|
Lamina Terminalis
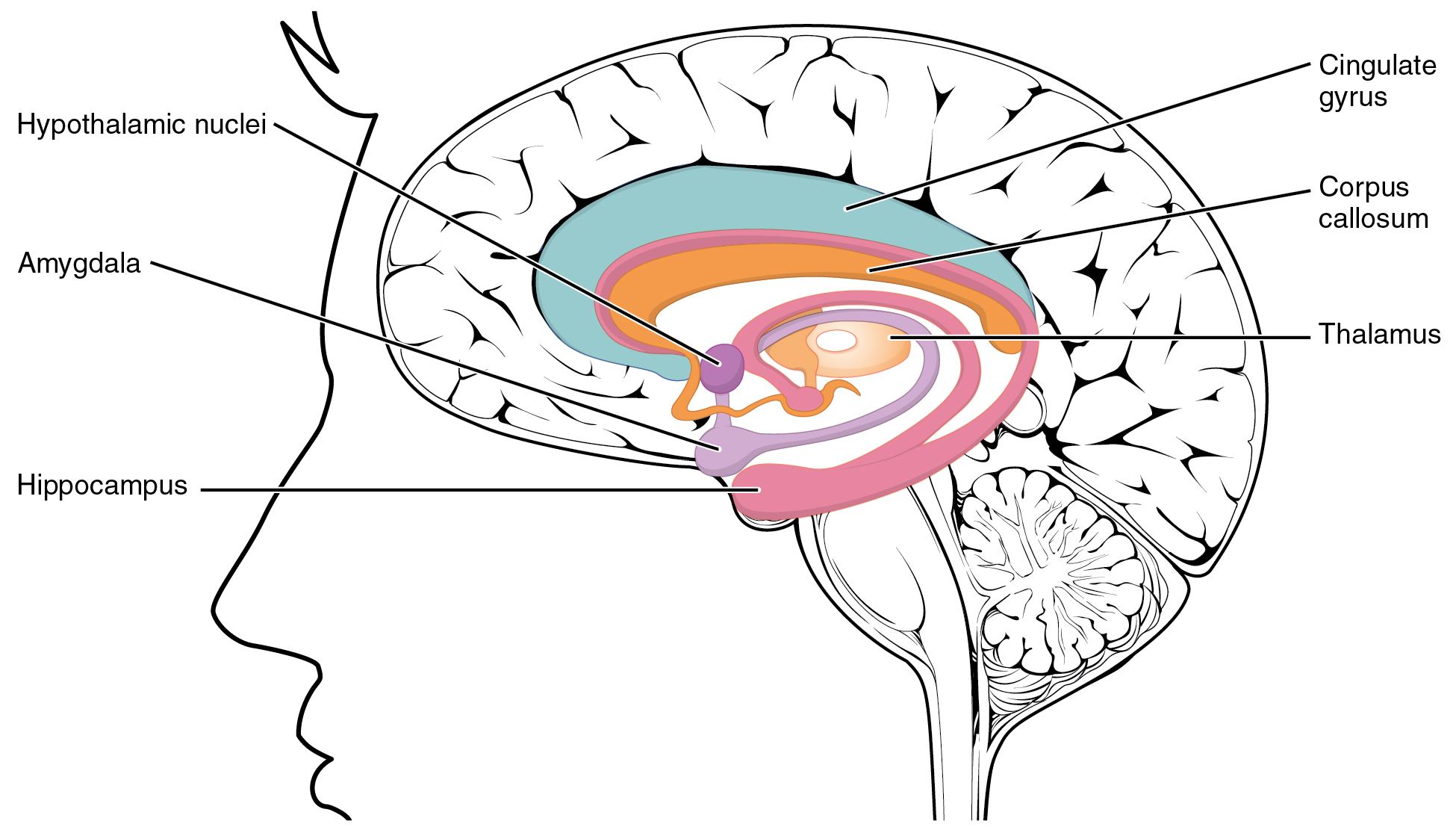
The median portion of the wall of the forebrain consists of a thin lamina, the lamina terminalis, which stretches from the interventricular foramen (Foramen of Monro) to the recess at the base of the optic stalk (optic nerve) and contains the vascular organ of the lamina terminalis, which regulates the osmotic concentration of the blood. The lamina terminalis is immediately anterior to the tuber cinereum; together they form the pituitary stalk. The lamina terminalis can be opened via endoscopic neurosurgery in an attempt to create a path that cerebrospinal fluid can flow through when a person has hydrocephalus and when it is not possible to perform an Endoscopic third ventriculostomy, but the effectiveness of this technique is not certain. This is the rostral end (tip) of the neural tube (embryological central nervous system) in the early weeks of development. Failure of the lamina terminalis to close properly at this stage of development will result in anencephaly or meroe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forebrain
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain (prosencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) are the three primary brain vesicles during the early development of the nervous system. The forebrain controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and the display of emotions. At the five-vesicle stage, the forebrain separates into the diencephalon ( thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, and epithalamus) and the telencephalon which develops into the cerebrum. The cerebrum consists of the cerebral cortex The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting o ..., underlying white matter, and the basal ganglia. In humans, by 5 weeks in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) is a surgical procedure for treatment of hydrocephalus in which an opening is created in the floor of the third ventricle using an endoscope placed within the ventricular system through a burr hole. This allows the cerebrospinal fluid to flow directly to the basal cisterns, bypassing the obstruction. Specifically, the opening is created in the translucent tuber cinereum on the third ventricular floor. Medical uses The ETV procedure is used as an alternative to a cerebral shuntHydrocephalus and Treatment: Shunts and Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy AboutKidsHealth.ca mainly to treat certain forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Organ Of Lamina Terminalis
The vascular organ of lamina terminalis (VOLT), organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis (OVLT), or supraoptic crest is one of the four sensory circumventricular organs of the brain, the others being the subfornical organ, the median eminence, and the area postrema in the brainstem. __TOC__ Anteroventral third ventricle region The VOLT, median eminence, and subfornical organ are interconnected with the mid-ventral hypothalamus, and together these three structures surround the third ventricle, a complex often called the "AV3V" region. This region functions in the regulation of fluid and electrolyte balance by controlling thirst, sodium excretion, blood volume regulation, and vasopressin secretion. Function The VOLT is one of the four sensory circumventricular organs providing information to other brain regions (others are median eminence, subfornical organ, and area postrema).Fry Mark, Ferguson Alastair V., (2007) The sensory circumventricular organs: Brain targets for circulati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond. The hypothalamus is responsible for regulating certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and maternal attachment behaviours, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms. Structure Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagittal
The sagittal plane (; also known as the longitudinal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into right and left sections. It is perpendicular to the transverse and coronal planes. The plane may be in the center of the body and divide it into two equal parts ( mid-sagittal), or away from the midline and divide it into unequal parts (para-sagittal). The term ''sagittal'' was coined by Gerard of Cremona. Variations in terminology Examples of sagittal planes include: * The terms ''median plane'' or ''mid-sagittal plane'' are sometimes used to describe the sagittal plane running through the midline. This plane cuts the body into halves (assuming bilateral symmetry), passing through midline structures such as the navel and spine. It is one of the planes which, combined with the Umbilical plane, defines the four quadrants of the human abdomen. * The term ''parasagittal'' is used to describe any plane parallel or adjacent to a given sagittal plane. Specific named pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary Gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypophysis rests upon the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone in the center of the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded by a small bony cavity ( sella turcica) covered by a dural fold ( diaphragma sellae). The anterior pituitary (or adenohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that regulates several physiological processes including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. The intermediate lobe synthesizes and secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone. The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence via a small tube called the pituitary stalk (also called the infundibular stalk or the infundibulum). Hormones secreted from the pituitary glan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anencephaly
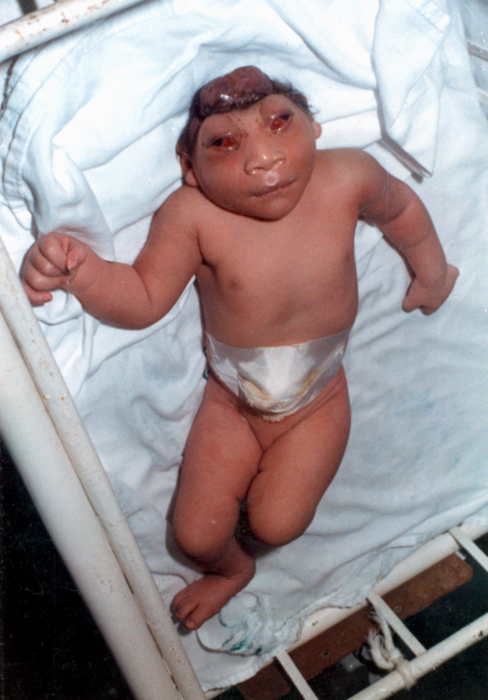
Anencephaly is the absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp that occurs during embryonic development. It is a cephalic disorder that results from a neural tube defect that occurs when the rostral (head) end of the neural tube fails to close, usually between the 23rd and 26th day following conception. Strictly speaking, the Greek term translates as "without a brain" (or totally lacking the inside part of the head), but it is accepted that children born with this disorder usually only lack a telencephalon, the largest part of the brain consisting mainly of the cerebral hemispheres, including the neocortex, which is responsible for cognition. The remaining structure is usually covered only by a thin layer of membrane—skin, bone, meninges, etc., are all lacking. With very few exceptions, infants with this disorder do not survive longer than a few hours or days after birth. Signs and symptoms The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural fold become elevated, and ultimately the folds meet and coalesce in the middle line and convert the groove into the closed neural tube. In humans, neural tube closure usually occurs by the fourth week of pregnancy (the 28th day after conception). The ectodermal wall of the tube forms the rudiment of the nervous system. The centre of the tube is the ''neural canal''.It is an important structure for the development of fetus's brain and spine Development The neural tube develops in two ways: primary neurulation and secondary neurulation. Primary neurulation divides the ectoderm into three cell types: * The internally located neural tube * The externally located epidermis * The neural crest cells, which develop in the region between the neural tube and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary incontinence, personality changes, or mental impairment. In babies, it may be seen as a rapid increase in head size. Other symptoms may include vomiting, sleepiness, seizures, and downward pointing of the eyes. Hydrocephalus can occur due to birth defects or be acquired later in life. Associated birth defects include neural tube defects and those that result in aqueductal stenosis. Other causes include meningitis, brain tumors, traumatic brain injury, intraventricular hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. The four types of hydrocephalus are communicating, noncommunicating, ''ex vacuo'', and normal pressure. Diagnosis is typically made by physical examination and medical imaging. Hydrocephalus is typically treated by the surg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamina
Lamina may refer to: Science and technology * Planar lamina, a two-dimensional planar closed surface with mass and density, in mathematics * Laminar flow, (or streamline flow) occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between the layers * Lamina (algae), a structure in seaweeds * Lamina (anatomy), with several meanings * Lamina (leaf), the flat part of a leaf, an organ of a plant * Lamina, the largest petal of a floret in an aster family flowerhead: see * ''Lamina'' (spider), a genus in the family Toxopidae * Lamina (neuropil), the most peripheral neuropil of the insect visual system *Nuclear lamina, another structure of a living cell *Basal lamina, a structure of a living cell * Lamina propria, the connective part of the mucous * Lamina of the vertebral arch *Lamination (geology), a layering structure in sedimentary rocks usually less than 1 cm in thickness * Laminae, a part of the horse hoof * Laminae, another name for the core lamiids, a clade in b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |