|
Lavr Proskuryakov
Lavr Dmitrievich Proskouriakov (18 August 1858, the village of Borisovka, Voronezh Governorate – 14 September 1926, Moscow) was one of the foremost authorities on bridge engineering and structural mechanics in the Russian empire and the early Soviet Union. Life and career Lavr Proskouriakov was born on 18 August, 1858 into a large peasant family. In 1884, he graduated from the Petersburg State Transport University, Saint-Petersburg Institute of Railway Engineers and began his career as a designer of bridges. Since 1887, he lectured at the same institute, and starting from 1896 Proskouriakov held the position of Full Professor at Moscow State University of Railway Engineering. Even the early Proskouriakov's projects for bridges across the rivers Western Bug (1885) and Sula River, Sula in the Ukrainian city of Romny (1887) attracted attention by their novelty and ingenuity. The drawings of those bridges were published by Professor L.F. Nikolai, the head of the bridge faculty at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavr Proskuryakov
Lavr Dmitrievich Proskouriakov (18 August 1858, the village of Borisovka, Voronezh Governorate – 14 September 1926, Moscow) was one of the foremost authorities on bridge engineering and structural mechanics in the Russian empire and the early Soviet Union. Life and career Lavr Proskouriakov was born on 18 August, 1858 into a large peasant family. In 1884, he graduated from the Petersburg State Transport University, Saint-Petersburg Institute of Railway Engineers and began his career as a designer of bridges. Since 1887, he lectured at the same institute, and starting from 1896 Proskouriakov held the position of Full Professor at Moscow State University of Railway Engineering. Even the early Proskouriakov's projects for bridges across the rivers Western Bug (1885) and Sula River, Sula in the Ukrainian city of Romny (1887) attracted attention by their novelty and ingenuity. The drawings of those bridges were published by Professor L.F. Nikolai, the head of the bridge faculty at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Bridge Over Yenissey River
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Belelubsky
Nikolai Apollonovich Belelubsky (russian: Никола́й Аполло́нович Белелю́бский; 1 March 3 March New Style1845, Kharkiv – August 4, 1922, Petrograd) was a distinguished Russian academic specialising in railway and civil engineering. Over the course of his life he became a member of many learned societies and the author of many papers and lectures. Early life Nikolai Belelubsky was born on 1 (13) March 1845 in Kharkiv into a noble Russian family descended from the 16th century. His family was not well off. He spent his childhood and youth in Taganrog, and graduated with a gold medal from the Taganrog Boys Gymnasium in 1862. In the same year he entered the Institute of Transport (today the St. Petersburg State Transport University), from which he graduated in 1867. Belelubsky was considered to be one of the Institute's greatest graduates. After his graduation he continued to work at the Institute as a private tutor. He developed an interest in scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage List
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the UNESCO, United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, scientific or other form of significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural heritage, cultural and natural heritage, natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to Human, humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site must be a somehow unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable and has special cultural or physical significance. For example, World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains, or wilderness areas. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humanity, and serve as evidence of our intellectual history on the planet, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 193 member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the non-governmental, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 national commissions that facilitate its global mandate. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations's International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). Its constitution establishes the agency's goals, governing structure, and operating framework. UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the Second World War, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboration and dialogue among nations. It pursues this objective t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exposition Universelle (1900)
The Exposition Universelle of 1900, better known in English as the 1900 Paris Exposition, was a world's fair held in Paris, France, from 14 April to 12 November 1900, to celebrate the achievements of the past century and to accelerate development into the next. It was held at the esplanade of Les Invalides, the Champ de Mars, the Trocadéro and at the banks of the Seine between them, with an additional section in the Bois de Vincennes, and it was visited by more than 50 million people. Many international congresses and other events were held within the framework of the Exposition, including the 1900 Summer Olympics. Many technological innovations were displayed at the Fair, including the ''Grande Roue de Paris'' ferris wheel, the '' Rue de l'Avenir'' moving sidewalk, the first ever regular passenger trolleybus line, escalators, diesel engines, electric cars, dry cell batteries, electric fire engines, talking films, the telegraphone (the first magnetic audio recorder), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuilenburg
Culemborg () is a municipality and a city in the centre of the Netherlands. The city had a population of 29,386 on 1 January 2022 and is situated just south of the Lek river. Direct train lines run from the railway station towards the cities of Utrecht and Den Bosch. History Culemborg, formerly also spelled Kuilenburg or Kuylenburgh, received city rights in 1318. For a long time, Culemborg was independent from any counties or duchies in the Netherlands. The city had gained the right of toll collection and the right of asylum: it was a so-called '''Vrijstad''' (free city). In practice, this meant that people who had fled to Culemborg from other cities (for example due to bankruptcy) could evade their creditors in Culemborg. The creditors would not be allowed entry into the city. This did not mean that criminals could escape justice in Culemborg: the city had its own justice system which could sentence criminals. In Amsterdam, the phrase '''Naar Culemborg gaan (Going to Culemborg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lek River
The Lek () is a river in the western Netherlands of some in length. It is the continuation of the Nederrijn after the Kromme Rijn branches off at the town of Wijk bij Duurstede. The main westbound waterway is hereafter called the Lek River. The Nederrijn is, itself, a distributary branch of the river Rhine. Portions of the river form the boundary between the provinces of Utrecht and Gelderland, and between Utrecht and South Holland. In Roman times, the Nederrijn flowed into the Kromme Rijn and these streams were the main outflow of the river Rhine. When the Kromme Rijn began to silt up in the Middle Ages, the Lek became the primary branch. A short distance past Wijk bij Duurstede, the river intersects with the Amsterdam-Rhine Canal, which continues south towards the Waal. A branch of this canal, the ''Lekkanaal'' (Lek Canal) is connected to the river at the city of Nieuwegein. Other major towns on its banks are Culemborg, Vianen, Schoonhoven, Nieuw-Lekkerland, Lekkerkerk and Kr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands
) , anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau") , image_map = , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands , established_title = Before independence , established_date = Spanish Netherlands , established_title2 = Act of Abjuration , established_date2 = 26 July 1581 , established_title3 = Peace of Münster , established_date3 = 30 January 1648 , established_title4 = Kingdom established , established_date4 = 16 March 1815 , established_title5 = Liberation Day (Netherlands), Liberation Day , established_date5 = 5 May 1945 , established_title6 = Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Kingdom Charter , established_date6 = 15 December 1954 , established_title7 = Dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, Caribbean reorganisation , established_date7 = 10 October 2010 , official_languages = Dutch language, Dutch , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = , languages2_type = Reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
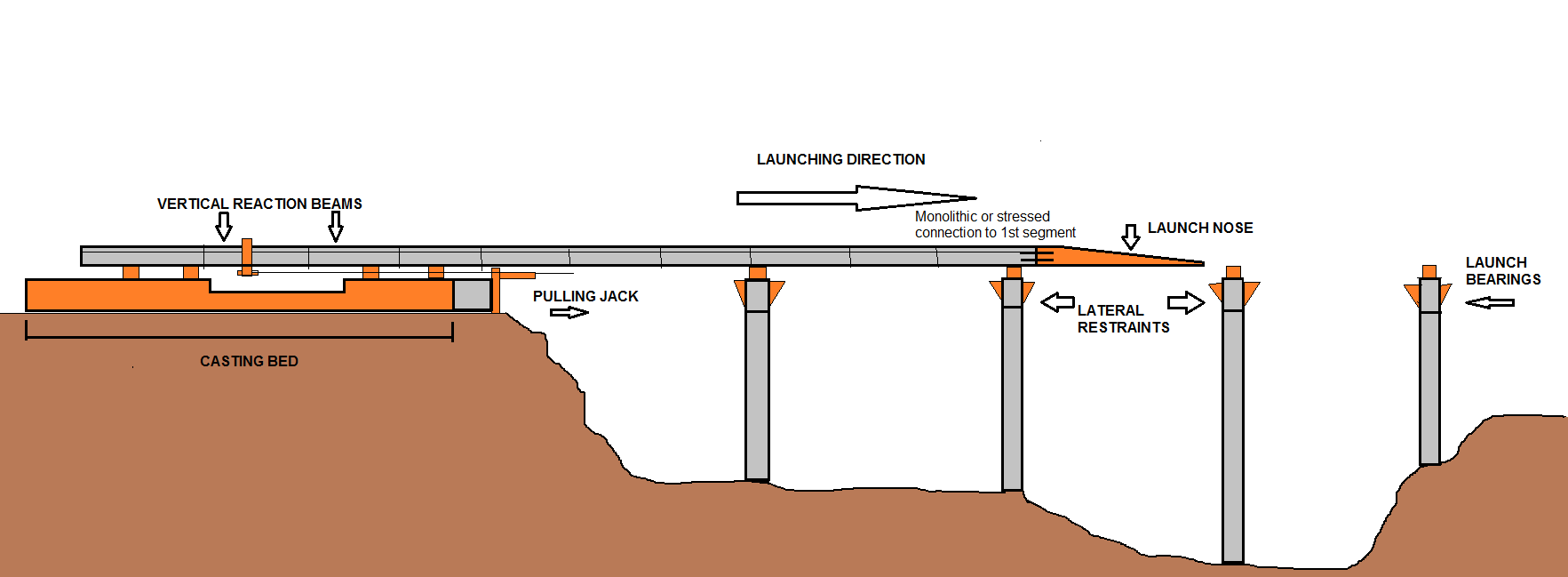
Incremental Launch
Incremental launch is a method in civil engineering of building a complete Deck (bridge), bridge deck from one abutment of the bridge only, manufacturing the Superstructure#Bridges, superstructure of the bridge by sections to the other side. In current applications, the method is highly mechanised and uses pre-stressed concrete. History The first bridge to have been incrementally launched appears to have been the Waldshut–Koblenz Rhine Bridge, a wrought iron lattice truss bridge, lattice truss railway bridge, completed in 1859. The second incrementally launched bridge was the Rhine Bridge, Kehl, Rhine Bridge, a railway bridge that spanned the Upper Rhine between Kehl, Germany and Strasbourg, France, completed in 1861 and subsequently destroyed and rebuilt on several occasions. The first incrementally launched concrete bridge was the Span (architecture), span box girder bridge over the Caroní River, completed in 1964. The second incrementally launched concrete bridge was ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influence Lines
In engineering, an influence line graphs the variation of a function (such as the shear, moment etc. felt in a structural member) at a specific point on a beam or truss caused by a unit load placed at any point along the structure.Kharagpur"Structural Analysis.pdf, Version 2 CE IIT". 7 August 2008. Accessed on 26 November 2010.Dr. Fanous, Fouad 20 April 2000. Accessed on 26 November 2010."Influence Line Method of Analysis" The Constructor. 10 February 2010. Accessed on 26 November 2010. The Foundation Coalition. 2 December 2010. Accessed on 26 November 2010.Hibbel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Wilhelm Schwedler
Johann Wilhelm Schwedler (23 June 1823, Berlin – 9 June 1894, Berlin) was a German civil engineer and civil servant who designed many bridges and public buildings and invented the Schwedler truss and the Schwedler cupola. He is an author of Schwedler's theorem, a theory defining relation between shear force and bending moment. Life and career Schwedler was the son of a cabinetmaker who died when he was still in school; his brother, already a construction supervisor, made it possible for him to finish his education at the City Trade School in 1842. After a further required examination in Latin to complete the equivalent of a lower-level '' Gymnasium'' education, he spent the next ten years training as a surveyor, studying for examinations in that and in road construction, studying for a year at the Berlin Academy of Construction, and completing the examinations to be a certified building inspector and construction supervisor. One of his practical examinations was waived afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |