|
Landsberg, Saxony-Anhalt
Landsberg is a town in the Saalekreis in the States of Germany, state of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany Geography The town is located between the cities of Halle (Saale), Halle, about in the southwest, Leipzig, about in the southeast, and Bitterfeld-Wolfen, about in the north. Located in the Leipzig Bay of the North German Plain, Landsberg lies within the larger Leipzig-Halle agglomeration in the Central German Metropolitan Region. The municipal area immediately borders the independent city of Halle in the southwest and the Nordsachsen district of Saxony in the southeast. After several incorporations in recent years, it currently comprises 11 localities (''Ortschaften''):Hauptsatzung der Stadt Landsberg January 2020. *Braschwitz *Hohenthurm *Landsberg *Niemberg *Oppin *Peißen, Saalekre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistisches Landesamt Sachsen-Anhalt
The statistical offices of the German states (German language, German: ) carry out the task of collecting official statistics in Germany together and in cooperation with the Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Federal Statistical Office. The implementation of statistics according to Article 83 of the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution is executed at state level. The Bundestag, federal government has, under Article 73 (1) 11. of the constitution, the exclusive legislation for the "statistics for federal purposes." There are 14 statistical offices for the States of Germany, 16 states: See also * Federal Statistical Office of Germany References {{Reflist National statistical services, Germany Lists of organisations based in Germany, Statistical offices Official statistics, Germany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oppin
Oppin is a village and a former municipality in the district Saalekreis, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu .... Since 1 January 2010, it is part of the town Landsberg. Location Oppin is situate 7 km north east of Halle on the Saale. The river Riede rises not far to the north of the village and flows through the village. References Former municipalities in Saxony-Anhalt Landsberg, Saxony-Anhalt {{Saalekreis-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
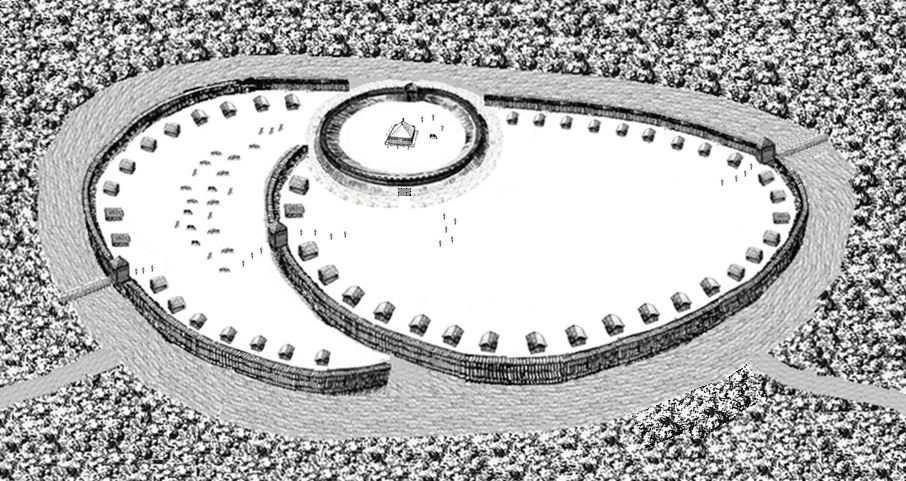
Polabian Slavs
Polabian Slavs, also known as Elbe Slavs and more broadly as Wends, is a collective term applied to a number of Lechites, Lechitic (West Slavs, West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germany. The approximate territory stretched from the Baltic Sea in the north, the Saale and the ''Limes Saxoniae''Christiansen, 18 in the west, the Ore Mountains and the Western Sudetes in the south, and medieval History of Poland (966–1385), Poland in the east. The Polabian Slavs, largely conquered by Saxons and Danish people, Danes from the 9th century onwards, were included and gradually cultural assimilation, assimilated within the Holy Roman Empire. The tribes became gradually Germanization, Germanized and assimilated in the following centuries; the Sorbs are the only descendants of the Polabian Slavs to have retained their identity and culture. The Polabian language is now extinct. However, the two Sorbian languages are spoken by approximate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), known as Otto the Great ( ) or Otto of Saxony ( ), was East Francia, East Frankish (Kingdom of Germany, German) king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the eldest son of Henry the Fowler and Matilda of Ringelheim. Otto inherited the Duchy of Saxony and the kingship of the Germans upon his father's death in 936. He continued his father's work of unifying all German tribes into a single kingdom and greatly expanded the king's powers at the expense of the aristocracy. Through strategic marriages and personal appointments, Otto installed members of his family in the kingdom's most important duchies. This reduced the various dukes, who had previously been co-equals with the king, to royal subjects under his authority. Otto transformed the church in Germany to strengthen royal authority and subjected its clergy to his personal control. After putting down a brief civil war among the rebellious duchies, Otto de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the History of agriculture, introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of sedentism, settlement. The term 'Neolithic' was coined by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, Sir John Lubbock in 1865 as a refinement of the three-age system. The Neolithic began about 12,000 years ago, when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East and Mesopotamia, and later in other parts of the world. It lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BCE), marked by the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halle–Cottbus Railway
The Halle–Cottbus railway is a 176 km long double-track electrified main line in the German states of Saxony-Anhalt, Saxony and Brandenburg. It was opened in 1871 and 1872. It formed the central section of the network of the Halle-Sorau-Guben Railway Company. Today it is part of a connection between the Central Germany (cultural area), Central Germany and Poland. Before German reunification, the line was also served by express trains, but it is now mainly used by regional and international freight traffic. History On 1 December 1871, the Halle-Sorau-Guben Railway Company (''Halle-Sorau-Gubener Eisenbahn'', HSGE) opened the Cottbus station, Cottbus–Falkenberg (Elster) station, Falkenberg/Elster section after its extension towards Guben was opened earlier the same year. Six months later, on 1 May 1872, trains ran via Falkenberg to Eilenburg station, Eilenburg and, two more months later, on 30 June 1872, operations on the line were extended as far as Halle (Saale) Haup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin–Halle Railway
The Berlin–Halle railway, sometimes called the Anhalt railway (German: ''Anhalter Bahn''), is a twin-track, electrified main line found in the German city and state of Berlin, and the states of Brandenburg and Sachsen-Anhalt. The railway was originally built and managed by the ''Berlin-Anhaltische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft''. The Anhalt railway runs from Berlin via Jüterbog and Lutherstadt Wittenberg railway station, Wittenberg to Halle (Saale) Hauptbahnhof, Halle. The line is part of the Berlin–Palermo railway axis, Line 1 of Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T). In the Berlin area, Anhalt Suburban Line, which carries Berlin S-Bahn services, runs parallel to the main line. History Early history and construction The ''Berlin-Anhaltische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'' (Berlin-Anhalt Railway Company, BAE) was one of the most important railway companies in Germany for about four decades in the 19th century. In addition to the main ''Anhalt Railway'', the BAE built a network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silage
Silage is fodder made from green foliage crops which have been preserved by fermentation (food), fermentation to the point of souring. It is fed to cattle, sheep and other ruminants. The fermentation and storage process is called ''ensilage'', ''ensiling'', or ''silaging''. The exact methods vary, depending on available technology, local tradition and prevailing climate. Silage is usually made from grass crops including maize, sorghum or other cereals, using the entire green plant (not just the grain). Specific terms may be used for silage made from particular crops: ''oatlage'' for oats, ''haylage'' for alfalfa (''haylage'' may also refer to high dry matter silage made from hay). History Using the same technique as the process for making sauerkraut, green fodder was preserved for animals in parts of Germany since the start of the 19th century. This gained the attention of French agriculturist Auguste Goffart of Sologne, near Orléans. He published a book in 1877 which describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vetch
''Vicia'' is a genus of over 240 species of flowering plants that are part of the legume family (Fabaceae), and which are commonly known as vetches. Member species are native to Europe, North America, South America, Asia and Africa. Some other genera of their subfamily Faboideae also have names containing "vetch", for example the vetchlings (''Lathyrus'') or the milk-vetches (''Astragalus''). The lentils are included in genus ''Vicia'', and were formerly classified in genus ''Lens''. The broad bean (''Vicia faba'') is sometimes separated in a monotypic genus ''Faba''; although not often used today, it is of historical importance in plant taxonomy as the namesake of the order Fabales, the Fabaceae and the Faboideae. The tribe Vicieae in which the vetches are placed is named after the genus' current name. The true peas (''Pisum'') are among the closest living relatives of vetches. Use by humans Bitter vetch ('' V. ervilia'') was one of the first domesticated crops. It wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryegrass
''Lolium'' is a genus of tufted grasses in the bluegrass subfamily (Pooideae). It is often called ryegrass, but this term is sometimes used to refer to grasses in other genera. They are characterized by bunch-like growth habits. ''Lolium'' is native to Europe, Asia and northern Africa, as well as being cultivated and naturalized in Australia, the Americas, and various oceanic islands. Ryegrasses are naturally diploid, with 2n=14, and are closely related to the fescues (''Festuca''). Ryegrass should not be confused with rye, which is a grain crop. Species the species of ''Lolium'' listed by Plants of the World Online include: ; Formerly included Several former ''Lolium'' species now regarded as part of other genera: '' Castellia'', '' Enteropogon'', '' × Festulolium'', '' Hainardia'', '' Lepturus'', '' Melica'', and '' Vulpia''. File:Perennial Ryegrass.jpg, Perennial ryegrass, used as winter lawn. File:Illustration Leymus arenarius and Lolium temulentum0.jpg, Pois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimson Clover
''Trifolium incarnatum'', known as crimson clover or Italian clover, is a species of herbaceous flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to most of Europe. It has been introduced to other areas, including the United States and Japan. This upright annual herb grows to 20–50 cm (8-20") tall, unbranched or branched only at the base. The leaves are trifoliate with a long petiole, each leaflet hairy, 8–16 mm across, with a truncated or bilobed apex. The flowers are produced throughout the spring and summer, rich red or crimson, congested on an elongated spike inflorescence 3–5 cm tall and 1.5 cm broad; the individual flowers are up to 10–13 mm long and have five petals. The banner of each flower does not sit upright, but folds forward. Uses Crimson clover is commonly used in agriculture as a nitrogen-fixing cover crop. The plant uses associations with ''Rhizobium'' bacteria to fix nitrogen. The plant is widely grown as a protein-rich forage c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |