|
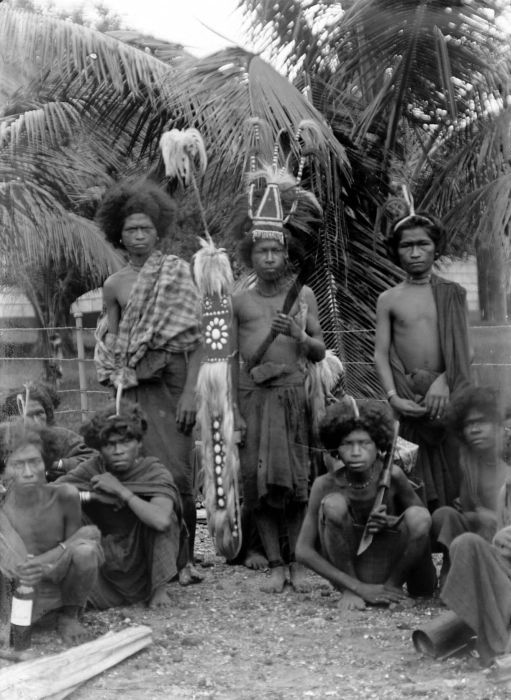
Lamaholot People
The Lamahalot or Solorese people are an indigenous tribe located on Flores Island, Indonesia, and some smaller islands around it (Solor, Adonara, and Lomblen). Lamaholot people speak the Lamaholot language with different dialects, the number of speakers counts between 150,000 and 200,000. Lamaholot people's famous traditional dance is a war dance known as ''Hedung''. History Since the 16th century the territory of the Lamaholot was the object of the claims of the Sultanate of Makassar, Portugal and the Netherlands. Until the middle of the 19th century Lamaholot were under the Portuguese colonial administration, then under the Netherlands in 1859–1942, and until the middle of the 20th century they were formally submitted to the Rajas of Larantuka and Adonara. Language The Lamaholot language belongs to the Malayo-Polynesian languages of the Austronesian languages family. The language is divided into many dialects, or possibly distinct languages as Adonara language, the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solor
Solor is a volcanic island located off the eastern tip of Flores island in the Lesser Sunda Islands of Indonesia, in the Solor Archipelago. The island supports a small population that has been whaling for hundreds of years. They speak the languages of Adonara and Lamaholot. There are at least five volcanoes on this island which measures only by . The island's area is , and it had a population of 34,029 at the 2020 Census. The official estimate as at mid 2021 was 35,045. Administrative Districts The island is divided into three districts (''kecamatan''), tabulated below with their areas (in km2) and their populations at the 2010 Census and 2020 Census, together with the official estimates as at mid 2021. The entire island is administered by the East Flores Regency. History of European contact In 1520, the Portuguese established a trading post in the village of Lamakera on the eastern side of the island as a transit harbor between Maluku and Portuguese Malacca. In 1562 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrilocal Residence
In social anthropology, patrilocal residence or patrilocality, also known as virilocal residence or virilocality, are terms referring to the social system in which a married couple resides with or near the husband's parents. The concept of location may extend to a larger area such as a village, town or clan territory. The practice has been found in around 70 percent of the world's modern human cultures that have been described ethnographically. Archaeological evidence for patrilocality has also been found among Neanderthal remains in Spain and for ancient hominids in Africa. Description In a patrilocal society, when a man marries, his wife joins him in his father's home or compound, where they raise their children. These children will follow the same pattern. Sons will stay and daughters will move in with their husbands' families. Families living in a patrilocal residence generally assume joint ownership of domestic sources. The household is led by a senior member, who also dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrilateral
The term matrilateral describes kin (relatives) "on the mother's side". Social anthropologists have underlined that even where a social group demonstrates a strong emphasis on one or other line of inheritance (matrilineal or patrilineal), relatives who fall outside this unilineal grouping will not simply be ignored. So, a strongly patrilineal orientation will be complemented by matrilateral ties with the mother's kin. Likewise within a strongly matrilineal organisation, patrilateral ties will enter the reckoning of relationships as an important balancing factor. This complementarity often has a moral or emotional tone to it: Malinowski's classic studies of the matrilineal Trobriand islanders showed that matrilineal ties were associated with discipline and authority, while patrilateral ties were characterised by nurturance and kindness (at least in principle). Likewise, in Chinua Achebe's novel Things Fall Apart, the hero, Okonkwo is forced into exile from his own ancestral village ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phratry
In ancient Greece, a phratry ( grc, φρᾱτρῐ́ᾱ, phrātríā, brotherhood, kinfolk, derived from grc, φρᾱ́τηρ, phrā́tēr, brother, links=no) was a group containing citizens in some city-states. Their existence is known in most Ionian cities and in Athens and it is thought that they existed elsewhere as well. Almost nothing is known about the functions and responsibilities of phratries outside Attica (the area around Athens). Within Athens, they played a prominent role in social and religious life, particularly in the major festival called the Apatouria. They played an important role in determining eligibility for Athenian citizenship and all citizens (with very few exceptions) and only citizens were enrolled in phratries. Particularly in anthropology, the term is also applied to similar descent groups of multiple clans in other societies. Ancient Greece The origins of the phratry in ancient Greece are unknown. It is possible that they are Ionian in origin and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotheistic Religion
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. A distinction may be made between exclusive monotheism, in which the one God is a singular existence, and both inclusive and pluriform monotheism, in which multiple gods or godly forms are recognized, but each are postulated as extensions of the same God. Monotheism is distinguished from henotheism, a religious system in which the believer worships one God without denying that others may worship different gods with equal validity, and monolatrism, the recognition of the existence of many gods but with the consistent worship of only one deity. The term ''monolatry'' was perhaps first used by Julius Wellhausen. Monotheism characterizes the traditions of Bábism, the Baháʼí Faith, Cheondoism, Christianity,Christianity's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraham (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices of Muhammad ('' sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (''hadith''). With an estimated population of almost 1.9 billion followers as of 2020 year estimation, Muslims comprise more than 24.9% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each continental landmass stands at: 45% of Africa, 25% of Asia and Oceania (collectively), 6% of Europe, and 1% of the Americas. Additionally, in subdivided geographical regions, the figure stands at: 91% of the Middle East–North Africa, 90% of Central Asia, 65% of the Caucasus, 42% of Southeast As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malay Language
Malay (; ms, Bahasa Melayu, links=no, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , Rejang script, Rencong: ) is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language that is an official language of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore, and that is also spoken in East Timor and parts of the Philippines and Thailand. Altogether, it is spoken by 290 million people (around 260 million in Indonesia alone in its own literary standard named "Indonesian language, Indonesian") across Maritime Southeast Asia. As the or ("national language") of several states, Standard Malay has various official names. In Malaysia, it is designated as either ("Malaysian Malay") or also ("Malay language"). In Singapore and Brunei, it is called ("Malay language"). In Indonesia, an autonomous normative variety called ("Indonesian language") is designated the ("unifying language" or lingua franca). However, in areas of Central to Southern Sumatra, where vernacular varieties of Malay are indigenous, Indonesians refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo-Polynesian Languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesian and Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula. Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan serve as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. The languages spoken south-westward from central Micronesia until Easter Island are sometimes referred to as the Polynesian languages. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family show the strong influence of Sanskrit and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam. Two morphological characteristics of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larantuka
Larantuka () is a ''kecamatan'' (district) and the seat capital of East Flores Regency, on the eastern end of Flores Island, East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. Like much of the region, Larantuka has a strong a colonial Portuguese influence. The town had 37,348 inhabitants at the 2010 census and 40,828 at the 2020 census. This overwhelmingly (95.4%) Roman Catholic area enjoys some international renown for its Holy Week celebrations. Indonesia Tourism: Larantuka (also known as Ende Malay), a local over 80% |


_(Musée_du_Caire)_(2076972086).jpg)

.jpg)

