|
Laciadae
Laciadae or Lakiadai ( grc, Λακιάδαι) was a deme of ancient Attica on the Sacred Way between Sciron and the Cephissus, and near the sacred fig-tree. It is celebrated as the deme to which the family of Miltiades and Cimon Cimon or Kimon ( grc-gre, Κίμων; – 450BC) was an Athenian ''strategos'' (general and admiral) and politician. He was the son of Miltiades, also an Athenian ''strategos''. Cimon rose to prominence for his bravery fighting in the naval Batt ... belonged. The site of Laciadae is tentatively located at . References Populated places in ancient Attica Former populated places in Greece Demoi {{AncientAttica-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimon
Cimon or Kimon ( grc-gre, Κίμων; – 450BC) was an Athenian ''strategos'' (general and admiral) and politician. He was the son of Miltiades, also an Athenian ''strategos''. Cimon rose to prominence for his bravery fighting in the naval Battle of Salamis (480 BC), during the Second Persian invasion of Greece. Cimon was then elected as one of the ten ''strategoi'', to continue the Persian Wars against the Achaemenid Empire. He played a leading role in the formation of the Delian League against Persia in 478 BC, becoming its commander in the early Wars of the Delian League, including at the Siege of Eion (476 BC). In 466 BC, Cimon led a force to Asia Minor, where he destroyed a Persian fleet and army at the Battle of the Eurymedon river. From 465 to 463 BC he suppressed the Thasian rebellion, in which the island of Thasos attempted to leave the Delian League. This event marked the transformation of the Delian League into the Athenian Empire. Cimon to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deme
In Ancient Greece, a deme or ( grc, δῆμος, plural: demoi, δημοι) was a suburb or a subdivision of Athens and other city-states. Demes as simple subdivisions of land in the countryside seem to have existed in the 6th century BC and earlier, but did not acquire particular significance until the reforms of Cleisthenes in 508 BC. In those reforms, enrollment in the citizen-lists of a deme became the requirement for citizenship; prior to that time, citizenship had been based on membership in a phratry, or family group. At this same time, demes were established in the main city of Athens itself, where they had not previously existed; in all, at the end of Cleisthenes' reforms, Athens was divided into 139 demes, to which one can be added Berenikidai (established in 224/223 BC), Apollonieis (201/200 BC), and Antinoeis (added in 126/127). The establishment of demes as the fundamental units of the state weakened the ''gene'', or aristocratic family groups, that had dominated t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Way
The Sacred Way ( grc, Ἱερὰ Ὁδός, ''Hierá Hodós''), in ancient Greece, was the road from Athens to Eleusis. It was so called because it was the route taken by a procession celebrating the Eleusinian Mysteries. The procession to Eleusis began at the Sacred Gate in the Kerameikos (the Athenian cemetery) on the 19th Boedromion. In the present day, the road from central Athens to Aegaleo and Chaidari (the old route to Eleusis) is called the Iera Odos after the ancient road. Mythos of Eleusis The sacred rites of Demeter were performed in Eleusis in Ancient Greece beginning as far back as the 15th Century BCE, according to some sources. According to the Homeric Hymns of the Archaic period, Demeter stopped at Eleusis during her quest for Persephone. The story describes how Demeter, persuaded to stay at the palace of Eleusis by its prince, Celeus, was given the task of raising Celeus's son Demophon. When she is discovered to be a Goddess by the queen Metaneira after try ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scirum
Scirum or Skiron ( grc, Σκίρον) or Skira (Σκίρα) was a small place in ancient Attica near a torrent of the same name, just outside the Athenian walls on the Sacred Way. It was not a demus, and derived its name from Scirus, a prophet of Dodona, who fell in the battle between the Eleusinii and Erechtheus Erechtheus (; grc, Ἐρεχθεύς) in Greek mythology was the name of an archaic king of Athens, the founder of the ''polis'' and, in his role as god, attached to Poseidon, as "Poseidon Erechtheus". The mythic Erechtheus and the historical Ere ..., and was buried in this spot. Scirum's site is unlocated. References Populated places in ancient Attica Former populated places in Greece Locations in Greek mythology Lost ancient cities and towns {{ancientAttica-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephissus (Athenian Plain)
Cephissus ( grc, Κήφισσος; el, Κηφισός, ''Kifisos'') is a river in the vicinity of Athens, Greece. Together with the neighbouring river Ilisos, it drains a catchment area of . The '' Bibliotheca'' (3.15.1) states that the legendary Erechtheus' wife Praxithea was daughter of Phrasimus (otherwise unknown to us) by Diogenia (otherwise unknown to us) daughter of Cephissus. The source of the river is in the saddle depression between the Parnitha and Penteli mountains. From there it flows generally southwest until it reaches the Phaleron Bay between Neo Faliro and Moschato Moschato ( el, Μοσχάτο) is a suburb in the southwestern part of the Athens agglomeration, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Moschato-Tavros, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. Geograph .... Presently the river flows near or under the Motorway 1 linking Athens and Thessaloniki for much of its length. This section of Motorway 1 is nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
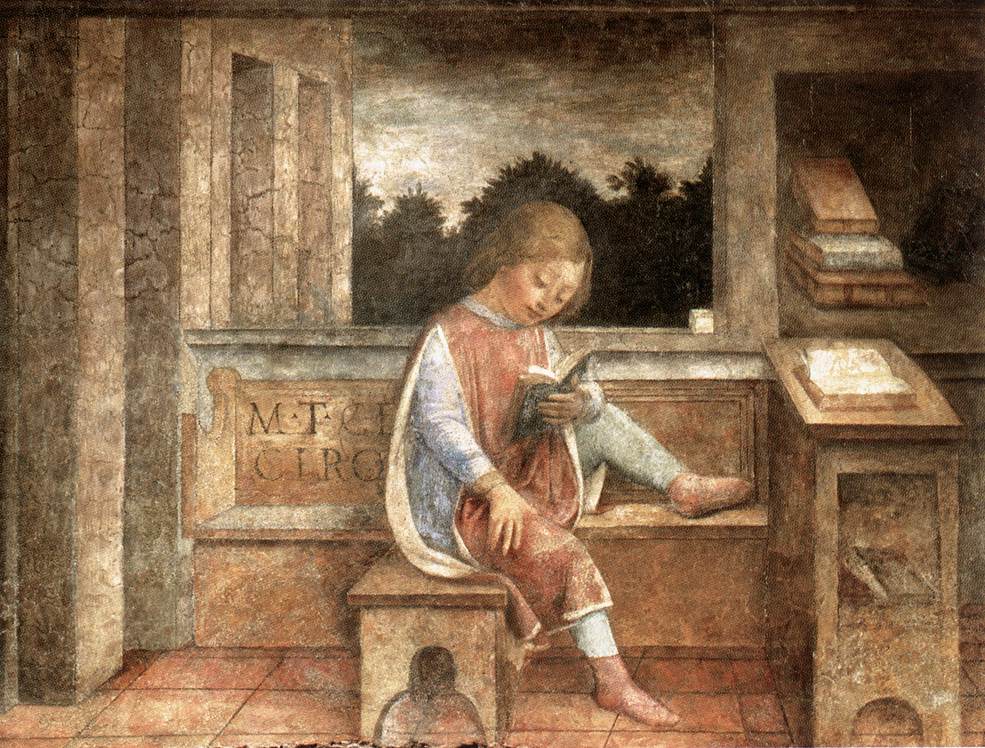
Miltiades
Miltiades (; grc-gre, Μιλτιάδης; c. 550 – 489 BC), also known as Miltiades the Younger, was a Greek Athenian citizen known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon, as well as for his downfall afterwards. He was the son of Cimon Coalemos, a renowned Olympic chariot-racer, and the father of Cimon, the noted Athenian statesman. Family Miltiades was a well-born Athenian, and considered himself a member of the Aeacidae, as well as a member of the prominent Philaid clan. He came of age during the tyranny of the Peisistratids. His family was prominent, due in good part to their success with Olympic chariot-racing.Creasy (1880) pg. 9 Plutarch claimed that Cimon, Miltiades' father, was known as "Coalemos", meaning "simpleton", because he had a reputation for being rough around the edges, but whose three successive chariot-racing victories at the Olympics made him popular, so popular in fact that, Herodotus claims, the sons of Peisistratos murdered him out of jeal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Life Early life Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His name is derived from Pluto (πλοῦτον), an epithet of Hades, and Archos (ἀρχός) meaning "Master", the whole name meaning something like "Whose master is Pluto". His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics, and he is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC. His influence on the Latin language was immense. He wrote more than three-quarters of extant Latin literature that is known to have existed in his lifetime, and it has been said that subsequent prose was either a reaction against or a return to his style, not only in Latin but in European languages up to the 19th century. Cicero introduced into Latin the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy and created a Latin philosophical vocabulary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Ancient Attica
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Greece
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |