|
Kyra Panagia
Kyra Panagia ( el, Κυρά Παναγιά ) is a Greek island in the Sporades. It is administratively part of the municipality of Alonnisos in the Sporades regional unit. The island is also known by the name of Pelagos and rarely Pelagonisi. . A bay in the south west of the island is named Agios Petros. Kyra Panagia has belonged to the Athonite monastery of Megisti Lavra since it was granted the island by the Byzantine emperor Nikephoros II Phokas in 963. There is a monastery renovated in 2017 after 8 years of work and inhabited by a single monk, on the east coast of the island. , the resident population of the island was 2. Kyra Panagia is in Zone B of the Alonnisos Marine Park. Nearest islands and islets Its nearest islands and islets are Gioura to the northeast and the main island of Alonnisos Alonnisos ( el, Αλόννησος ), also transliterated as Alonissos, is a Greek island in the Aegean Sea. After Skiathos and Skopelos it is the third member of the Northern Sporades. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporades
The (Northern) Sporades (; el, Βόρειες Σποράδες, ) are an archipelago along the east coast of Greece, northeast of the island of Euboea,"Skyros - Britannica Concise" (description), Britannica Concise, 2006, webpageEB-Skyrosnotes "including Skiathos, Skopelos, Skyros, and Alonnisos." in the Aegean Sea. They consist of 24 islands, four of which are permanently inhabited: Alonnisos, Skiathos, Skopelos and Skyros. They may also be referred to as the Thessalian Sporades (). Etymology "Sporades" means "those scattered" (compare with "sporadic"). From Classical Antiquity the name has referred to the Aegean island groups outside the central archipelago of the Cyclades. Geography In modern geographical parlance, there are five different Sporades groups: * Thessalian Sporades () or Northern Sporades. Since 1960, the term "Sporades" refers mainly to these islands: **Skopelos ** Alonnisos ** Skiathos ** Skyros ** Kyra Panagia ** Peristera ** Gioura ** Skantzoura ** Piperi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
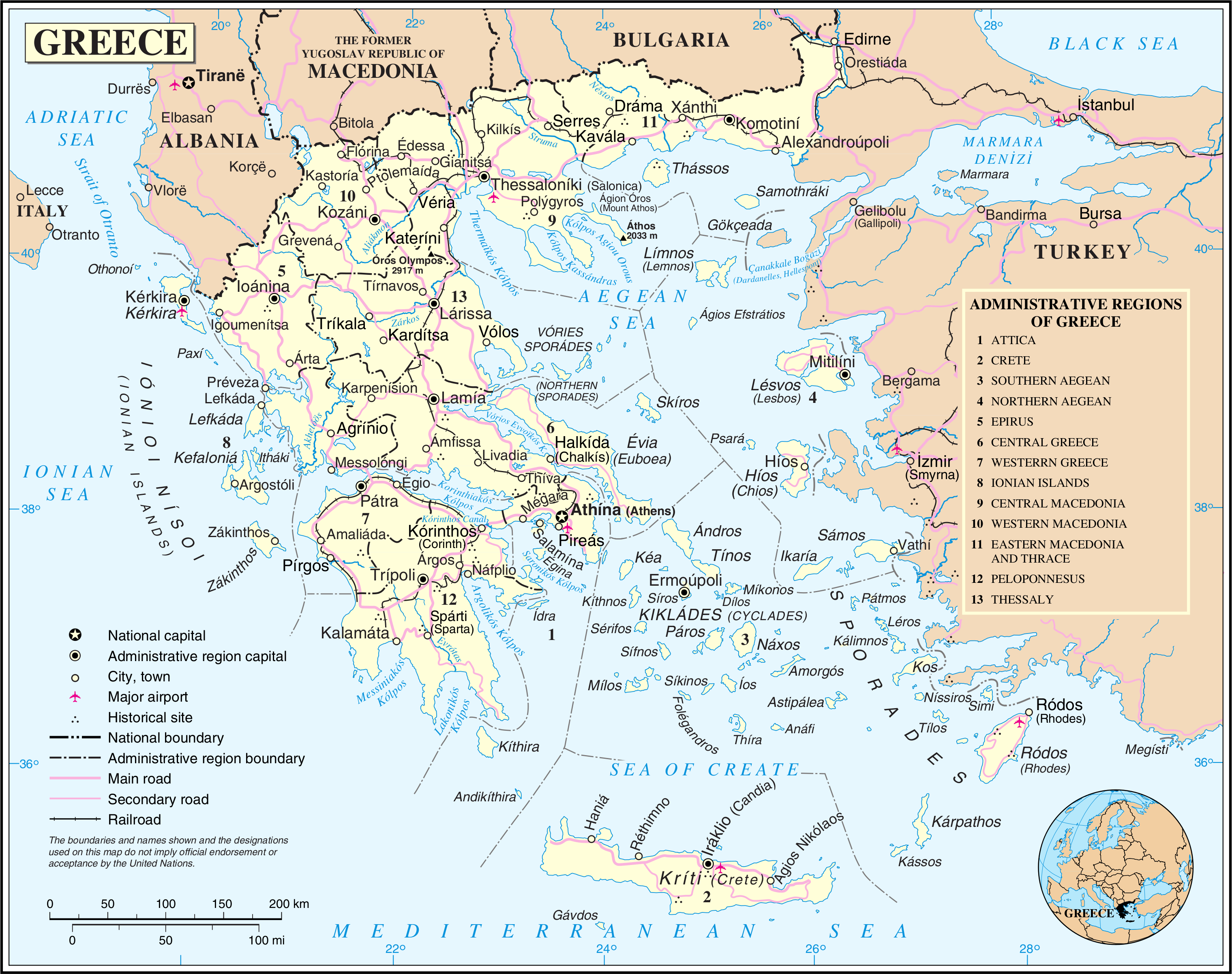
Modern Regions Of Greece
The regions of Greece ( el, περιφέρειες, translit=periféries) are the country's thirteen first-level administrative entities, each comprising several second-level units, originally known as prefectures and, since 2011, as regional units. History The current regions were established in July 1986 (the presidential decree officially establishing them was signed in 1987), by decision of the interior minister, Menios Koutsogiorgas, as second-level administrative entities, complementing the prefectures (Law 1622/1986). Ν.1622/86 "Τοπική Αυτοδιοίκηση - Περιφερειακή Ανάπτυξη - Δημοκρατικός Προγραμματισμός", (ΦΕΚ 92/τ.Α΄/14-7-1986) Before 1986, there was a traditional division into broad historical–geographical regions (γεωγραφικά διαμερίσματα), which, however, was often arbitrary; not all of the pre-1986 traditional historical-geographic regions had official administrative bodie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thessaly was known as Aeolia (, ), and appears thus in Homer's ''Odyssey''. Thessaly became part of the modern Greek state in 1881, after four and a half centuries of Ottoman rule. Since 1987 it has formed one of the country's 13 regions and is further (since the Kallikratis reform of 2011) sub-divided into five regional units and 25 municipalities. The capital of the region is Larissa. Thessaly lies in northern Greece and borders the regions of Macedonia on the north, Epirus on the west, Central Greece on the south, and the Aegean Sea on the east. The Thessaly region also includes the Sporades islands. Name and etymology Thessaly is named after the ''Thessaloi'', an ancient Greek tribe. The meaning of the name of this tribe is unknow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Units Of Greece
The 74 regional units of Greece ( el, περιφερειακές ενότητες, ; sing. , ) are the country's Seventy-four second-level administrative units. They are divisions of the country's 13 regions, and are further divided into municipalities. They were introduced as part of the Kallikratis administrative reform on 1 January 2011 and are comparable in area and, in the mainland, coterminous with the 'pre-Kallikratis' prefectures of Greece During the first administrative division of independent Greece in 1833–1836 and again from 1845 until their abolition with the Kallikratis reform in 2010, the prefectures ( el, νομοί, sing. νομός, translit=nomoi, sing. nomós) were .... List References {{Articles on second-level administrative divisions of European countries Regional units Greece transport-related lists Subdivisions of Greece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alonnisos
Alonnisos ( el, Αλόννησος ), also transliterated as Alonissos, is a Greek island in the Aegean Sea. After Skiathos and Skopelos it is the third member of the Northern Sporades. It is (2 nm) east of the island of Skopelos. Alonnisos is also the name of a village on the island, as well as the Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality that encompasses the island and the village. The village of Alonnisos is located on the southern part of the island. It is locally known as Chora and signposted as The Old Village. The main port of the island is located in the southeast and is called Patitiri. There are ferry, catamaran ("flying cat") and hydrofoil ("flying dolphin") services from Patitiri to Volos, Agios Konstantinos, Phthiotis, Agios Konstantinos, and Thessaloniki on the mainland and to the islands of Skiathos, Skopelos and Skyros. The bay at the southern end of the island is also called Alonnisos. The Municipality of Alonnisos includes the nearby islands o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands. The country consists of nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions, and has a population of approximately 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilization, being the birthplace of Athenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch ''eiland'' ("island"), German ''Eiland'' ("small island")). However, the spelling of the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome known as the Greco-Roman world. It is the period in which both Greek and Roman societies flourished and wielded huge influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia. Conventionally, it is taken to begin with the earliest-recorded Epic Greek poetry of Homer (8th–7th-century BC), and continues through the emergence of Christianity (1st century AD) and the fall of the Western Roman Empire (5th-century AD). It ends with the decline of classical culture during late antiquity (250–750), a period overlapping with the Early Middle Ages (600–1000). Such a wide span of history and territory covers many disparate cultures and periods. ''Classical antiquity'' may also refer to an idealized v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Athos
Mount Athos (; el, Ἄθως, ) is a mountain in the distal part of the eponymous Athos peninsula and site of an important centre of Eastern Orthodox monasticism in northeastern Greece. The mountain along with the respective part of the peninsula have been governed as the monastic community of Mount Athos, an autonomous region within the Hellenic Republic, ecclesiastically under the direct jurisdiction of the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople, while the remainder of the peninsula forms part of the Aristotelis municipality. Mount Athos has been inhabited since ancient times and is known for its long Christian presence and historical monastic traditions, which date back to at least AD 800 and the Byzantine era. Because of its long history of religious importance, the well-preserved agrarian architecture within the monasteries, and the preservation of the flora and fauna around the mountain, Mount Athos was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1988. In modern Greek, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megisti Lavra
The Monastery of Great Lavra ( el, Μονή Μεγίστης Λαύρας) is the first monastery built on Mount Athos. It is located on the southeastern foot of the Mount at an elevation of . The founding of the monastery in AD 963 by Athanasius the Athonite marks the beginning of the organized monastic life at Mount Athos. At the location of the monastery, there was one of the ancient cities of the Athos peninsula, perhaps Akrothooi, from which the sarcophagi of the monastery that are in the oil storage house come. The history of the monastery is the most complete compared to the history of the other monasteries, because its historical archives were preserved almost intact. It is possible that the study of these archives may contribute to the completion of the knowledge of the history of other monasteries, whose archives were partially or completely lost. Founding The founder of Great Lavra, Athanasius, began the construction of the buildings in 963, according to the will of hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros II Phokas
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless included brilliant military exploits which contributed to the resurgence of the Byzantine Empire during the 10th century. In the east, Nikephoros completed the conquest of Cilicia and even retook the islands of Crete and Cyprus, thus opening the path for subsequent Byzantine incursions reaching as far as Upper Mesopotamia and the Levant; these campaigns earned him the sobriquet "pale death of the Saracens". Meanwhile in the west, he inflamed conflict with the Bulgarians and saw Sicily completely turn over to the Muslims, while he failed to make any serious gains in Italy following the incursions of Otto I. At home, Nikephoros' administrative policies caused controversy. He financed his wars with increased taxes both on the people and on the church, while maintaining unpopular th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alonnisos Marine Park
The National Marine Park of Alonnisos Northern Sporades ( el, Εθνικό Θαλάσσιο Πάρκο Αλοννήσου Βορείων Σποράδων, ΕΘΠΑΒΣ) was founded by Presidential Decree on May 16, 1992. It was the first of its kind in Greece, and is currently the largest marine protected area in Europe (approximately 2,260 km2). Besides the sea area, the park includes the island of Alonnisos, six smaller islands ( Peristera, Kyra Panagia, Gioura, Psathoura, Piperi and Skantzoura), as well as 22 uninhabited islets and rocky outcrops. It is located in the region of the Northern Sporades Islands, in the northern Aegean Sea. There is one other marine park in Greece, namely Zakynthos Marine Park. History Thomas Schultze-Westrum, a German zoologist and maker of animal documentaries, after a series of exploratory missions to the islands in 1976, noted the great ecological and biological value for the first time and proposed the creation of protected area. Six yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |