|
Kura (deity)
Kura was a god worshiped in Ebla (modern Tell Mardikh in Syria) in the third millennium BCE. He was the tutelary god of the city, as well as the head of the local pantheon. While his functions are difficult to ascertain, it is well attested that he was connected to the institution of kingship. The etymology of his name is presently unknown, and it is commonly assumed that it belongs to an unknown linguistic substrate, similar to the names of some of the other Eblaite deities, such as Aštabi, Hadabal or Ishara. Kura's spouse was the goddess Barama, who like him was only worshiped in Ebla. After the destruction of the city both of them disappear from records. A number of proposals have been made regarding identification of deities attested from later periods with Kura, but most of them are not widely accepted. Name and origin The oldest attestations of Kura come from administrative texts predating the destruction of Ebla by thirty five to forty years. The name of the god is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
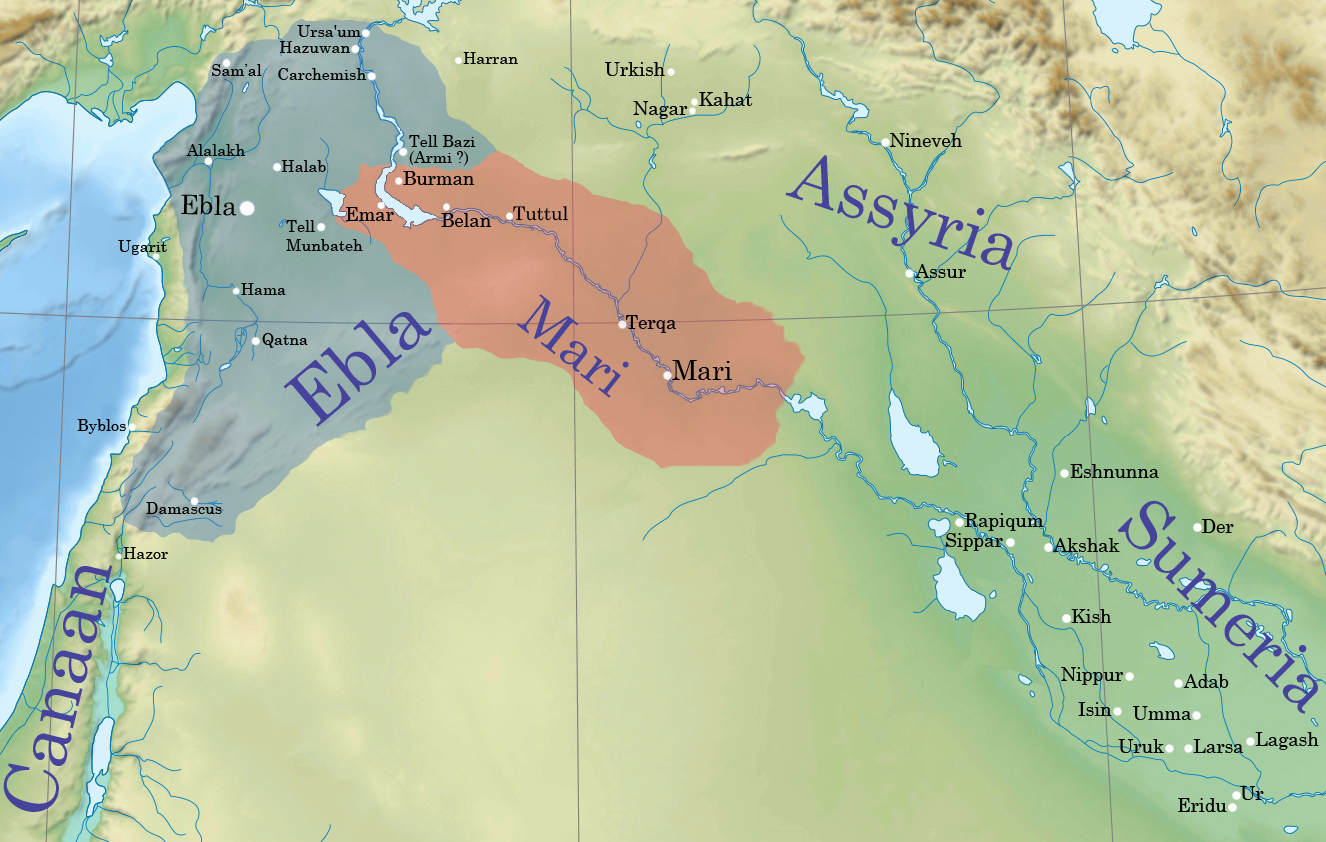
Ebla
Ebla ( Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla was a continuation of the first, ruled by a new royal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadad
Hadad ( uga, ), Haddad, Adad (Akkadian: 𒀭𒅎 '' DIM'', pronounced as ''Adād''), or Iškur ( Sumerian) was the storm and rain god in the Canaanite and ancient Mesopotamian religions. He was attested in Ebla as "Hadda" in c. 2500 BCE. From the Levant, Hadad was introduced to Mesopotamia by the Amorites, where he became known as the Akkadian (Assyrian-Babylonian) god Adad. Adad and Iškur are usually written with the logogram —the same symbol used for the Hurrian god Teshub. Hadad was also called Pidar, Rapiu, Baal-Zephon, or often simply Baʿal (Lord), but this title was also used for other gods. The bull was the symbolic animal of Hadad. He appeared bearded, often holding a club and thunderbolt while wearing a bull-horned headdress. Hadad was equated with the Greek god Zeus, the Roman god Jupiter (and in the cult-center near Doliche in Asia Minor he was addressed as Jupiter Dolichenus), as well as the Hittite storm-god Teshub. The Baal Cycle, also known as the Epi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagan (god)
Dagon ( he, דָּגוֹן, ''Dāgōn'') or Dagan ( sux, 2= dda-gan, ; phn, 𐤃𐤂𐤍, Dāgān) was a god worshipped in ancient Syria across the middle of the Euphrates, with primary temples located in Tuttul and Terqa, though many attestations of his cult come from cities such as Mari and Emar as well. In settlements situated in the upper Euphrates area he was regarded as the "father of gods" similar to Mesopotamian Enlil or Hurrian Kumarbi, as well as a lord of the land, a god of prosperity, and a source of royal legitimacy. A large number of theophoric names, both masculine and feminine, attests that he was a popular deity. He was also worshiped further east, in Mesopotamia, where many rulers regarded him as the god capable of granting them kingship over the western areas. Attestations of Dagan from coastal areas are much less frequent and come mostly from the northern city of Ugarit, where Dagan's cult had a limited scope. According to the Hebrew Bible, Dagan was als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Brak
Tell Brak (Nagar, Nawar) was an ancient city in Syria; its remains constitute a tell located in the Upper Khabur region, near the modern village of Tell Brak, 50 kilometers north-east of Al-Hasaka city, Al-Hasakah Governorate. The city's original name is unknown. During the second half of the third millennium BC, the city was known as Nagar and later on, Nawar. Starting as a small settlement in the seventh millennium BC, Tell Brak evolved during the fourth millennium BC into one of the biggest cities in Upper Mesopotamia, and interacted with the cultures of southern Mesopotamia. The city shrank in size at the beginning of the third millennium BC with the end of Uruk period, before expanding again around c. 2600 BC, when it became known as Nagar, and was the capital of a regional kingdom that controlled the Khabur river valley. Nagar was destroyed around c. 2300 BC, and came under the rule of the Akkadian Empire, followed by a period of independence as a Hurrian city-state, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouflons
The mouflon (''Ovis gmelini'') is a wild sheep native to Cyprus, the Caspian region from eastern Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran. It is thought to be the ancestor of all modern domestic sheep breeds. Taxonomy ''Ovis gmelini'' was the scientific name proposed by Edward Blyth in 1841 for wild sheep in the Middle East. In the 19th and 20th centuries, several wild sheep were described that are considered mouflon subspecies today: * ''Ovis ophion'' by Blyth in 1841 for wild sheep in Cyprus; * ''Ovis laristanica'' by Nikolai Nasonov in 1909 for wild sheep in Lar in southern Iran; * ''Ovis orientalis isphahanica'' by Nasonov in 1910 for wild sheep in the Zagros Mountains. Subspecies Five mouflon subspecies of are distinguished by MSW3: * Armenian mouflon (Armenian red sheep), ''O. g. gmelini'' : nominate subspecies; native to northwestern Iran, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. It has been introduced to Texas in the U.S. * Esfahan mouflon, ''O. g. isphahanica'' : Zagros Mountains, Ira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dying God
A dying god, or departure of the gods, is a motif in mythology in which one or more gods (of a pantheon) die, are destroyed, or depart permanently from their place on Earth to elsewhere. Frequently cited examples of dying gods are Baldr in Norse mythology, or Quetzalcoatl in Aztec mythology. A special subcategory is the death of an entire pantheon, the most notable example being Ragnarök in Norse mythology, or Cronus and the Titans from Greek mythology, with other examples from Ireland, India, Hawaii and Tahiti. Examples of the disappearing god in Hattian and Hittite mythology include Telipinu and Hannahanna. "Death or departure of the gods" is motif A192 in Stith Thompson's '' Motif-Index of Folk-Literature'', with the following subcategories:S. Thompson, ''Motif-index of folk-literature : a classification of narrative elements in folktales, ballads, myths, fables, medieval romances, exempla, fabliaux, jest-books, and local legends'', Revised and enlarged. edition. Blooming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baal
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific meaning "owner", "lord" in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during Ancient Near East, antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied to gods. Scholars previously associated the theonym with solar god, solar cults and with a variety of unrelated patron deity, patron deities but inscriptions have shown that the name Ba'al was particularly associated with the storm god, storm and fertility god Hadad and his local manifestations. The Hebrew Bible includes use of the term in reference to various Levantine mythology, Levantine deities, often with application towards Hadad, who was decried as a false god. That use was taken over into Christianity and Islam, sometimes under the form Beelzebub in demonology. Etymology The spelling of the English term "Baal" derives from the Koine Greek, Greek ''Báal'' ( which appears in the New Testament and Septuagint, and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ninurta
, image= Cropped Image of Carving Showing the Mesopotamian God Ninurta.png , caption= Assyrian stone relief from the temple of Ninurta at Kalhu, showing the god with his thunderbolts pursuing Anzû, who has stolen the Tablet of Destinies from Enlil's sanctuary (Austen Henry Layard ''Monuments of Nineveh'', 2nd Series, 1853) , parents=Enlil and Ninhursag As Urash, An , deity_of=God of agriculture, hunting, and war , abode=Eshumesha temple in NippurLater Kalhu, during Assyrian times , symbol=Plow and perched bird , consort= ''As Ninurta:'' Gula''As Ninĝirsu:'' Bau , children= , planet=Saturn, Mercury , mount= Beast with the body of a lion and the tail of a scorpion , equivalent1_type = Caananite , equivalent1 = Attar , equivalent2_type = Eblaite , equivalent2 = Aštabi Ninurta ( sux, : , possible meaning "Lord fBarley"), also known as Ninĝirsu ( sux, : , meaning "Lord fGirsu"), is an ancient Mesopotamian god associated with farming, healing, hunting, law, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nergal
Nergal ( Sumerian: d''KIŠ.UNU'' or ; ; Aramaic: ܢܸܪܓܲܠ; la, Nirgal) was a Mesopotamian god worshiped through all periods of Mesopotamian history, from Early Dynastic to Neo-Babylonian times, with a few attestations under indicating his cult survived into the period of Achaemenid domination. He was primarily associated with war, death, and disease and has been described as the "god of inflicted death." He reigned over Kur, the Mesopotamian underworld, depending on the myth either on behalf of his parents Enlil and Ninlil, or in later periods as a result of his marriage with the goddess Ereshkigal. Originally either Mammitum, a goddess possibly connected to frost, or Laṣ, sometimes assumed to be a minor medicine goddess, were regarded as his wife, though other traditions existed, too. His primary cult center was Kutha, located in northern Mesopotamia. His main temple was the E-Meslam and he was also known by the name Meslamtaea, "he who comes out of Meslam." Initially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resheph
Resheph (also Reshef and many other variants, see below; phn, 𐤓𐤔𐤐, ''ršp''; Eblaite ''Rašap'', Egyptian ') was a deity associated with plague (or a personification of plague), either war or strong protection, and sometimes thunder in ancient Canaanite religion. The originally Eblaite and Canaanite god was then more famously adopted into ancient Egyptian religion in the late Bronze Age during the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt (late fifteenth century BC), also becoming associated with horses and chariots. In Biblical Hebrew, ''resheph'' is a noun interpreted as "flame, lightning" but also "burning fever, plague, pestilence". Etymology Resheph is known by a multitude of names, including Rahshaf, Rasap, Rashap, Resep, Reshef, Reshpu, Rapha, Repheth, and others that are not standardized. Ebla The name is found in third millennium BCE tablets from Ebla, as ''Rašap'' (''Ra-ša-ap''), listed as divinity of the cities of Atanni, Gunu, Tunip, and Shechem. Rasap wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammarik
Ammarik, also transcribed as Ammarig or Hammarigu, was a god worshiped in Ebla in the third millennium BCE. He was most likely a deified mountain. After the fall of Ebla, he was incorporated into the pantheon of the Hurrians. Character Ammarik was most likely a deified mountain in origin. It is possible that the corresponding landmark is located to the northwest of Ebla, in the proximity of Church of Saint Simeon Stylites. According to Hittite documents, it was located in the land of Mukish. A proposed identity is Mount Simeon, which according to Alfonso Archi is visible from Ebla. In a Hittite document dealing with the borders of the areas under the control of Carchemish, Ammarik is mentioned as a mountain, designated with the determinative ḪUR.SAG. In later periods, the mountain was apparently seen as the residence of a weather deity, as evidenced by the annals of Ḫattušili I. Ammarik and Adarwan In a ritual text from Ammarik occurs next to Adarwan, most likely also a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abarsal
Abarsal was a city-state of Mesopotamia in the area of the Euphrates. Very litte is known of the history of the town and the site is unidentified at the moment. It could be the city of Aburru mentioned in various texts of the tablets of Mari, which was located south of Emar to Qalat Gabir. A second theory says that could be Apishal. About 2420 BC, King Iblul-Il Iblul-Il (reigned c. 2380 BC), was the most energetic king ( Lugal) of the second Mariote kingdom, noted for his extensive campaigns in the middle Euphrates valley against the Eblaites, and in the upper Tigris region against various opponents, w ... was called King of Mari Abarsal. Vizier of Ebla Ibrium (24th-century BC) campaigned against the city of Abarsal during the time of vizier Arrukum.Mario Liverani (2013). The Ancient Near East: History, Society and Economy. p. 119. References {{reflist Ancient cities of the Middle East Mesopotamia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |