|
Kul Sharif
Kul Sharif or Qol Şärif ( tt-Cyrl, Кол Шәриф; ; died 1552) was an Old Tatar language-poet, statesman, university professor and imam of the Khanate of Kazan. He participated in some diplomatic missions on behalf of List of Kazan khans, Kazan khans to the Tsardom of Russia and there carried out negotiations for the khanate's independence. In 1552 he was one of leaders of Kazan's defense against the Russian troops of Ivan the Terrible. He also participated in the negotiations with Russian representatives in Sviyazhsk (''Zöyä''). After the Siege of Kazan started, he organized a group of students and defended the Khan Palace. He was killed during the battle. Later, four of his poems were included in "The Book of Baqırğan". Qolşärif's literary legacy was published in "İ küñel, bu dönyadır (O soil, may be this world...)", a collection of verses (Kazan, 1997). It is believed that the authorship of the dastan "Qíssai Xöbbi xuca" also belongs to him. It was published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Tatar Language
The Old Tatar ( imlâ: يسكى تاتار تلى, translit. tt-Cyrl, иске татар теле, translit=İske Tatar Tele, Volga Turki; ba, Урал-Волга буйы төрки теле) was a literary language used by some ethnic groups of the Volga-Ural region ( Tatars and others) from the Middle Ages till the 19th century. Old Tatar is a member of the Kipchak (or Northwestern) group of Turkic languages, although it is partly derived from the ancient Bulgar language (the first poem, considered to be written by Qol Ghali in Old Tatar dates back to Volga Bulgaria's epoch). It included many Persian and Arabic loans. In its written form the language was spelled uniformly among different ethnic groups, speaking different Turkic languages of the Kipchak group, but pronunciation differed from one people to another, approximating to the spoken language, making this written form universal for different languages. The main reason for this universal usage was that the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, serve as community leaders, and provide religious guidance. Thus for Sunnis, anyone can study the basic Islamic sciences and become an Imam. For most Shia Muslims, the Imams are absolute infallible leaders of the Islamic community after the Prophet. Shias consider the term to be only applicable to the members and descendents of the '' Ahl al-Bayt'', the family of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. In Twelver Shiasm there are 14 infallibles, 12 of which are Imams, the final being Imam Mahdi who will return at the end of times. The title was also used by the Zaidi Shia Imams of Yemen, who eventually founded the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen (1918–1970). Sunni imams Sunni Islam does not have imams in the same sense as the Shi'a, an importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanate Of Kazan
The Khanate of Kazan ( tt, Казан ханлыгы, Kazan xanlıgı; russian: Казанское ханство, Kazanskoye khanstvo) was a medieval Tatar Turkic state that occupied the territory of former Volga Bulgaria between 1438 and 1552. The khanate covered contemporary Tatarstan, Mari El, Chuvashia, Mordovia, and parts of Udmurtia and Bashkortostan; its capital was the city of Kazan. It was one of the successor states of the Golden Horde (Kipchak Khanate), and it came to an end when it was conquered by the Tsardom of Russia. Geography and population The territory of the khanate comprised the Muslim Bulgar-populated lands of the Bolğar, Cükätäw, Kazan, and Qaşan duchies and other regions that originally belonged to Volga Bulgaria. The Volga, Kama and Vyatka were the main rivers of the khanate, as well as the major trade ways. The majority of the population were Kazan Tatars. Their self-identity was not restricted to Tatars; many identified themselves simply a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Kazan Khans
List of Kazan khans who ruled the Khanate of Kazan before it was conquered by Russia. The First List has local spelling and dynasty. The Second List has very short biographies. First List *''Ghiasetdin of Kazan, Ghiyath-ud-din Khan taking advantage of the troubles of the Golden Horde established himself as an independent ruler of Kazan Ulus (Kazan district) during the 1420s. Eventually the former ruler of the Golden Horde, Olugh Mokhammad of Kazan, Ulugh Muhammad, would take over Kazan and establish his own separate Khanate of Kazan breaking the Golden Horde Empire.'' *''Blue rows signify influence of Grand Duchy of Moscow.'' **''Green row signifies brief interruption under Khan of Sibir Khanate.'' ***''Pink rows signify Qasim Khanate rule.'' ****''Yellow rows signify Giray dynasty from Crimean Khanate.'' *****''Brown row signifies prince from Khanate of Astrakhan rule.'' Second List with short biographies This information comes from Howorth's 1880 book Henry Howorth, History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsardom Of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I in 1721. From 1551 to 1700, Russia grew by 35,000 km2 per year. The period includes the upheavals of the transition from the Rurik to the Romanov dynasties, wars with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Sweden and the Ottoman Empire, and the Russian conquest of Siberia, to the reign of Peter the Great, who took power in 1689 and transformed the Tsardom into the Russian Empire. During the Great Northern War, he implemented substantial reforms and proclaimed the Russian Empire after victory over Sweden in 1721. Name While the oldest endonyms of the Grand Duchy of Moscow used in its documents were "Rus'" () and the "Russian land" (), a new form of its name, ''Rusia'' or ''Russia'', appeared and became common in the 15th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazan
Kazan ( ; rus, Казань, p=kɐˈzanʲ; tt-Cyrl, Казан, ''Qazan'', IPA: ɑzan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka rivers, covering an area of , with a population of over 1.2 million residents, up to roughly 1.6 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Kazan is the fifth-largest city in Russia, and the most populous city on the Volga, as well as the Volga Federal District. Kazan became the capital of the Khanate of Kazan and was conquered by Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century, becoming a part of Russia. The city was seized and largely destroyed during Pugachev's Rebellion of 1773–1775, but was later rebuilt during the reign of Catherine the Great. In the following centuries, Kazan grew to become a major industrial, cultural and religious centre of Russia. In 1920, after the Russian SFSR became a part of the Soviet Union, Kazan became the capital of the Tat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sviyazhsk
Sviyazhsk (russian: Свия́жск; tt-Cyrl, Зөя, ''Zöya'') is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, rural locality (a ''village#Russia, selo'') in the Republic of Tatarstan, Russia, located at the confluence of the Volga River, Volga and Sviyaga Rivers. It is often referred to as an island since the 1955 construction of the Kuybyshev Reservoir downstream at Tolyatti, but it is in fact connected to the mainland by a causeway. In 2017 the Assumption Cathedral, Sviyazhsk, Assumption Cathedral and Monastery were added to the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Sviyazhsk was founded in 1551 as a fortress, which was built within four weeks from parts made in Uglich and transported down the Volga. It became a military base of the Imperial Russian Army, Russian army during the siege of Kazan (1552). Since the 18th century, Sviyazhsk served as a center of an uyezd. In 1920–1927, it was a center of Sviyazhsky canton (subnational entity), Kanton; in 1927–1931—the adminis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
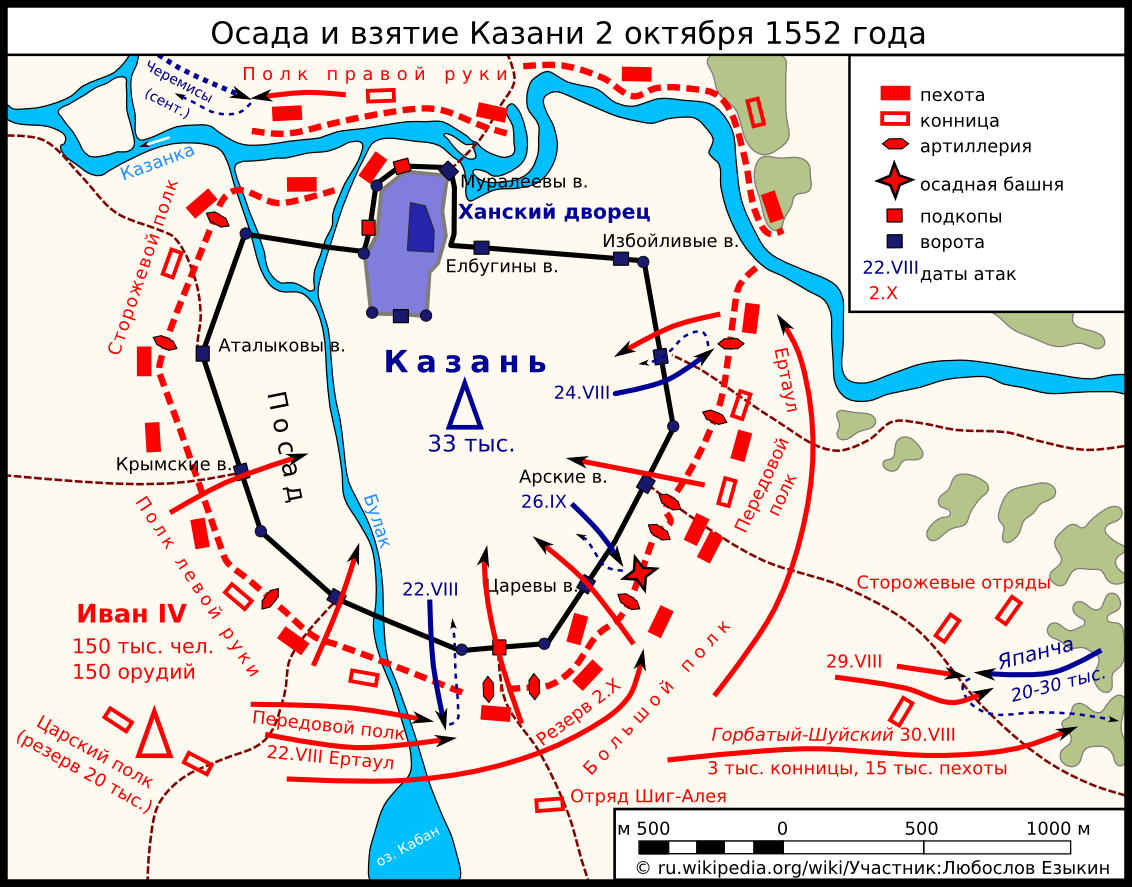
Siege Of Kazan
The siege of Kazan in 1552 was the final battle of the Russo-Kazan Wars and led to the fall of the Khanate of Kazan. Conflict continued after the fall of Kazan, however, as rebel governments formed in Çalım and Mişätamaq, and a new khan was invited from the Nogais. This guerrilla war lingered until 1556. Background During the existence of the khanate (1438-1552) Russian forces besieged Kazan at least ten times (1469, 1478, 1487, 1506, 1524, 1530, 1545, 1547, 1549-1550, 1552). In 1547 and in 1549-1550, Ivan the Terrible besieged Kazan, but supply difficulties forced him to withdraw. The Russians pulled back and built the town or fort of Sviyazhsk. They also annexed land west of the Volga which weakened the khanate. The peace party agreed to accept the pro-Russian Shah Ali as khan. The patriotic party regained power, Shah Ali fled and Yadegar Mokhammad of Kazan was called in as khan. Religious leaders like Qolsharif inspired the people to a determined resistance. The siege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dastan
Dastan ( fa, داستان ''dâstân'', meaning "story" or "tale") is an ornate form of oral history from Central Asia, Iran, Turkey and Azerbaijan. A dastan is generally centered on one individual who protects his tribe or his people from an outside invader or enemy, although only occasionally can this figure be traced back to a historical person. This main character sets an example of how one should act, and the dastan becomes a teaching tool — for example the Sufi master and Turkic poet Ahmed Yesevi said "Let the scholars hear my wisdom, treating my words like a dastan". Alongside the wisdom, each dastan is rich with cultural history of interest to scholars. During the Russian conquest of Central Asia, many new dastans were created to protest the Russian occupation. It is possible that they came into contact and influenced each other. According to Turkish historian Hasan Bülent Paksoy, the Bolsheviks tried to destroy these symbols of culture by only publishing them in insu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In Tatarstan
Islam in Tatarstan existed prior to the tenth century, but it began major growth in 922, when Bulgar ruler Almış converted to Islam.Azade-Ayse Rolich, The Volga Tatars, 1986, page 11. Richard Frye, Ibn Fadlan's Journey to Russia, 2005, page 44 gives 16 May 922 for the first meeting with the ruler. This seems to be the official date of the conversion. This was followed by an increase in missionary activity in Volga Bulgaria. Islam remained the dominant religion through the Mongol invasion and subsequent Khanate of Kazan. In 1552, the region was finally conquered by Russia, bringing the Volga Tatars and Bashkirs on the Middle Volga into the tsardom. Under Russian rule, Islam was suppressed for many years, first during the Tsardom and Empire and later during the Soviet era. Today, Islam is a major faith in Tatarstan, adhered to by 33.8–55 percent [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kul Sharif Mosque
The Kul Sharif Mosque ( tt-Cyrl, Кол Шәриф мәчете; ) located in Kazan Kremlin, was reputed to be – at the time of its construction – one of the largest mosques in Russia, and in Europe outside of Istanbul. History Originally, the mosque was built in the Kazan Kremlin in the 16th century. It was named after Kul Sharif, who was a religious scholar who served there. Kul Sharif died with his numerous students while defending Kazan from Russian forces in 1552 during the Siege of Kazan, and the mosque was destroyed by Ivan the Terrible's forces. It is believed that the building featured minarets, both in the form of cupolas and tents. Its design was traditional for Volga Bulgaria, although elements of early Renaissance and Ottoman architecture could have been used as well. Several countries contributed to the fund that was set up to rebuild Kul Sharif Mosque, namely Saudi Arabia, and United Arab Emirates. Nowadays the mosque predominantly serves as a museu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |