|
Lateral Cutaneous Nerve Of The Forearm
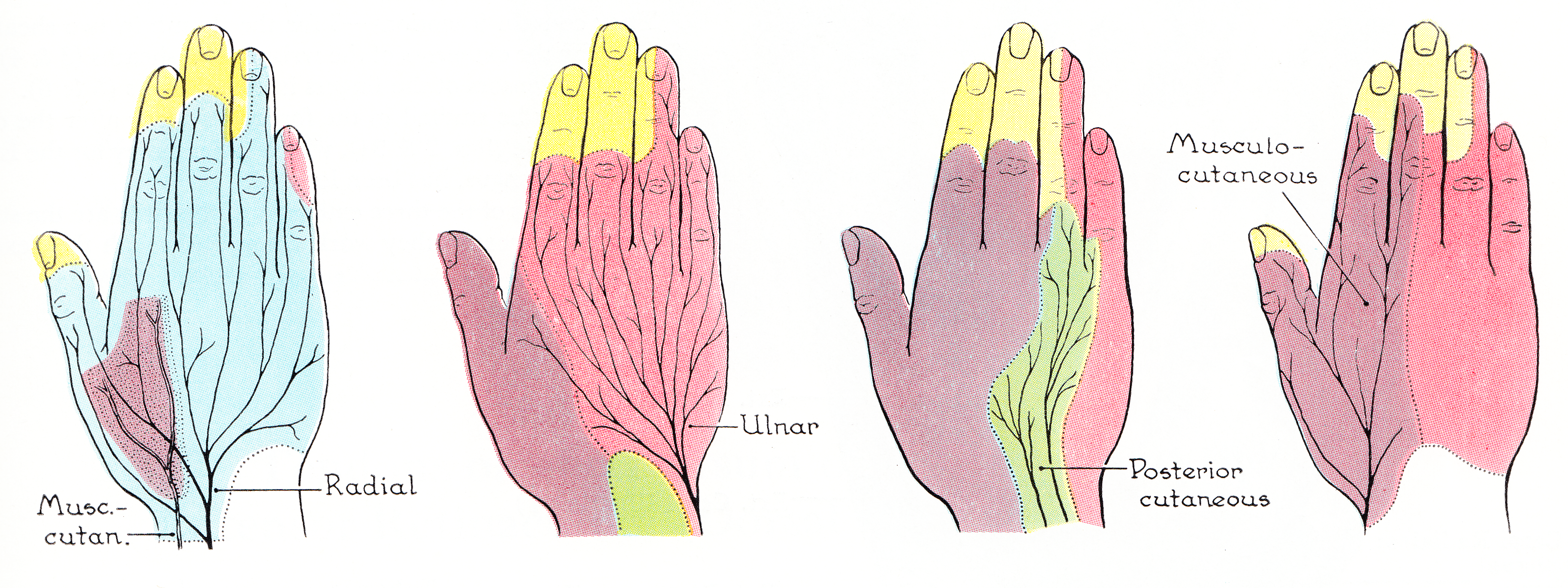
The lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve (or lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm) (branch of musculocutaneous nerve, also sometimes spelled "antebrachial") passes behind the cephalic vein, and divides, opposite the elbow-joint, into a volar and a dorsal branch. Volar branch The volar branch (ramus volaris; anterior branch) descends along the radial border of the forearm to the wrist, and supplies the skin over the lateral half of its volar surface. At the wrist-joint it is placed in front of the radial artery, and some filaments, piercing the deep fascia, accompany that vessel to the dorsal surface of the carpus. The nerve then passes downward to the ball of the thumb, where it ends in cutaneous filaments. It communicates with the superficial branch of the radial nerve, and with the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve. Dorsal branch The dorsal branch (ramus dorsalis; posterior branch) descends, along the dorsal surface of the radial side of the forearm to the wrist. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musculocutaneous Nerve
The musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, opposite the lower border of the pectoralis major, its fibers being derived from C5, C6 and C7. Structure The musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, courses through the anterior part of the arm, and terminates at 2 cm above elbow as the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm. Musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus with root value of C5 to C7 of the spinal cord. It follows the course of the third part of the axillary artery (part of the axillary artery distal to the pectoralis minor) laterally and enters the frontal aspect of the arm where it penetrates the coracobrachialis muscle. It then passes downwards and laterally between the biceps brachii (above) and the brachialis muscles (below), to the lateral side of the arm; at 2 cm above the elbow it pierces the deep fascia lateral to the tendon of the biceps brachii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb is ''pollex'' (compare ''hallux'' for big toe), and the corresponding adjective for thumb is ''pollical''. Definition Thumb and fingers The English word ''finger'' has two senses, even in the context of appendages of a single typical human hand: # Any of the five terminal members of the hand. # Any of the four terminal members of the hand, other than the thumb Linguistically, it appears that the original sense was the first of these two: (also rendered as ) was, in the inferred Proto-Indo-European language, a suffixed form of (or ), which has given rise to many Indo-European-family words (tens of them defined in English dictionaries) that involve, or stem from, concepts of fiveness. The thumb shares the following with each of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Cutaneous Nerve Of Forearm
The posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm is a nerve found in humans and other animals. It is also known as the dorsal antebrachial cutaneous nerve, the external cutaneous branch of the musculospiral nerve, and the posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve. It is a cutaneous nerve (a nerve that supplies skin) of the forearm. Origin It arises from the radial nerve in the posterior compartment of the arm, often along with the posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm. Course It perforates the lateral head of the triceps brachii muscle at the triceps' attachment to the humerus. The upper and smaller branch of the nerve passes to the front of the elbow, lying close to the cephalic vein, and supplies the skin of the lower half of the arm. The lower branch pierces the deep fascia below the insertion of the Deltoideus, and descends along the lateral side of the arm and elbow, and then along the back of the forearm to the wrist, supplying the skin in its course, and joining, near its termination, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Cutaneous Nerve Of Forearm
The medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm (medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve) branches from the medial cord of the brachial plexus. It contains axons from the ventral rami of the eighth cervical (C8) and first thoracic (T1) nerves. It gives off a branch near the axilla, which pierces the fascia and supplies the skin covering the biceps brachii, nearly as far as the elbow. The nerve then runs down the ulnar side of the arm medial to the brachial artery, pierces the deep fascia with the basilic vein, about the middle of the arm, and divides into a volar and an ulnar branch. Volar branch The ''volar branch'' (ramus volaris; anterior branch), the larger, passes usually in front of, but occasionally behind, the vena mediana cubiti (median basilic vein). It then descends on the front of the ulnar side of the forearm, distributing filaments to the skin as far as the wrist, and communicating with the palmar cutaneous branch of the ulnar nerve. Ulnar branch The ''ulnar branch'' (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Antebrachial Cutaneous Branch
The posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm is a nerve found in humans and other animals. It is also known as the dorsal antebrachial cutaneous nerve, the external cutaneous branch of the musculospiral nerve, and the posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve. It is a cutaneous nerve (a nerve that supplies skin) of the forearm. Origin It arises from the radial nerve in the posterior compartment of the arm, often along with the posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm. Course It perforates the lateral head of the triceps brachii muscle at the triceps' attachment to the humerus. The upper and smaller branch of the nerve passes to the front of the elbow, lying close to the cephalic vein, and supplies the skin of the lower half of the arm. The lower branch pierces the deep fascia below the insertion of the Deltoideus, and descends along the lateral side of the arm and elbow, and then along the back of the forearm to the wrist, supplying the skin in its course, and joining, near its terminati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the Carpal bones, carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal bones." (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius (bone), radius and the Carpal bones, carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as ''wrist joints''. "With the large number of bones composing the wrist (ulna, radius, eight carpas, and five metacarpals), it makes sense that there are many, many joints that make up the structure known as the wrist." This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the Flexor retinaculum of the hand, flexor retinaculum, and the ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Nerve
The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus. The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has contributions from ventral roots of C5-C7 (lateral cord) and C8 and T1 (medial cord). The median nerve is the only nerve that passes through the carpal tunnel. Carpal tunnel syndrome is the disability that results from the median nerve being pressed in the carpal tunnel. Structure The median nerve arises from the branches from lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, courses through the anterior part of arm, forearm, and hand, and terminates by supplying the muscles of the hand. Arm After receiving inputs from both the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, the median nerve enters the arm from the axilla at the inferior margin of the teres major muscle. It then passes vertically down and courses lateral to the brachial ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Nerve
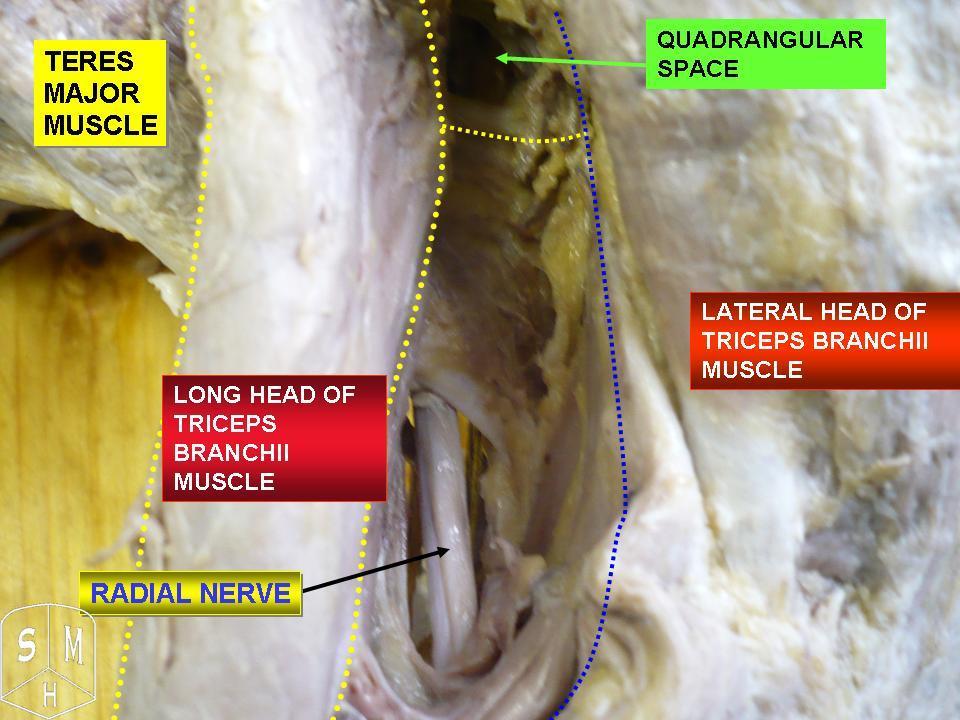
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin. It originates from the brachial plexus, carrying fibers from the ventral roots of spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8 & T1. The radial nerve and its branches provide motor innervation to the dorsal arm muscles (the triceps brachii and the anconeus) and the extrinsic extensors of the wrists and hands; it also provides cutaneous sensory innervation to most of the back of the hand, except for the back of the little finger and adjacent half of the ring finger (which are innervated by the ulnar nerve). The radial nerve divides into a deep branch, which becomes the posterior interosseous nerve, and a superficial branch, which goes on to innervate the dorsum (back) of the hand. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpal Bones
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (or carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the wrist is to facilitate effective positioning of the hand and powerful use of the extensors and flexors of the forearm, and the mobility of individual carpal bones increase the freedom of movements at the wrist.Kingston 2000, pp 126-127 In tetrapods, the carpus is the sole cluster of bones in the wrist between the radius and ulna and the metacarpus. The bones of the carpus do not belong to individual fingers (or toes in quadrupeds), whereas those of the metacarpus do. The corresponding part of the foot is the tarsus. The carpal bones allow the wrist to move and rotate vertically. Structure Bones The eight carpal bones may be conceptually organized as either two transverse rows, or three longitudinal columns. When c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musculocutaneous Nerve
The musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, opposite the lower border of the pectoralis major, its fibers being derived from C5, C6 and C7. Structure The musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, courses through the anterior part of the arm, and terminates at 2 cm above elbow as the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm. Musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus with root value of C5 to C7 of the spinal cord. It follows the course of the third part of the axillary artery (part of the axillary artery distal to the pectoralis minor) laterally and enters the frontal aspect of the arm where it penetrates the coracobrachialis muscle. It then passes downwards and laterally between the biceps brachii (above) and the brachialis muscles (below), to the lateral side of the arm; at 2 cm above the elbow it pierces the deep fascia lateral to the tendon of the biceps brachii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Artery
In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm. Structure The radial artery arises from the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the antecubital fossa. It runs distally on the anterior part of the forearm. There, it serves as a landmark for the division between the anterior compartment of the forearm, anterior and posterior compartment of the forearm, posterior compartments of the forearm, with the posterior compartment beginning just lateral to the artery. The artery winds laterally around the wrist, passing through the anatomical snuff box and between the heads of the first dorsal interossei of the hand, dorsal interosseous muscle. It passes anteriorly between the heads of the adductor pollicis, and becomes the deep palmar arch, which joins with the deep branch of the ulnar artery. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein, the radial vein. Branches The named branches of the radial artery may be divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forearm
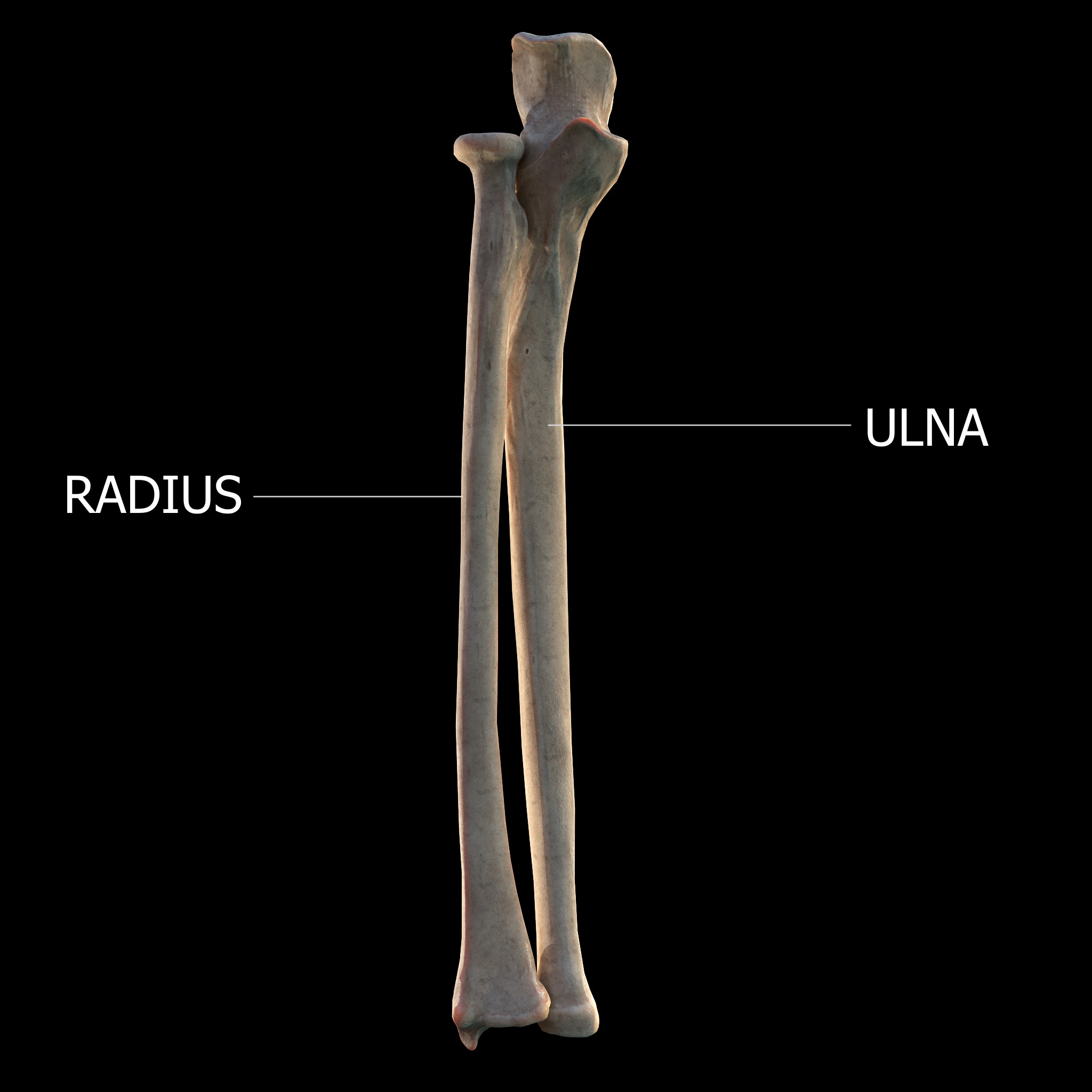
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow (brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |