|
Lake Killarney (Washington)
Lake Killarney is a lake in King County, Washington. It is located on the city line of Federal Way, Washington and the Lakeland South, Washington census designated place. It is popular for recreation, with fishing opportunities and a public park. The lake has suffered from arsenic pollution. Lake Killarney is one of several lakes in Lakeland South, including Lake Geneva, Fivemile Lake, and Trout Lake. Description Lake Killarney Open Space Park is a large park located on the lake's western shore. There is also a Washington State Department of Fish and Wildlife boat ramp on the northeastern corner, across the road from Lake Geneva. It has many fish species, including bluegill, brown bullhead, largemouth bass, pumpkinseed sunfish, rainbow trout, and yellow perch. Lake Killarney has a watershed. It is a moderately productive, mesotrophic lake. Nutrient concentrations have been generally decreasing over time, improving water quality. Arsenic pollution Lake Killarney is located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstate 5 In Washington
Interstate 5 (I-5) is an Interstate Highway on the West Coast of the United States that serves as the region's primary north–south route. It spans across the state of Washington, from the Oregon state border at Vancouver, through the Puget Sound region, to the Canadian border at Blaine. Within the Seattle metropolitan area, the freeway connects the cities of Tacoma, Seattle, and Everett. I-5 is the only interstate to traverse the whole state from north to south and is Washington's busiest highway, with an average of 274,000 vehicles traveling on it through Downtown Seattle on a typical day. The segment in Downtown Seattle is also among the widest freeways in the United States, at 13 lanes, and includes a set of express lanes that reverse direction depending on time of the day. Most of the freeway is four lanes in rural areas and six to eight lanes in suburban areas, utilizing a set of high-occupancy vehicle lanes in the latter. I-5 also has three related auxiliary In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
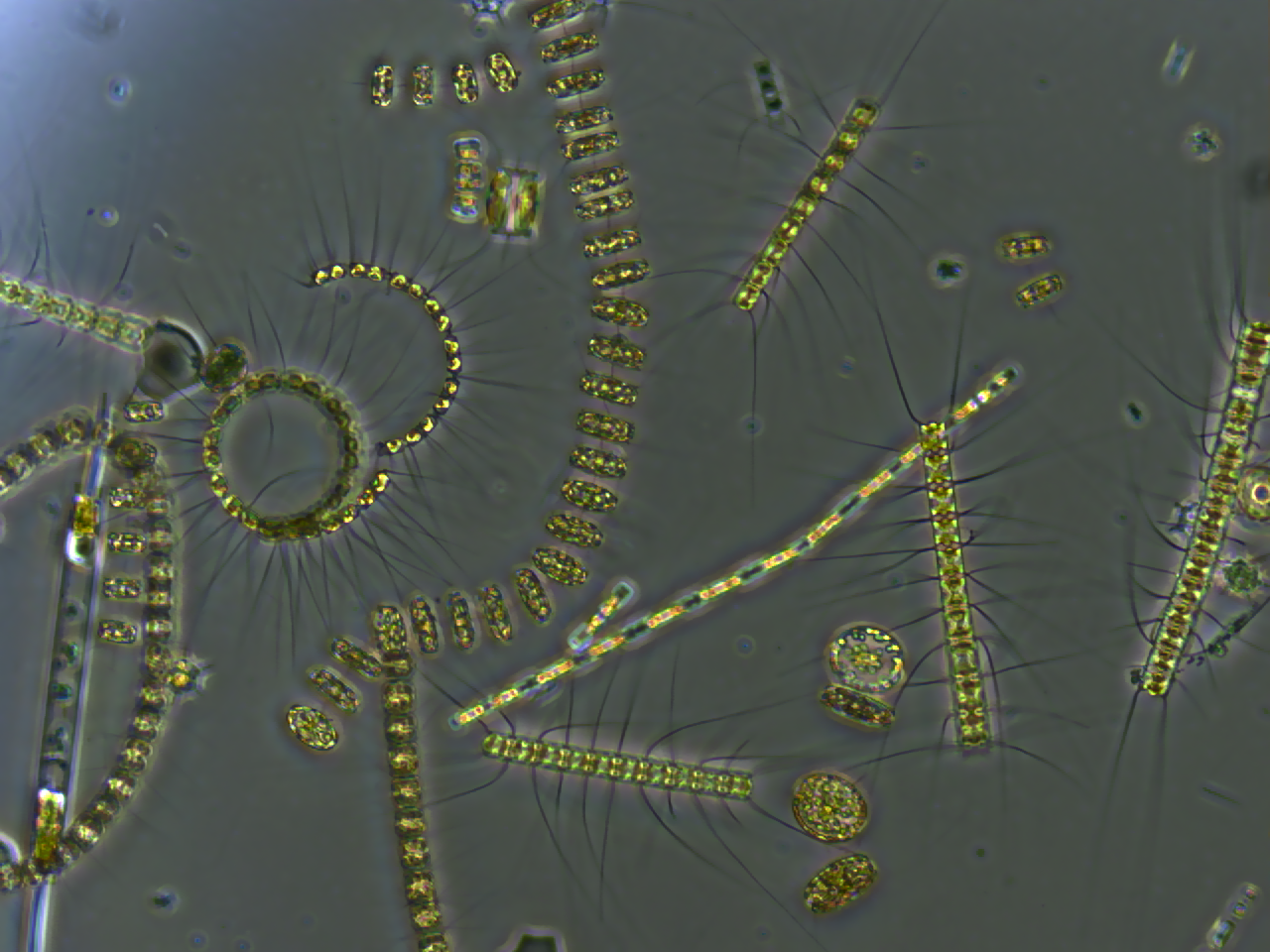
Mesotrophic Lake
The Trophic State Index (TSI) is a classification system designed to rate water bodies based on the amount of biological productivity they sustain. Although the term "trophic index" is commonly applied to lakes, any surface water body may be indexed. The TSI of a water body is rated on a scale from zero to one hundred. Under the TSI scale, water bodies may be defined as: * oligotrophic (TSI 0–40, having the least amount of biological productivity, "good" water quality); * mesotrophic (TSI 40–60, having a moderate level of biological productivity, "fair" water quality); or * eutrophic to hypereutrophic (TSI 60–100, having the highest amount of biological productivity, "poor" water quality). The quantities of nitrogen, phosphorus, and other biologically useful nutrients are the primary determinants of a water body's TSI. Nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus tend to be limiting resources in standing water bodies, so increased concentrations tend to result in increased p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakes Of King County, Washington
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation is the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a substance at a rate faster than that at which the substance is lost or eliminated by catabolism and excretion. Thus, the longer the biological half-life of a toxic substance, the greater the risk of chronic poisoning, even if environmental levels of the toxin are not very high. Bioaccumulation, for example in fish, can be predicted by models. Hypothesis for molecular size cutoff criteria for use as bioaccumulation potential indicators are not supported by data. Biotransformation can strongly modify bioaccumulation of chemicals in an organism. Toxicity induced by metals is associated with bioaccumulation and biomagnification. Storage or uptake of metals faster than the rate at which an organism metabolizes and excretes lead to the accumulation of that metal. The presence of various chemicals and harmful substances in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomagnification
Biomagnification, also known as bioamplification or biological magnification, is any concentration of a toxin, such as pesticides, in the tissues of tolerant organisms at successively higher levels in a food chain. This increase can occur as a result of: * Persistence – where the substance cannot be broken down by environmental processes * Food chain energetics – where the substance's concentration increases progressively as it moves up a food chain * Low or non-existent rate of internal degradation or excretion of the substance – mainly due to water-insolubility Biological magnification often refers to the process whereby certain substances such as pesticides or heavy metals work their way into lakes, rivers and the ocean, and then move up the food chain in progressively greater concentrations as they are incorporated into the diet of aquatic organisms such as zooplankton, which in turn are eaten perhaps by fish, which then may be eaten by bigger fish, large birds, ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram (compare copper at about 0.06 grams). In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate. Elemental phosphorus was first isolated as white phosphorus in 1669. White phosphorus emits a faint glow when exposed to oxygen – hence the name, taken from Greek mythology, meaning 'light-bearer' (Latin ), referring to the " Morning Star", the planet Venus. The term '' phosphorescence'', meaning glow after illumination, derives from this property of phosphorus, although the word has since been used for a different physical process that produces a glow. The glow of phosphorus is caused by oxidation of the white (but not red) phosphorus — a process now called chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Stratification
Lake stratification is the tendency of lakes to form separate and distinct thermal layers during warm weather. Typically stratified lakes show three distinct layers, the Epilimnion comprising the top warm layer, the thermocline (or Metalimnion): the middle layer, which may change depth throughout the day, and the colder Hypolimnion extending to the floor of the lake. Definition The thermal stratification of lakes refers to a change in the temperature at different depths in the lake, and is due to the density of water varying with temperature. Cold water is denser than warm water and the epilimnion generally consists of water that is not as dense as the water in the hypolimnion. However, the temperature of maximum density for freshwater is 4 °C. In Temperate climate, temperate regions where lake water warms up and cools through the seasons, a cyclical pattern of overturn occurs that is repeated from year to year as the cold dense water at the top of the lake sinks (see stab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Lake (Washington)
Angle Lake is an L-shaped lake in SeaTac, Washington, United States, occupying between Interstate 5 and State Route 99. The lake most likely was so named on account of its outline. On the western shore is a park, Angle Lake Park, administered by the City of SeaTac Parks and Recreation department. The remainder of the shoreline is ringed with private homes. The lake is stocked with rainbow trout by the Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife. It is also home to kokanee, largemouth bass, crappie, catfish, and yellow perch The yellow perch (''Perca flavescens''), commonly referred to as perch, striped perch, American perch, American river perch or preacher is a freshwater perciform fish native to much of North America. The yellow perch was described in 1814 by Sam .... The lake is open to fishing year-round. The Angle Lake light rail station is named for the lake, and is located to the southwest. Park Angle Lake Park was established in the 1920s. The entrance to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Washington
The University of Washington (UW, simply Washington, or informally U-Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington. Founded in 1861, Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast; it was established in Seattle approximately a decade after the city's founding. The university has a 703 acre main campus located in the city's University District, as well as campuses in Tacoma and Bothell. Overall, UW encompasses over 500 buildings and over 20 million gross square footage of space, including one of the largest library systems in the world with more than 26 university libraries, art centers, museums, laboratories, lecture halls, and stadiums. The university offers degrees through 140 departments, and functions on a quarter system. Washington is the flagship institution of the six public universities in Washington state. It is known for its medical, engineering, and scientific research. Washington is a member of the Association of American Universiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited to organolead compounds. Like the lighter members of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry. The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices. It is also a component of the III-V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the toxicity of arsenic and its compounds. A few species of bacteria are able to use arsenic compounds as respiratory metabolites. Trace quantities of arsenic are an essential dietary element in rats, ham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |