|
Lawlor Island
Lawlor Island or Lawlor's Island is a small island near the mouth of Halifax Harbour in Eastern Passage, Nova Scotia, Canada. It was the site of a major quarantine facility for immigration from 1866 to 1938 and is today owned by the Nova Scotia Department of Natural Resources as part of the McNabs Island provincial park reserve. Geography Measuring approximately 55 hectares (136 acres), it is located opposite MacCormacks Beach in Eastern Passage, just east of McNabs Island in the Halifax Regional Municipality. The island is covered with heavy grown woodland and serves as the protected home of deer and osprey. History The Mi'kmaq people occupied the island seasonally in the summer and knew the area around the island as "Tuitnuik", meaning little passage, because of the narrow band of water between the island and the mainland. Following the foundation of Halifax in 1749, Captain Thomas Bloss was granted an island in Halifax Harbour on September 30, 1750 which later bore his name. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halifax Harbour
Halifax Harbour is a large natural harbour on the Atlantic coast of Nova Scotia, Canada, located in the Halifax Regional Municipality. Halifax largely owes its existence to the harbour, being one of the largest and deepest ice-free natural harbours in the world. Before Confederation it was one of the most important commercial ports on the Atlantic seaboard. In 1917, it was the site of the world's largest man-made accidental explosion, when the blew up in the Halifax Explosion of December 6. The harbour was formed by a drowned glacial valley which succumbed to sea level rise after glaciation. The Sackville River now empties into the upper end of the harbour in Bedford Basin. The harbour also includes the Northwest Arm and The Narrows, a constricted passage to Bedford Basin Halifax Harbour has been polluted as a result of two centuries of direct raw sewage discharge into its waters. Health concerns in the 1990s caused the shut-down of all harbour beaches. The Harbour Soluti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North End (Halifax)
The North End of Halifax is a neighbourhood of Halifax, Nova Scotia occupying the northern part of Halifax Peninsula immediately north of Downtown Halifax. History Prior to European colonization, the Mi'kmaq inhabited the land throughout Atlantic Canada and Northern Maine. The North End of Halifax began as an agricultural expansion north from central Halifax as African American and German Foreign Protestant settlers arrived in the province. It became the focus of industry in Halifax with the construction of the Nova Scotia Railway in the 1850s which located its terminal in the North End. Factories such as the Nova Scotia Cotton Manufacturing Company, Hillis & Sons Foundry, and the Acadia Sugar Refinery, made the North End the focus of manufacturing in Halifax. Railway growth intensified with the extension of railways further into the North End and construction of the North Street Station in 1878, the largest station east of Montreal. Wharves warehouses lined the waterfront, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Halifax, Nova Scotia
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime History Of Canada
Maritime may refer to: Geography * Maritime Alps, a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps * Maritime Region, a region in Togo * Maritime Southeast Asia * The Maritimes, the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island * Maritime County, former county of Poland, existing from 1927 to 1939, and from 1945 to 1951 * Neustadt District, Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia, known from 1939 to 1942 as ''Maritime District'', a former district of Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia, Nazi Germany, from 1939 to 1945 * The Maritime Republics, thalassocratic city-states on the Italian peninsula during the Middle Ages Museums * Maritime Museum (Belize) * Maritime Museum (Macau), China * Maritime Museum (Malaysia) * Maritime Museum (Stockholm), Sweden Music * ''Maritime'' (album), a 2005 album by Minotaur Shock * Maritime (band), an American indie pop group * "The Maritimes" (song), a song on the 2005 album ''Boy-Cott-In the Industry'' by Classified * "Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
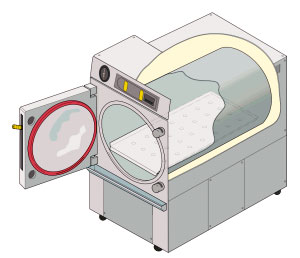
Autoclave
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing of composites. Many autoclaves are used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to pressurized saturated steam at for around 30-60 minutes at a pressure of 15 psi (103 kPa or 1.02 atm) depending on the size of the load and the contents. The autoclave was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, although a precursor known as the steam digester was created by Denis Papin in 1679. The name comes from Greek ''auto-'', ultimately meaning self, and Latin ''clavis'' meaning key, thus a self-locking device. Uses Sterilization au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of Russia since the latter half of the 16th century, after the Russians conquered lands east of the Ural Mountains. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to merely one-fifth of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk and Omsk are the largest cities in the region. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic region and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia extends eastwards from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. The river Yenisey divides Siberia into two parts, Western and Eastern. Siberia stretches southwards from the Arctic Ocean to the hills of nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grosse Isle, Quebec
Grosse Isle (french: Grosse Île, "big island") is an island located in the St. Lawrence River in Quebec, Canada. It is one of the islands of the 21-island Isle-aux-Grues archipelago. It is part of the municipality of Saint-Antoine-de-l'Isle-aux-Grues, located in the Chaudière-Appalaches region of the province. Also known as Grosse Isle and the Irish Memorial National Historic Site, the island was the site of an immigration depot which housed predominantly Irish immigrants coming to Canada to escape the Great Famine of 1845–1849. In 1832, the Lower Canadian Government had previously set up this depot to contain an earlier cholera epidemic that was believed to be caused by the large influx of European immigrants, and the station was reopened in the mid-19th century to accommodate Irish immigrants who had contracted typhus during their voyages. Thousands of Irish were quarantined on Grosse Isle from 1832 to 1848. It is believed that over 3,000A. CharbonneauParks Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Montizambert
Frederick Montizambert (February 3, 1843 – November 2, 1929) was a Canadian physician and civil servant. He was the first Director General of Public Health in Canada. Born in Quebec City, Canada East, the son of Edward Lewis Montizambert and Lucy Bowen, Montizambert was a descendant of Pierre Boucher and his grandfather was Edward Bowen. Montizambert was educated at the High School of Montreal and at Upper Canada College from 1856 to 1859. He studied medicine at Université Laval from 1859 to 1861 and then studied at the University of Edinburgh for three years receiving his MD in 1865. He returned to Quebec in 1865 and married Mary Jane Walker, the daughter of William Walker who was a member of the Legislative Council of Quebec from 1842 to 1863. He was not interested in private practice but rather worked in public health as the medical director at the Grosse Isle quarantine station. Starting in 1866, he held the post for thirty years. In 1894, he was also appointed to be supe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratique
Pratique is the license given to a ship to enter a port, that indicates to local authorities (on assurance from the captain) that it is free from contagious disease. The clearance granted is commonly referred to as ''free pratique''. A ship can signal a request for ''pratique'' by flying a solid yellow square-shaped flag. This yellow flag is the Q flag in the set of international maritime signal flags International maritime signal flags are various flags used to communicate with ships. The principal system of flags and associated codes is the International Code of Signals. Various navies have flag systems with additional flags and codes, and .... In the event that ''free pratique'' is not granted, a vessel will be held in quarantine, according to the customs and health regulations prevailing at the port of entry, typically until a customs or biosecurity officer makes a satisfactory inspection. Since flying the Q flag involves a request for boarding by Port State Control, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doukhobor
The Doukhobours or Dukhobors (russian: духоборы / духоборцы, dukhobory / dukhobortsy; ) are a Spiritual Christian ethnoreligious group of Russian origin. They are one of many non-Orthodox ethno-confessional faiths in Russia and are often categorized as "folk-Protestants", Spiritual Christians, sectarians, and heretics. Doukhobours are pacifist Christians who lived in their own villages, rejected personal materialism, worked together, and developed a tradition of oral history, memorizing, hymn-singing, and verse. Before 1886, the Doukhobors had a series of single leaders. The origin of the Doukhobors is uncertain; they first appear in first written records from 1701, although some scholars suspect the group has earlier origins. Doukhobors reject the Russian Orthodox priesthood, the use of icons, and all associated church rituals. Doukhobors believe the Bible alone is not enough to reach divine revelation and that doctrinal conflicts can interfere with thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan. The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. Kievan Rus' arose as a state in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Tolstoy
Count Lev Nikolayevich TolstoyTolstoy pronounced his first name as , which corresponds to the romanization ''Lyov''. () (; russian: link=no, Лев Николаевич Толстой,In Tolstoy's day, his name was written as in pre-reformed Russian. ; ), usually referred to in English as Leo Tolstoy, was a Russian writer who is regarded as one of the greatest authors of all time. He received nominations for the Nobel Prize in Literature every year from 1902 to 1906 and for the Nobel Peace Prize in 1901, 1902, and 1909; the fact that he never won is a major controversy. Born to an aristocratic Russian family in 1828, Tolstoy's notable works include the novels '' War and Peace'' (1869) and '' Anna Karenina'' (1878), often cited as pinnacles of realist fiction. He first achieved literary acclaim in his twenties with his semi-autobiographical trilogy, '' Childhood'', '' Boyhood'', and ''Youth'' (1852–1856), and '' Sevastopol Sketches'' (1855), based upon his experiences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)