' corresponds to the two ancient Greek words (), meaning "numerous", and (), meaning "branch". It refers to the ramified shape of the intestine in these flatworms. Most polyclads hide away from direct light. However, some of the brightly colored species often are active during the day. With their flamboyant col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |