|
Late Cypriot
The Prehistoric Period is the oldest part of Cypriot history. This article covers the period 10,000 to 800 BC and ends immediately before the documented history of Cyprus begins. Epipalaeolithic Cyprus was not settled in the Paleolithic (before agriculture), which allowed survival of numerous dwarf animal species, such as dwarf elephants (''Elephas cypriotes'') and pygmy hippos (''Hippopotamus minor'') well into the Holocene. These animals are thought to have arrived on the island as a result of being swept out to sea while swimming off the coast of the nearby mainland. There are claims of an association of this fauna with artifacts of Epipalaeolithic foragers at Aetokremnos near Limassol on the southern coast of Cyprus. The extinction of the pygmy hippos and dwarf elephants has been linked to the earliest arrival of ''Homo sapiens'' on Cyprus. There is evidence of this because of the piles of burned bones in the camps occupied by these early humans in caves on the southernmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kastros
Kastros is an early Neolithic settlement in Cyprus. Location It lies at the north-easternmost tip of the Karpasia Peninsula (Cape Apostolos Andreas), about 4 km north of Apostolos Andreas Monastery. The settlement is situated on a little plateau at the steep flank of the limestone promontory, about halfway between the main plateau of the peninsula and the sea in a very inaccessible situation. History of excavations Between 1970 and 1973 three campaigns of excavations have been conducted by a French team headed by Alain Le Brun. The excavation was interrupted by the 1974 war in Cyprus. Today, the structures remain open to the sky and are slowly eroding. Houses The settlement consists of small round or roundish houses. Their diameter is between 2.5 and 2.8 m, which gives a living surface of between 5 and 6.8 m2. The houses contain a hearth and sometimes container-bins in the floor. The walls are thin, composed of a single course of dry stone walling. Sometimes several of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bean
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes throughout the world. Terminology The word "bean" and its Germanic cognates (e.g. German '' Bohne'') have existed in common use in West Germanic languages since before the 12th century, referring to broad beans, chickpeas, and other pod-borne seeds. This was long before the New World genus '' Phaseolus'' was known in Europe. After Columbian-era contact between Europe and the Americas, use of the word was extended to pod-borne seeds of ''Phaseolus'', such as the common bean and the runner bean, and the related genus ''Vigna''. The term has long been applied generally to many other seeds of similar form, such as Old World soybeans, peas, other vetches, and lupins, and even to those with slighter resemblances, such as coffee beans, vanilla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lentil
The lentil (''Lens culinaris'' or ''Lens esculenta'') is an edible legume. It is an annual plant known for its lens-shaped seeds. It is about tall, and the seeds grow in pods, usually with two seeds in each. As a food crop, the largest producer is Canada, producing 45% of the world’s total lentils. In cuisines of the Indian subcontinent, where lentils are a staple, split lentils (often with their hulls removed) known as dal are often cooked into a thick curry/gravy that is usually eaten with rice or '' rotis''. Botanical description Name Many different names in different parts of the world are used for the crop lentil. The first use of the word ''lens'' to designate a specific genus was in the 16th century by the botanist Tournefort. The word "lens" for the lentil is of classical Roman/Latin origin: McGee points out that a prominent Roman family took the name " Lentulus", just as the family name "Cicero" was derived from the chickpea, '' Cicer arietinum'', or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cereal
A cereal is any Poaceae, grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, Cereal germ, germ, and bran. Cereal Grain, grain crops are grown in greater quantities and provide more food energy worldwide than any other type of crop and are therefore Staple food, staple crops. They include wheat, rye, Oat, oats, and barley. Edible grains from other plant families, such as buckwheat, quinoa and Salvia hispanica, chia, are referred to as pseudocereals. In their unprocessed whole grain form, cereals are a rich source of vitamins, Mineral (nutrient), minerals, carbohydrates, fats, oils, and Protein (nutrient), protein. When processed by the removal of the bran and germ the remaining endosperm is mostly carbohydrate. In some Developing country, developing countries, grain in the form of rice, wheat, millet, or maize constitutes a majority of daily sustenance. In Developed country, developed countries, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with the advent of metalworking. Though some simple metalworking of malleable metals, particularly the use of gold and copper for purposes of ornamentation, was known in the Stone Age, it is the melting and smelting of copper that marks the end of the Stone Age. In Western Asia, this occurred by about 3,000 BC, when bronze became widespread. The term Bronze Age is used to describe the period that followed the Stone Age, as well as to describe cultures that had developed techniques and technologies for working copper alloys (bronze: originally copper and arsenic, later copper and tin) into tools, supplanting stone in many uses. Stone Age artifacts that have been discovered include tools used by modern humans, by their predecessor species in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andesite
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predominantly of sodium-rich plagioclase plus pyroxene or hornblende. Andesite is the extrusive equivalent of plutonic diorite. Characteristic of subduction zones, andesite represents the dominant rock type in island arcs. The average composition of the continental crust is andesitic. Along with basalts, andesites are a component of the Martian crust. The name ''andesite'' is derived from the Andes mountain range, where this rock type is found in abundance. It was first applied by Christian Leopold von Buch in 1826. Description Andesite is an aphanitic (fine-grained) igneous rock that is intermediate in its content of silica and low in alkali metals. It has less than 20% quartz and 10% feldspathoid by volume, with at least 65% of the fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
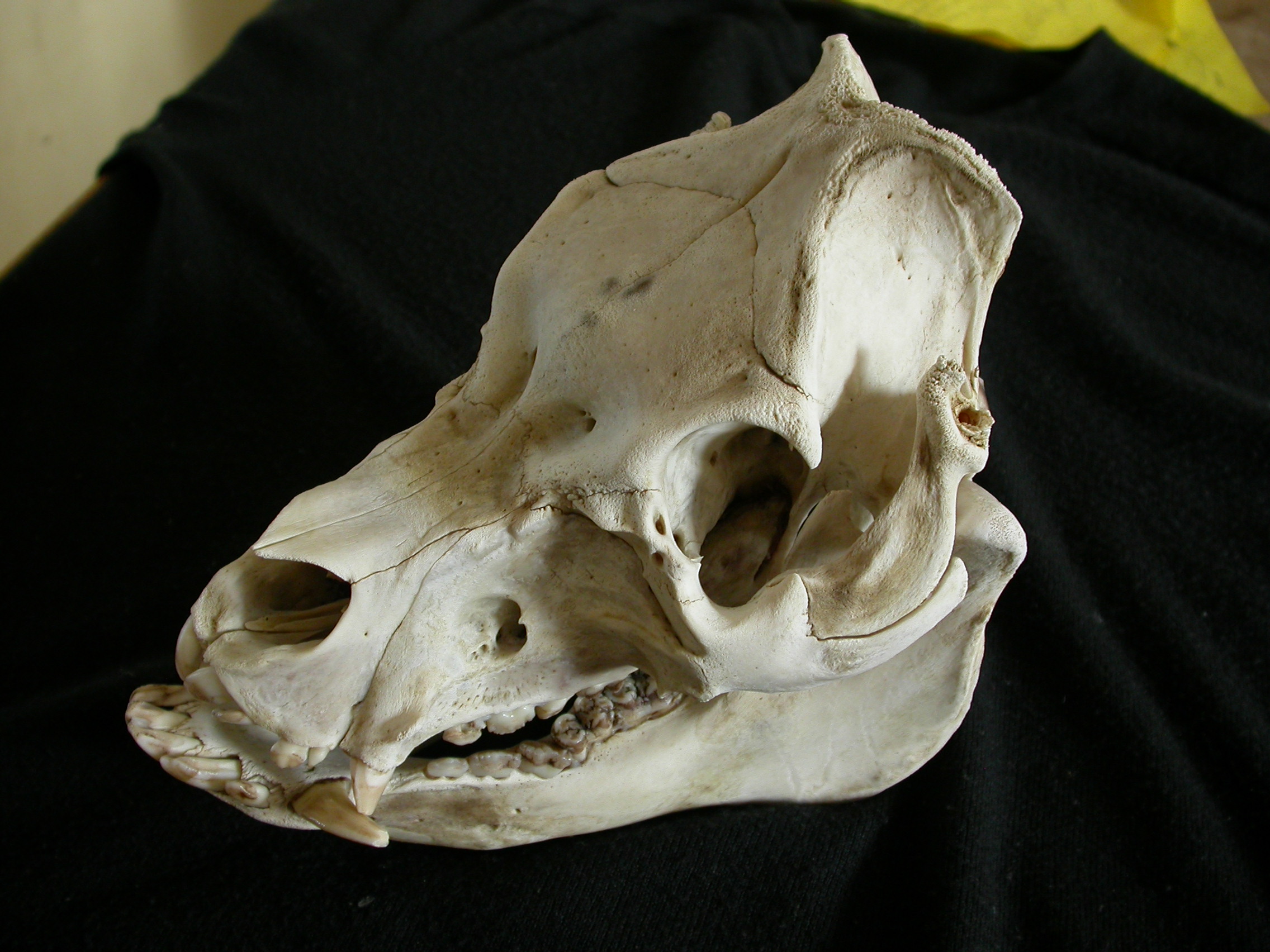
Pigs
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus scrofa'' (the wild boar or Eurasian boar) or a distinct species. The pig's head-plus-body length ranges from , and adult pigs typically weigh between , with well-fed individuals even exceeding this range. The size and weight of hogs largely depends on their breed. Compared to other artiodactyls, a pig's head is relatively long and pointed. Most even-toed ungulates are herbivorous, but pigs are omnivores, like their wild relative. Pigs grunt and make snorting sounds. When used as livestock, pigs are farmed primarily for the production of meat, called pork. A group of pigs is called a ''passel'', a ''team'', or a ''sounder''. The animal's bones, hide, and bristles are also used in products. Pigs, especially miniature breeds, are kept as pets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the animal family Bovidae and the tribe Caprini, meaning it is closely related to the sheep. There are over 300 distinct breeds of goat.Hirst, K. Kris"The History of the Domestication of Goats".''About.com''. Accessed August 18, 2008. It is one of the oldest domesticated species of animal, according to archaeological evidence that its earliest domestication occurred in Iran at 10,000 calibrated calendar years ago. Goats have been used for milk, meat, fur, and skins across much of the world. Milk from goats is often turned into goat cheese. Female goats are referred to as ''does'' or ''nannies'', intact males are called ''bucks'' or ''billies'', and juvenile goats of both sexes are called ''kids''. Castrated males are called ''wethers''. Whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sheep. Like all ruminants, sheep are members of the order Artiodactyla, the even-toed ungulates. Numbering a little over one billion, domestic sheep are also the most numerous species of sheep. An adult female is referred to as a ''ewe'' (), an intact male as a ''ram'', occasionally a ''tup'', a castrated male as a ''wether'', and a young sheep as a ''lamb''. Sheep are most likely descended from the wild mouflon of Europe and Asia, with Iran being a geographic envelope of the domestication center. One of the earliest animals to be domesticated for agricultural purposes, sheep are raised for fleeces, meat (lamb, hogget or mutton) and milk. A sheep's wool is the most widely used animal fiber, and is usually harvested by shearing. In Commonw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aceramic
Aceramic is defined as "not producing pottery". In archaeology, the term means "without pottery". Aceramic societies usually used bark, basketry, gourds and leather for containers. It is sometimes used to refer to a specific early Neolithic period before a culture develops ceramics, such as the Middle Eastern Pre-Pottery Neolithic A, in which case it is a synonym of preceramic (or pre-pottery). It should be distinguished from the specific term Pre-Ceramic, which is a period in many chronologies of the archaeology of the Americas, typically showing some agriculture and developed textiles but no fired pottery. For example, in the Norte Chico civilization and other cultures of Peru, the cultivation of cotton seems to have been very important in economic and power relations, from around 3200 BC. Here, Cotton Pre-Ceramic may be used as a period. The Pre-Ceramic may be followed by "Ceramic" periods or a formative stage. "Aceramic" is also used to describe a culture at any time prior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choirokoitia
Khirokitia (sometimes spelled Choirokoitia; el, Χοιροκοιτία , suggested meaning ''Pig-cradle'', from 'pig, boar' + 'place of origin, cradle'; tr, Hirokitya) is an archaeological site on the island of Cyprus dating from the Neolithic age. It has been listed as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO since 1998. The site is known as one of the most important and best preserved prehistoric sites of the eastern Mediterranean. Much of its importance lies in the evidence of an organised functional society in the form of a Collective farming, collective settlement, with surrounding fortifications for communal protection. The Neolithic aceramic period is represented by this settlement and around 20 other similar settlements spread throughout the island. Discovery The site was discovered in 1934 by Porphyrios Dikaios, director of the Department of Antiquities (Cyprus), Department of Antiquities who carried out six excavations between 1934 and 1946. His initial findings were publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |