|
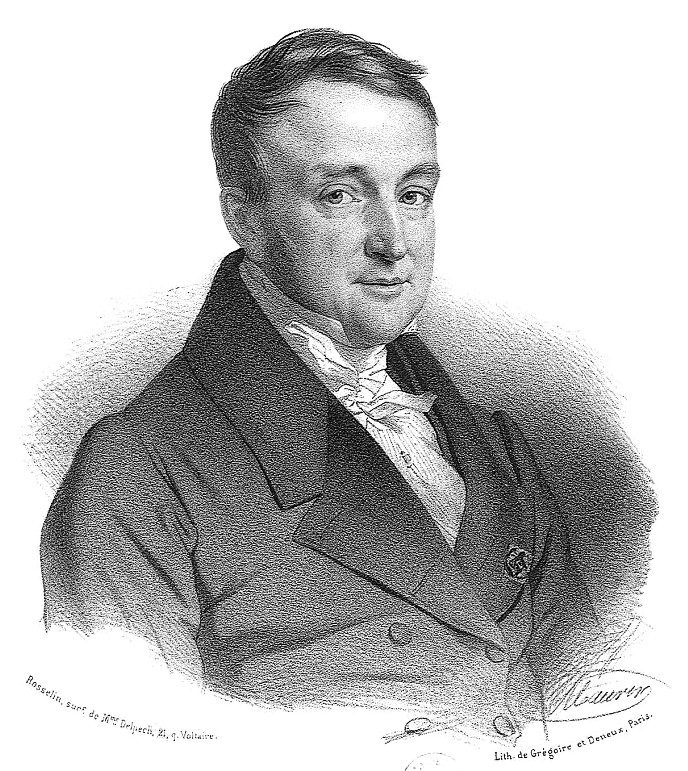
Laurent Cerise
Laurent Alexis Philibert Cerise (27 February 1807 – 5 October 1869) was a French physician born in Aosta (today part of Italy). He studied medicine at the University of Turin, obtaining his doctorate in 1828. In 1831 he relocated to Paris, where he subsequently drew a large clientele, both rich and poor. His early written articles appeared in the magazine ''L'Européen'', and due to their social and philosophical content, gained the attention of the learned society in Paris. In 1836 he published "''Le Médecin des salles d'asile''", a treatise in which he maintains that underprivileged children should have the same access to a physician as do children of the wealthy. The same year he released "''L'Exposé et examen critique du système phrénologique de Gall''" (Presentation and review of Franz Joseph Gall's phrenological system), where he disparages the limitations of purely "materialistic medicine". Another noted work of his was "''Des fonctions et des maladies nerveuses dan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurent Cerise
Laurent Alexis Philibert Cerise (27 February 1807 – 5 October 1869) was a French physician born in Aosta (today part of Italy). He studied medicine at the University of Turin, obtaining his doctorate in 1828. In 1831 he relocated to Paris, where he subsequently drew a large clientele, both rich and poor. His early written articles appeared in the magazine ''L'Européen'', and due to their social and philosophical content, gained the attention of the learned society in Paris. In 1836 he published "''Le Médecin des salles d'asile''", a treatise in which he maintains that underprivileged children should have the same access to a physician as do children of the wealthy. The same year he released "''L'Exposé et examen critique du système phrénologique de Gall''" (Presentation and review of Franz Joseph Gall's phrenological system), where he disparages the limitations of purely "materialistic medicine". Another noted work of his was "''Des fonctions et des maladies nerveuses dan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aosta
Aosta (, , ; french: Aoste , formerly ; frp, Aoûta , ''Veulla'' or ''Ouhta'' ; lat, Augusta Praetoria Salassorum; wae, Augschtal; pms, Osta) is the principal city of Aosta Valley, a bilingual region in the Italian Alps, north-northwest of Turin. It is situated near the Italian entrance of the Mont Blanc Tunnel, at the confluence of the Buthier and the Dora Baltea, and at the junction of the Great and Little St Bernard Pass routes. History Aosta was settled in proto-historic times and later became a centre of the Salassi, many of whom were killed or sold into slavery by the Romans in 25 BC. The campaign was led by Terentius Varro, who then founded the Roman colony of ''Augusta Praetoria Salassorum'', housing 3,000 retired veterans. After 11 BC Aosta became the capital of the Alpes Graies ("Grey Alps") province of the Empire. Its position at the confluence of two rivers, at the end of the Great and the Little St Bernard Pass, gave it considerable military importance, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Turin
The University of Turin (Italian language, Italian: ''Università degli Studi di Torino'', UNITO) is a public university, public research university in the city of Turin, in the Piedmont (Italy), Piedmont region of Italy. It is one of the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, oldest universities in Europe and continues to play an important role in research and training. It is steadily ranked among the top 5 Italian universities and it is ranked third for research activities in Italy, according to the latest data by ANVUR. History Overview The University of Turin was founded as a ''studium'' in 1404, under the initiative of Prince Louis of Piedmont, Ludovico di Savoia. From 1427 to 1436 the seat of the university was transferred to Chieri and Savigliano. It was closed in 1536 and reestablished by Duke Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy, Emmanuel Philibert thirty years later. It started to gain its modern shape following the model of the University of Bologna, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Joseph Gall
Franz Josef Gall (; 9 March 175822 August 1828) was a German neuroanatomist, physiologist, and pioneer in the study of the localization of mental functions in the brain. Claimed as the founder of the pseudoscience of phrenology, Gall was an early and important researcher in his fields. His contributions to the field of neuropsychology were controversial at the time and are now widely referred to as pseudoscience. However, Gall's study of phrenology helped establish psychology, contributed to the emergence of the naturalistic approach to the study of man, and played an important part in the development of evolutionist theories, anthropology, and sociology. Early life Gall was born in the village of Tiefenbronn to a wealthy Roman Catholic wool merchant. The Galls, originally a noble family from Lombardy, had been the leading family in the area for over a century. His father was the mayor of Tiefenbronn and he was one of 12 children, only 7 of whom lived to adulthood. Gall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrenology
Phrenology () is a pseudoscience which involves the measurement of bumps on the skull to predict mental traits.Wihe, J. V. (2002). "Science and Pseudoscience: A Primer in Critical Thinking." In ''Encyclopedia of Pseudoscience'', pp. 195–203. California: Skeptics Society.Hines, T. (2002). ''Pseudoscience and the Paranormal''. New York: Prometheus Books. p. 200 It is based on the concept that the brain is the organ of the mind, and that certain brain areas have localized, specific functions or modules. It was said that the brain was composed of different muscles, so those that were used more often were bigger, resulting in the different skull shapes. This led to the reasoning behind why everyone had bumps on the skull in different locations. The brain "muscles" not being used as frequently remained small and were therefore not present on the exterior of the skull. Although both of those ideas have a basis in reality, phrenology generalized beyond empirical knowledge in a way that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques-Joseph Moreau
Jacques-Joseph Moreau (3 June 1804 – 26 June 1884), nicknamed "Moreau de Tours", was a French psychiatrist and member of the Club des Hashischins. Moreau was the first physician to do systematic work on drugs' effects on the central nervous system, and to catalogue, analyze, and record his observations. Works After a long trip (1836–1840) in the Orient, he discovered the effect of hashish. He studied it in order to understand the relation between madness and dreams, which are similar deliriums, according to Moreau. He was the author of the 184''Du Hachisch et de l'aliénation mentale'' later translated into English and published as ''Hashish and Mental Illness''. He was the first doctor to publish a work about a drug and its effect on the central nervous system.Hans Bangen: ''Geschichte der medikamentösen Therapie der Schizophrenie.'' Berlin 1992, Page 22. "In an era which finally viewed the human psyche in a natural humanist terms rather than as the uncontrollable s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Baillarger
Jules Baillarger, full name Jules Gabriel François Baillarger (25 March 1809 – 31 December 1890), was a French neurologist and psychiatrist. Biography Baillarger was born in Montbazon, France. He studied medicine at the University of Paris under Jean-Étienne Dominique Esquirol (1772–1840), and while a student worked as an intern at the Charenton mental institution. In 1840 he accepted a position at the Salpêtrière, and soon after became director of a ''maison de santé'' in Ivry-sur-Seine. Among his assistants at Ivry was Louis-Victor Marcé (1828-1864). With Jacques-Joseph Moreau (1804–1884) and others, he founded the influential ''Annales médico-psychologiques'' (Medical-Psychological Annals). Contributions and theories In 1840 Baillarger was the first physician to discover that the cerebral cortex was divided into six layers of alternate white and grey laminae. His name is associated with the inner and outer bands of Baillarger, which are two layers of white ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Achille Longet
François Achille Longet (25 May 1811 – 20 April 1871) was a French anatomist and physiologist who was a native of Saint Germain-en-Laye, Yvelines. He was a student of François Magendie (1783–1855), and a pioneer in the field of experimental physiology. In 1853 he attained the chair of physiology of the Faculté de Médecine de Paris, Faculté de Médecine in Paris. One of his better known students was German physiologist Moritz Schiff (1823–1896). Longet is remembered for extensive research of the autonomic nervous system, and physiological experiments of the anterior and posterior columns of the spinal cord in regards to sensory and motor functionality. Also, he is credited with providing a detailed comprehensive description of nerve innervation of the larynx. History of Medicine With Jean P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single state in 1861, the Kingdom of Italy. Inspired by the rebellions in the 1820s and 1830s against the outcome of the Congress of Vienna, the unification process was precipitated by the Revolutions of 1848, and reached completion in 1871 after the Capture of Rome and its designation as the capital of the Kingdom of Italy. Some of the states that had been targeted for unification ('' terre irredente'') did not join the Kingdom of Italy until 1918 after Italy defeated Austria-Hungary in the First World War. For this reason, historians sometimes describe the unification period as continuing past 1871, including activities during the late 19th century and the First World War (1915–1918), and reaching completion only with the Armistice of Villa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Académie De Médecine
An academy ( Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, '' Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Aosta
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century French Physicians
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_1938.jpg)
