|
Lambdopsalidae
Lambdopsalidae is a family of extinct multituberculate mammals from the Late Paleocene of Asia. They are part of Taeniolabidoidea, a clade otherwise present in the Early Paleocene (and possibly the Late Cretaceous) of North America; lambdopsalids, therefore, probably evolved from a single radiation that spread into Asia from North America in the mid-Paleocene or earlier. They are represented by the genus '' Lambdopsalis'', '' Sphenopsalis'' and '' Prionessus''. Though they haven't become as large as ''Taeniolabis'', lambdopsalids were still large by multituberculate standards, the largest species weighting around 30 kg. They are notable for their unique dental speciations such as hypsodonty, which seem to imply speciations towards grazing. ''Lambdopsalis'' is notable for offering direct evidence of hair and enamel and tooth prism patterns among multituberculates. Lambdopsalids lived in the final stages of the Paleocene, disappearing around the PETM. They co-existed with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taeniolabidoidea
Taeniolabidoidea is a group of extinct mammals known from North America and Asia. They were the largest members of the extinct order Multituberculata, as well as the largest non-therian mammals. '' Lambdopsalis'' even provides direct fossil evidence of mammalian fur in a fairly good state of preservation for a 60-million-year-old animal. Some of these animals were large for their time; '' Taeniolabis taoensis'' is the largest known multituberculate and though smaller, '' Yubaatar'' is the largest known Mesozoic Asian multituberculate.L. Xu, X. Zhang, H. Pu, S. Jia, and J. Zhang, J., and J. Meng. 2015. Largest known Mesozoic multituberculate from Eurasia and implications for multituberculate evolution and biology. Scientific Reports 5(14950):1-11 Average members of the Taeniolaboidea were about beaver-sized and the largest even reached sizes comparable to the largest beavers like ''Castoroides'', up to about 100 kilograms. The group was initially established as a suborder, before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multituberculate
Multituberculata (commonly known as multituberculates, named for the multiple tubercles of their teeth) is an extinct order of rodent-like mammals with a fossil record spanning over 130 million years. They first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, and reached a peak diversity during the Late Cretaceous and Paleocene. They eventually declined from the mid Paleocene onwards, disappearing from the known fossil record in the late Eocene. They are the most diverse order of Mesozoic mammals with more than 200 species known, ranging from mouse-sized to beaver-sized. These species occupied a diversity of ecological niches, ranging from burrow-dwelling to squirrel-like arborealism to jerboa-like hoppers. Multituberculates are usually placed as crown mammals outside either of the two main groups of living mammals—Theria, including placentals and marsupials, and MonotremataAgustí-Antón 2002, pp 3-4—but usually as closer to Theria than to monotremes. They are considered to be close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimolodonts
Cimolodonta is a taxon of extinct mammals that lived from the Cretaceous to the Eocene. They were some of the more derived members of the extinct order Multituberculata. They probably lived something of a rodent-like existence until their ecological niche was assumed by true rodents. The more basal multituberculates are found in a different suborder, "Plagiaulacida", a paraphyletic group containing all non cimolodontan multituberculates. Cimolodonta is apparently a natural (monophyletic) suborder. Remains have been identified from across the Northern Hemisphere. They first appeared during the Aptian, and completely replaced the more primitive plagiaulacidans by the early Late Cretaceous. The taxon is recognized as the informal Paracimexomys group and the superfamilies Djadochtatherioidea, Taeniolabidoidea, and Ptilodontoidea. Additionally, and of uncertain affinities, are the families Cimolomyidae, Boffiidae, Eucosmodontidae, Kogaionidae, Microcosmodontidae and the two genera ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by Chicxulub impact, an asteroid impact and possibly volcanism, marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of living species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grazing
In agriculture, grazing is a method of animal husbandry whereby domestic livestock are allowed outdoors to roam around and consume wild vegetations in order to convert the otherwise indigestible (by human gut) cellulose within grass and other forages into meat, milk, wool and other animal products, often on land unsuitable for arable farming. Farmers may employ many different strategies of grazing for optimum production: grazing may be continuous, seasonal, or rotational within a grazing period. Longer rotations are found in ley farming, alternating arable and fodder crops; in rest rotation, deferred rotation, and mob grazing, giving grasses a longer time to recover or leaving land fallow. Patch-burn sets up a rotation of fresh grass after burning with two years of rest. Conservation grazing proposes to use grazing animals to improve the biodiversity of a site, but studies show that the greatest benefit to biodiversity comes from removing grazing animals from the landscape. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Extinctions
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for New Zealand, Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/richochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Rabbits, hares, and pikas, whose i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major Tissue (biology), tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many other animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the Crown (tooth), crown. The other major tissues are dentin, cementum, and Pulp (tooth), dental pulp. It is a very hard, white to off-white, highly mineralised substance that acts as a barrier to protect the tooth but can become susceptible to degradation, especially by acids from food and drink. Calcium hardens the tooth enamel. In rare circumstances enamel fails to form, leaving the underlying dentin exposed on the surface. Features Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and contains the highest percentage of minerals (at 96%),Ross ''et al.'', p. 485 with water and organic material composing the rest.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nancy, Elsevier, pp. 70–94 The primary mineral is hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate. Enamel is formed o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
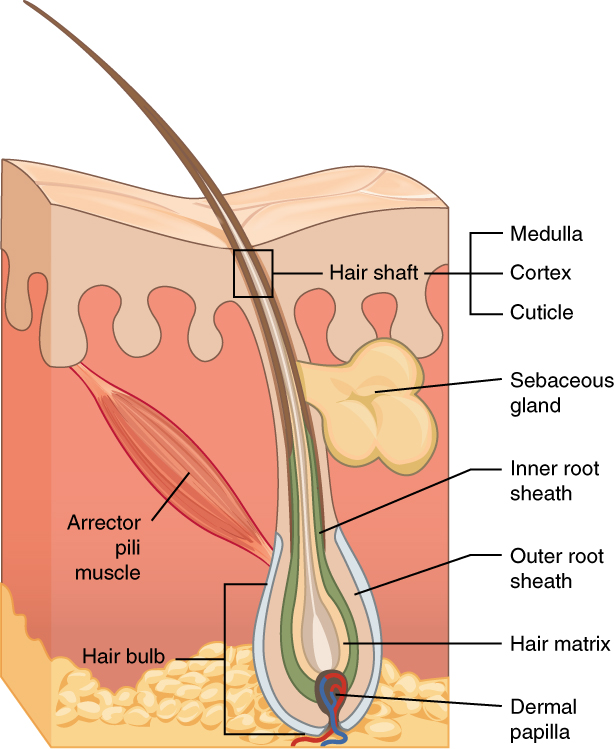
Hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair. Most common interest in hair is focused on hair growth, hair types, and hair care, but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably alpha-keratin. Attitudes towards different forms of hair, such as hairstyles and hair removal, vary widely across different cultures and historical periods, but it is often used to indicate a person's personal beliefs or social position, such as their age, sex, or religion. Overview The word "hair" usually refers to two distinct structures: #the part beneath the skin, called the hair follicle, or, when pulled from the skin, the bulb or root. This organ is located in the dermis and maintains stem cells, which not only re-grow the hair after it falls out, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taeniolabis
''Taeniolabis'' ("banded incisor") is a genus of extinct multituberculate mammal from the Paleocene of North America. Description It is the largest known member of the extinct order Multituberculata, as well as the largest non-therian mammal: ''T. taoensis'', a species known from Danian deposits in the Denver Formation of Colorado, possibly exceeds 100 kg. Taxonomy It is within the suborder of Cimolodonta and is a member of the superfamily Taeniolabidoidea. The genus was named by Edward Drinker Cope in 1882. Species have also been placed with the genera '' Catopsalis'' and ''Polymastodon''. The species ''Taeniolabis lamberti'' was named by N.B. Simmons in 1987. It has been found in the Puercan (Paleocene)-age Tullock Formation of Montana. It is not quite as large as ''T. taoensis'', but still a hefty size for a multituberculate. The species ''Taeniolabis taoensis'' was named by Cope E.D. in 1882. It is also known as ''Catopsalis pollux'' (Cope, 1882); ''Polymast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypsodonty
Hypsodont is a pattern of dentition with high-crowned teeth and enamel extending past the gum line, providing extra material for wear and tear. Some examples of animals with hypsodont dentition are cows and horses; all animals that feed on gritty, fibrous material. The opposite condition is called brachydont. Evolution Since the morphology of the hypsodont tooth is suited to a more abrasive diet, hypsodonty was thought to have evolved concurrently with the spread of grasslands. Grass contains phytoliths, silica-rich granules, which wear away dental tissue more quickly. Analysis has shown however, that the development of this morphology is out of sync with the flourishing of grasslands. Instead, the ingestion of grit and soil is hypothesized to be the primary driver of hypsodonty (the Grit, not grass hypothesis). Morphology Hypsodont dentition is characterized by: * high-crowned teeth * A rough, flattish occlusal surface adapted for crushing and grinding * Cementum both above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |