|
LUSAS
LUSAS is a UK-based developer and supplier of Finite Element Analysis (FEA) application software products that bear the same name. History LUSAS has its origins back in 1970 when a group of research workers at the University of London (now incorporated into Imperial College London) began work on the London University Stress Analysis System, "LUSAS". This team was led by Dr. Paul Lyons, who, in 1982, set up an independent company, Finite Element Analysis Ltd., to further develop, and subsequently market the software as a general purpose structural analysis system. In 1997, following the introduction of a range of specialist application software packages, the company, for awareness reasons, then started to trade under the LUSAS name. Software LUSAS software consists of a Windows-based Modeller, used for model building and viewing of results, and a Solver for carrying out an analysis. Four commercial application products cater for the following industries: * Civil & Structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
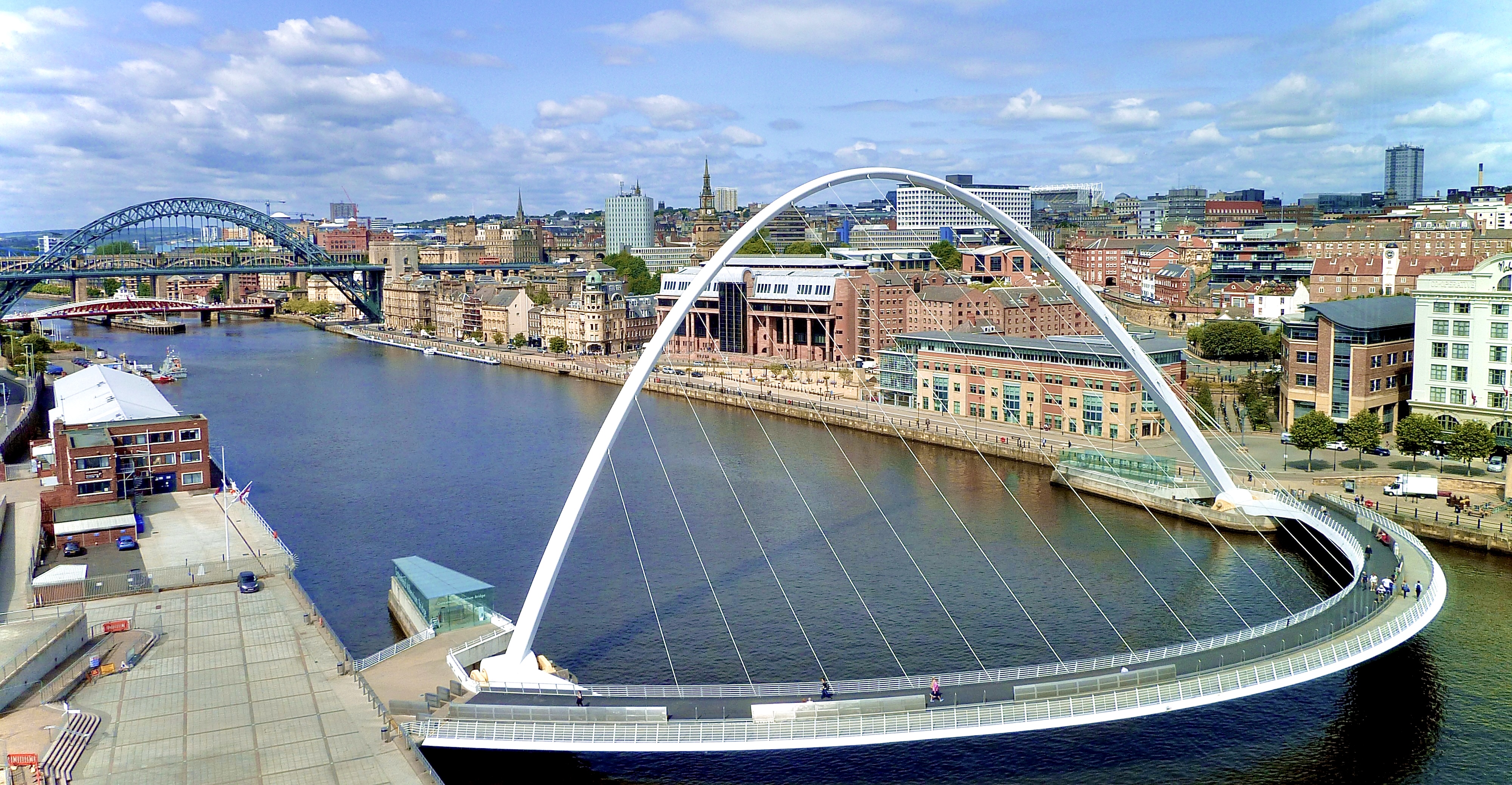
Gateshead Millennium Bridge
The Gateshead Millennium Bridge is a pedestrian and cyclist tilt bridge spanning the River Tyne between Gateshead arts quarter on the south bank and Newcastle upon Tyne's Quayside area on the north bank. It was the first tilting bridge ever to be constructed. Opened for public use in 2001, the award-winning structure was conceived and designed by architectural practice WilkinsonEyre and structural engineering firm Gifford. The bridge is sometimes called the 'Blinking Eye Bridge' or the 'Winking Eye Bridge' due to its shape and its tilting method. The Millennium Bridge stands as the twentieth tallest structure in the city, and is shorter in stature than the neighbouring Tyne Bridge. History Historical context Gateshead Millennium Bridge is part of a long history of bridges built across the River Tyne, the earliest of which was constructed in the Middle Ages. As quay-based industries grew during the Industrial Revolution and Victorian era due to its accessible port, the ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Cloud
The ''Quantum Cloud'' is a contemporary sculpture, designed by Antony Gormley, located next to The O2 in London. The sculpture was commissioned for the site and was completed in 1999. At high, it is Gormley's tallest sculpture to date (taller than the ''Angel of the North''). It is constructed from a collection of tetrahedral units made from long sections of steel. The steel sections were arranged using a computer model with a random walk algorithm starting from points on the surface of an enlarged figure based on Gormley's body that forms a residual outline at the centre of the sculpture. In designing ''Quantum Cloud'', Antony Gormley was influenced by Basil Hiley, quantum physicist (and long-time colleague of David Bohm). The idea for ''Quantum Cloud'' came from Hiley's thoughts on ''pre-space'' as a mathematical structure underlying space-time and matter, and his comment that “algebra is the relationship of relationships.” The comment was made during a conversation betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinnaker Tower
The Spinnaker Tower is a landmark observation tower in Portsmouth, England. It is the centrepiece of the redevelopment of Portsmouth Harbour, which was supported by a National Lottery grant. The tower's design was chosen by Portsmouth residents from a selection of three different designs in a 1998 public poll. It has three viewing platforms one on top of the other at heights of 100 m, 105 m and 110 m. The tower was designed by local firm HGP Architects and engineering consultants Scott Wilson and built by Mowlem. The Spinnaker Tower reflects Portsmouth's maritime history through its design and is named after a spinnaker, a type of sail that balloons outward. The tower was opened on 18 October 2005. The tower is owned by Portsmouth City Council and is operationally managed by Continuum Leading Attractions, a cultural attractions group based in York. Continuum also runs five other visitor attractions across the country. The Spinnaker Tower was repainted and rebranded as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone. The first version of Windows was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Windows is the most popular desktop operating system in the world, with Usage share of operating systems, 75% market share , according to StatCounter. However, Windows is not the most used operating system when including both mobile and desktop OSes, due to Android (operating system), Android's massive growth. , the most recent version of Windows is Windows 11 for consumer Personal compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delamination
Delamination is a mode of failure where a material fractures into layers. A variety of materials including laminate composites and concrete can fail by delamination. Processing can create layers in materials such as steel formed by rolling and plastics and metals from 3D printing which can fail from layer separation. Also, surface coatings such as paints and films can delaminate from the coated substrate. In laminated composites, the adhesion between layers often fails first causing the layers to separate. For example, in fiber-reinforced plastics, sheets of high strength reinforcement (e.g., carbon fiber, fiberglass) are bound together by a much weaker polymer matrix (e.g., epoxy). In particular, loads applied perpendicular to the high strength layers, and shear loads can cause the polymer matrix to fracture or the fiber reinforcement to debond from the polymer. Delamination also occurs in reinforced concrete when metal reinforcements near the surface corrode. The oxidize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Material
A composite material (also called a composition material or shortened to composite, which is the common name) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions. Typical Materials, engineered composite materials include: *Reinforced concrete and masonry *Composite wood such as plywood *Reinforced plastics, such as fibre-reinforced polymer or fiberglass *Ceramic matrix composites (composite armor, composite ceramic and metal matrices) *Metal matrix composites *and other Advanced composite materials (engineering), advanced composite materials There are various reasons where new material can be favoured. Typical examples include materials which are less ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hip Replacement
Hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the hip joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant, that is, a hip prosthesis. Hip replacement surgery can be performed as a total replacement or a hemi (half) replacement. Such joint replacement orthopaedic surgery is generally conducted to relieve arthritis pain or in some hip fractures. A total hip replacement (total hip arthroplasty or THA) consists of replacing both the acetabulum and the femoral head while hemiarthroplasty generally only replaces the femoral head. Hip replacement is one of the most common orthopaedic operations, though patient satisfaction varies widely. Approximately 58% of total hip replacements are estimated to last 25 years. The average cost of a total hip replacement in 2012 was $40,364 in the United States, and about $7,700 to $12,000 in most European countries. Medical uses Total hip replacement is most commonly used to treat joint failure caused by osteoarthritis. Other indications include rheumatoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, and brick. The earliest ceramics made by humans were pottery objects (''pots,'' ''vessels or vases'') or figurines made from clay, either by itself or mixed with other materials like silica, hardened and sintered in fire. Later, ceramics were glazed and fired to create smooth, colored surfaces, decreasing porosity through the use of glassy, amorphous ceramic coatings on top of the crystalline ceramic substrates. Ceramics now include domestic, industrial and building products, as well as a wide range of materials developed for use in advanced ceramic engineering, such as in semiconductors. The word "'' ceramic''" comes from the Greek word (), "of pottery" or "for pottery", from (), "potter's clay, tile, pottery". The earliest k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titan (mythology), Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll process, Kroll and Hunter process, Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide, is a popular photocatalysis, photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
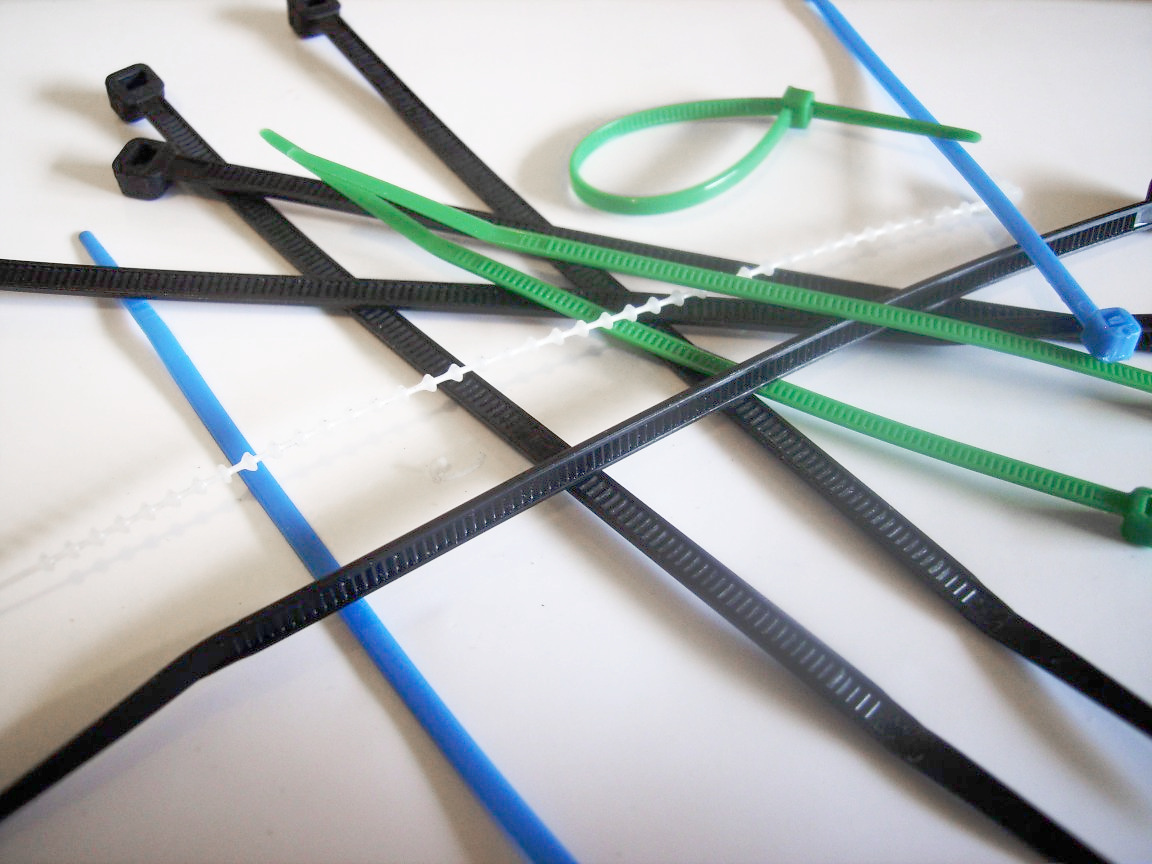
Cable Tie
A cable tie (also known as a hose tie, zip tie, or tie wrap) is a type of fastener for holding items together, primarily electrical cables and wires. Because of their low cost, ease of use, and binding strength, cable ties are ubiquitous, finding use in a wide range of other applications. Cable ties were first manufactured by Thomas & Betts under the brand name . The common cable tie, normally made of nylon, has a flexible tape section with teeth that engage with a pawl in the head to form a ratchet so that as the free end of the tape section is pulled the cable tie tightens and does not come undone. Some ties include a tab that can be depressed to release the ratchet so that the tie can be loosened or removed, and possibly reused. Stainless steel versions, some coated with a rugged plastic, cater for exterior applications and hazardous environments. Design and use The most common cable tie consists of a flexible nylon tape with an integrated gear rack, and on one end a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Loading Arm
A marine loading arm, also known as a mechanical loading arm, loading arm, or MLA is a mechanical arm consisting of articulated steel pipes that connect a tankship such as an oil tanker or chemical tanker to a cargo terminal. Genericized trademarks such as Chiksan (often misspelled Chicksan) are often used to refer to marine loading arms.Huber, 2001, p.83.Hayler and Keever, 2001, p. G-7. Operation and design A marine loading arm is an alternative to direct hose hookups that is particularly useful for larger vessels and transfers at higher loading rates and pressures. Controlled manually or hydraulically, a loading arm employs swivel joints and can, to some extent, follow the movement of a moored vessel.Hayler and Keever, 2001, p. 14-10 to 14-11. Many loading arm systems feature quick-connect fittings. Gasket or o-ring arrangements are required to make a secure seal to the ship's manifold flange. A loading arm must be drained or closed off before the connection is broken off.Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It is one of the oldest and broadest of the engineering branches. Mechanical engineering requires an understanding of core areas including mechanics, dynamics, thermodynamics, materials science, structural analysis, and electricity. In addition to these core principles, mechanical engineers use tools such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and product lifecycle management to design and analyze manufacturing plants, industrial equipment and machinery, heating and cooling systems, transport systems, aircraft, watercraft, robotics, medical devices, weapons, and others. Mechanical engineering emerged as a field during the Industrial Revolution in Europe in the 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |