|
Lactobacillus Salivarius
''Ligilactobacillus salivarius'' is a probiotic bacteria species that has been found to live in the gastrointestinal tract and exert a range of therapeutic properties including suppression of pathogenic bacteria. Therapeutic research Irritable bowel syndrome ''Ligilactobacillus salivarius'' has been found to be of benefit in the alleviation of the symptom flatulence in individuals suffering from irritable bowel syndrome. Pancreatic necrosis Pancreatic necrosis, if left untreated, has an almost 100 percent fatality rate due to bacterial translocation. ''Ligilactobacillus salivarius'' has been found to have a wide spectrum of coverage against pathogenic organisms that translocate from the gastrointestinal tract thereby demonstrating therapeutic benefit in the management of pancreatic necrosis. Research has shown that the addition of this species along with other probiotic species (specifically '' Bifidobacterium bifidum'', '' Bifidobacterium infantis'', '' Lactobacillus a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreatic Necrosis
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. Causes in order of frequency include: 1) a gallstone impacted in the common bile duct beyond the point where the pancreatic duct joins it; 2) heavy alcohol use; 3) systemic disease; 4) trauma; 5) and, in minors, mumps. Acute pancreatitis may be a single event; it may be recurrent; or it may progress to chronic pancreatitis. Mild cases are usually successfully treated with conservative measures: hospitalization, pain control, nothing by mouth, intravenous nutritional support, and intravenous fluid rehydration. Severe cases often require admission to an intensive care unit to monitor and manage complications of the disease. Complications are associated with a high mortality, even with optimal management. Signs and symptoms Common *severe epigastric pain (upper abdominal pain) radiating to the back in 50% of cases *nausea *vomiting *loss of appetite *fever *chills (shivering) *hemodynamic instability, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter. The small intestine has three distinct regions – the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum, the shortest, is where preparation for absorption through small finger-like protrusions called villi begins. The jejunum is specialized for the absorption through its lining by enterocytes: small nutrient particles which have been previously digested by enzymes in the duodenum. The main function of the ileum is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokines
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral and cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and Functio laesa, loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immune system, innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactococcus Lactis
''Lactococcus lactis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium used extensively in the production of buttermilk and cheese, but has also become famous as the first genetically modified organism to be used alive for the treatment of human disease. ''L. lactis'' cells are cocci that group in pairs and short chains, and, depending on growth conditions, appear ovoid with a typical length of 0.5 - 1.5 µm. ''L. lactis'' does not produce spores ( nonsporulating) and are not motile ( nonmotile). They have a homofermentative metabolism, meaning they produce lactic acid from sugars. They've also been reported to produce exclusive L-(+)-lactic acid. However, reported D-(−)-lactic acid can be produced when cultured at low pH. The capability to produce lactic acid is one of the reasons why ''L. lactis'' is one of the most important microorganisms in the dairy industry. Based on its history in food fermentation, ''L. lactis'' has generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status, with few case reports o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacticaseibacillus Casei
''Lacticaseibacillus casei ''is an organism that belongs to the largest genus in the family '' Lactobacillaceae'', a lactic acid bacteria (LAB), that was previously classified as ''Lactobacillus casei-01''. This bacteria has been identified as facultatively anaerobic or microaerophilic, acid-tolerant, non-spore-forming bacteria. The taxonomy of this group has been debated for several years because researchers struggled to differentiate between the strains of ''L. casei'' and ''L. paracasei''. It has recently been accepted as a single species with five subspecies: ''L. casei'' subsp. ''rhamnosus'', ''L. casei'' subsp. ''alactosus'', ''L. casei'' subsp. ''casei'', ''L. casei'' subsp. ''tolerans'', and ''L. casei'' subsp. ''pseudoplantarum''. The taxonomy of this genus was determined according to the phenotypic, physiological, and biochemical similarities. This species is a non-sporing, rod-shaped, gram positive microorganism that can be found within the reproductive and digestive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Acidophilus
''Lactobacillus acidophilus'' (New Latin 'acid-loving milk-bacillus') is a rod-shaped, Gram-positive, homofermentative, anaerobic microbe first isolated from infant feces in the year 1900. The species is most commonly found in humans, specifically the gastrointestinal tract, oral cavity, and vagina, as well as various fermented foods such as fermented milk or yogurt. The species most readily grows at low pH levels (below 5.0), and has an optimum growth temperature of 37 °C. Certain strains of ''L. acidophilus'' show strong probiotic effects, and are commercially used in dairy production. The genome of ''L. acidophilus'' has been sequenced. ''L. acidophilus'' has antagonistic effects on the growth for ''Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium,'' and ''Clostridium perfringens''. Out of the four organisms, ''Staphylococcus aureus'' is the most affected. Along with ''S. aureus'', the other Gram-positive bacteria, ''C. perfringens,'' was affected more by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bifidobacterium Infantis
''Bifidobacterium longum'' is a Gram-positive, catalase-negative, rod-shaped bacterium present in the human gastrointestinal tract and one of the 32 species that belong to the genus ''Bifidobacterium''. It is a microaerotolerant anaerobe and considered to be one of the earliest colonizers of the gastrointestinal tract of infants. When grown on general anaerobic medium, ''B. longum'' forms white, glossy colonies with a convex shape. While ''B. longum'' is not significantly present in the adult gastrointestinal tract, it is considered part of the gut microbiota and its production of lactic acid is believed to prevent growth of pathogenic organisms. ''B. longum'' is non-pathogenic and is often added to food products. Classification In 2002, three previously distinct species of ''Bifidobacterium'', ''B. infantis'', ''B. longum'', and ''B. suis'', were unified into a single species named ''B. longum'' with the biotypes ''infantis, longum,'' and ''suis'', respectively. This occurred a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bifidobacterium Bifidum
''Bifidobacterium bifidum'' is a bacterial species of the genus ''Bifidobacterium''. ''B. bifidum'' is one of the most common probiotic bacteria that can be found in the body of mammals, including humans. Structure and characteristics ''B. bifidum'' is a Gram-positive, anaerobic bacterium that is neither motile nor spore-forming. The bacterium is rod-shaped and can be found living in clusters, pairs, or even independently. The majority of the population of ''B. bifidum'' is found in the colon, lower small intestine, breast milk, and often in the vagina. ''B. bifidum'' is an essential bacteria found in the human intestine. When it is low or absent all together in the human intestine, it is an indication of being in an unhealthy state. Intestinal flora can be improved if someone takes oral ''B. bifidum''. Also, oral ''B. bifidum'' is used for other things such as therapy for enteric and hepatic disorders, for activating the immune response, and for preventing some cancers. ''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
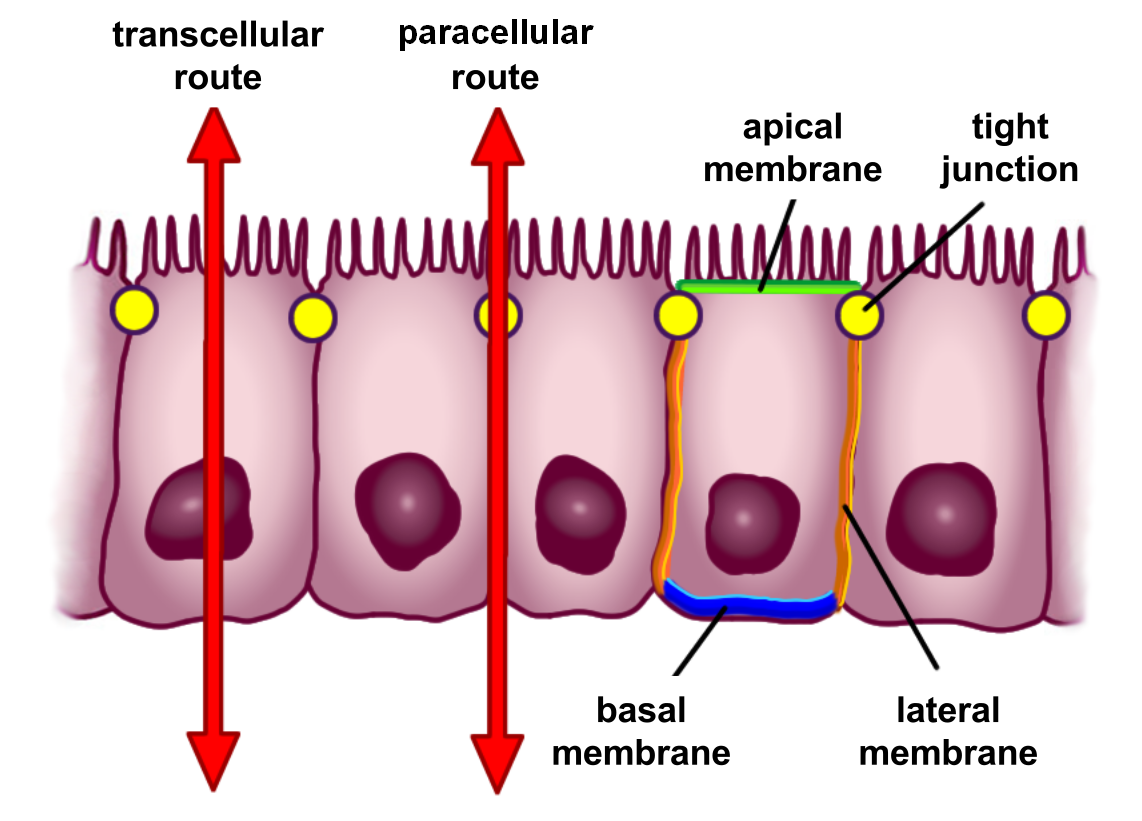
Bacterial Translocation
Intestinal permeability is a term describing the control of material passing from inside the gastrointestinal tract through the cells lining the gut wall, into the rest of the body. The intestine normally exhibits some permeability, which allows nutrients to pass through the gut, while also maintaining a barrier function to keep potentially harmful substances (such as antigens) from leaving the intestine and migrating to the body more widely. In a healthy human intestine, small particles (< 4 Å in radius) can migrate through tight junction claudin pore pathways, and particles up to 10–15 Å (3.5 kDa) can transit through the paracellular space uptake route. There is some evidence abnormally increased intestinal permeability may play a role in some chronic diseases and inflammatory conditions. The most well understood condition with observed increased intestinal permeability is celiac disease. Physiology The barrier formed by the intestinal epithelium separates the exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a "disorder of gut-brain interaction" characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain and or abdominal bloating and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may occur over a long time, sometimes for years. IBS can negatively affect quality of life and may result in missed school or work (absenteeism) or reduced productivity at work (presenteeism). Disorders such as anxiety, major depression, and chronic fatigue syndrome are common among people with IBS.The cited review is based on sources ranging from 1988 to 2001 and is probably biased relative to a more recent research. The causes of IBS may well be multi-factorial. Theories include combinations of " gut–brain axis" problems, alterations in gut motility, visceral hypersensitivity, infections including small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, neurotransmitters, genetic factors, and food sensitivity. Onset may be triggered by an intestina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)