|
Lactucopicrin
Lactucopicrin (Intybin) is a bitter substance that has a sedative and analgesic effect, acting on the central nervous system. It is a sesquiterpene lactone, and is a component of lactucarium, derived from the plant ''Lactuca virosa'' (wild lettuce), as well as being found in some related plants such as ''Cichorium intybus''. It is also found in dandelion coffee. As well as their traditional use as sedatives and analgesics, these plants have also been used as antimalarials, and both lactucin and lactucopicrin have demonstrated antimalarial effects ''in vitro''. Lactucopicrin has also been shown to act as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. See also * Lactucin Lactucin is a bitter substance that forms a white crystalline solid and belongs to the group of sesquiterpene lactones. It is found in some varieties of lettuce and is an ingredient of lactucarium. It has been shown to have analgesic and sedativ ... References {{Acetylcholine metabolism and transport modulators Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactucarium
Lactucarium is the milky fluid secreted by several species of lettuce, especially ''Lactuca virosa'', usually from the base of the stems. It is known as lettuce opium because of its sedative and analgesic properties. It has also been reported to promote a mild sensation of euphoria. Because it is a latex, lactucarium physically resembles opium, in that it is excreted as a white fluid and can be reduced to a thick smokable solid. History "Lettuce opium" was used by the ancient Egyptians, and was introduced as a drug in the United States as early as 1799. The drug was prescribed and studied extensively in Poland during the nineteenth century, and was viewed as an alternative to opium, weaker but lacking side-effects, such as not being highly addictive, and in some cases preferable. However, early efforts to isolate an active alkaloid were unsuccessful. It is described and standardized in the 1898 United States Pharmacopoeia and 1911 ''British Pharmaceutical Codex'' for use in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesquiterpene Lactones
Sesquiterpene lactones (SLs) are a class of sesquiterpenoids that contain a lactone ring. They are most often found in plants of the family Asteraceae (daisies, asters). Other plant families with SLs are Umbelliferae (celery, parsley, carrots) and Magnoliaceae (magnolias). A collection of colorless, lipophilic solids, SLs are a rich source of drugs. They can be allergenic and toxic in grazing livestock causing severe neurological problems in horses. Some are also found in corals such as '' Maasella edwardsi''. Types Sesquiterpene lactones can be divided into several main classes including germacranolides, heliangolides, guaianolides, pseudoguaianolides, hypocretenolides, and eudesmanolides. Examples Artemisinin, a new, highly-effective anti-malarial compound, is a sesquiterpene lactone found in ''Artemisia annua''. Lactucin, desoxylactucin, lactucopicrin, lactucin-15-oxalate, lactucopicrin-15-oxalate are some of the most prominent found in lettuce and spinach, giving mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesquiterpene Lactone
Sesquiterpene lactones (SLs) are a class of sesquiterpenoids that contain a lactone ring. They are most often found in plants of the family Asteraceae (daisies, asters). Other plant families with SLs are Umbelliferae (celery, parsley, carrots) and Magnoliaceae (magnolias). A collection of colorless, lipophilic solids, SLs are a rich source of drugs. They can be allergenic and toxic in grazing livestock causing severe neurological problems in horses. Some are also found in corals such as '' Maasella edwardsi''. Types Sesquiterpene lactones can be divided into several main classes including germacranolides, heliangolides, guaianolides, pseudoguaianolides, hypocretenolides, and eudesmanolides. Examples Artemisinin, a new, highly-effective anti-malarial compound, is a sesquiterpene lactone found in ''Artemisia annua''. Lactucin, desoxylactucin, lactucopicrin, lactucin-15-oxalate, lactucopicrin-15-oxalate are some of the most prominent found in lettuce and spinach, giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactuca Virosa
''Lactuca virosa'' is a plant in the ''Lactuca'' (lettuce) genus, often ingested for its mild analgesic and sedative effects. It is related to common lettuce ('' L. sativa''), and is often called wild lettuce, bitter lettuce, laitue vireuse, opium lettuce, poisonous lettuce, tall lettuce, great lettuce or rakutu-karyumu-so. Description ''Lactuca virosa'' is biennial, similar to prickly lettuce ''Lactuca serriola'' but taller – it can grow to 200 cm (80 inches or almost 7 feet). It is also stouter, the stem and leaves are more purple flushed, and the leaves are less divided, but more spreading, similarly to '' Mycelis muralis'' but showing more than 5 florets. The achene is purple black, without bristles at the tip. The pappus is the same as ''Lactuca serriola''. In the northern hemisphere, it flowers from July until September. Distribution Found coastally in Great Britain, rarely in north-east of Ireland. ''Lactuca virosa'' is widespread across much of central and sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cichorium Intybus
Common chicory (''Cichorium intybus'') is a somewhat woody, perennial herbaceous plant of the family Asteraceae, usually with bright blue flowers, rarely white or pink. Native to the Old World, it has been introduced to North America and Australia. Many varieties are cultivated for salad leaves, chicons ( blanched buds), or roots (var. ''sativum''), which are baked, ground, and used as a coffee substitute and food additive. In the 21st century, inulin, an extract from chicory root, has been used in food manufacturing as a sweetener and source of dietary fiber. Chicory is grown as a forage crop for livestock. "Chicory" is also the common name in the United States for curly endive ('' Cichorium endivia''); these two closely related species are often confused. Description When flowering, chicory has a tough, grooved, and more or less hairy stem. It can grow to tall. The leaves are stalked, lanceolate and unlobed; they range from in length (smallest near the top) and wide. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedative
A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement. They are CNS depressants and interact with brain activity causing its deceleration. Various kinds of sedatives can be distinguished, but the majority of them affect the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). In spite of the fact that each sedative acts in its own way, most produce relaxing effects by increasing GABA activity. This group is related to hypnotics. The term ''sedative'' describes drugs that serve to calm or relieve anxiety, whereas the term ''hypnotic'' describes drugs whose main purpose is to initiate, sustain, or lengthen sleep. Because these two functions frequently overlap, and because drugs in this class generally produce dose-dependent effects (ranging from anxiolysis to loss of consciousness) they are often referred to collectively as ''sedative-hypnotic'' drugs. Sedatives can be used to produce an overly-calming effect ( alcohol being the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetate Esters
An acetate is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. alkaline, earthy, metallic, nonmetallic or radical base). "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion (specifically, the negatively charged ion called an anion) typically found in aqueous solution and written with the chemical formula . The neutral molecules formed by the combination of the acetate ion and a ''positive'' ion (called a cation) are also commonly called "acetates" (hence, ''acetate of lead'', ''acetate of aluminum'', etc.). The simplest of these is hydrogen acetate (called acetic acid) with corresponding salts, esters, and the polyatomic anion , or . Most of the approximately 5 billion kilograms of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In nature, acetate is the most common building block for biosynthesis. Nomenclature and common formula When part of a salt, the formula of the acetate ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
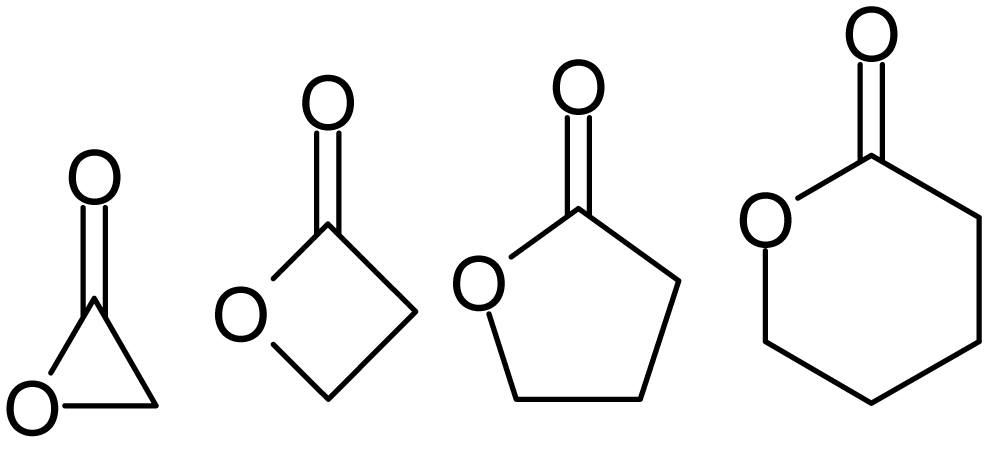
Lactones
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (— O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule. Phenols are both synthesized industrially and produced by plants and microorganisms. Properties Acidity Phenols are more acidic than typical alcohols. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12). Deprotonation of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides (aryloxides according to the IUPAC Gold Book). Condensation with aldehydes and ketones Phenols are susceptible to Electrophilic aromatic substitutions. Condensation with formald ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like TEPP and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The active centre of cholinesterases feature two important sites, namely the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |