|
Kokufu Shrine
are the capitals of the historical Provinces of Japan. History As part of the Taika Reform (645) which aimed at a centralization of the administration following the Chinese model (''ritsuryō''), the kokufu and with it the office of the kokushi, replacing the older ''Kuni no miyatsuko'', developed in the 660s. The ''Wamyō Ruijushō'' (Collection of Japanese Names) from 935 contains the earliest listing of the capitals of the provinces and their location. The location of the original capitals of the 8th and 9th century are not passed down. When during the Muromachi Period, starting in the 14th century, the functions of the kokushi were increasingly transferred to military governors (''shugo''), the provincial governments (''kokuga'') lost their importance. Organisation In the center of the kokufu lay the provincial government (''kokuga'') with its offices (administration, farming, finance, police and military) and the official building of the kokushi, known as . In the peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Japan
were first-level administrative divisions of Japan from the 600s to 1868. Provinces were established in Japan in the late 7th century under the Ritsuryō law system that formed the first central government. Each province was divided into and grouped into one of the geographic regions or Circuit (administrative division), circuits known as the ''Gokishichidō'' (Five Home Provinces and Seven Circuits). Provincial borders often changed until the end of the Nara period (710 to 794), but remained unchanged from the Heian period (794 to 1185) until the Edo period (1603 to 1868). The provinces coexisted with the ''Han system, han'' (domain) system, the personal estates of feudal lords and warriors, and became secondary to the domains in the late Muromachi period (1336 to 1573). The Provinces of Japan were replaced with the current Prefectures of Japan, prefecture system in the ''Fuhanken sanchisei'' during the Meiji Restoration from 1868 to 1871, except for Hokkaido, which was For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heijō-kyō
was the Capital of Japan during most of the Nara period, from 710 to 740 and again from 745 to 784. The imperial palace is a listed UNESCO World Heritage together with other places in the city of Nara (cf. Historic Monuments of Ancient Nara). Empress Genmei ordered the Imperial capital moved from Fujiwara-kyō to Heijō-kyō in 708, and the move to Heijō-kyō was complete in 710. Heijō-kyō was modeled after Chang'an, the capital of Tang-dynasty China, although Heijō-kyō lacked walls. In the city, merchants and traders from China, Korea and India introduced various foreign cultures to Heijō-kyō through the Silk Road. As a result, Heijō-kyō flourished as Japan's first international and political capital, with a peak population of between 50,000 and 100,000. The overall form of the city was an irregular rectangle, and the area of city is more than 25 km2. Architecture In the area of Heijō-kyō, there are ancient Buddhist temples, and some temples are also l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichinomiya
is a Japanese historical term referring to the Shinto shrines with the highest rank in a province. Shrines of lower rank were designated , , , and so forth. ''Encyclopedia of Shinto'' ''Ichi no miya'' retrieved 2013-5-14. The term gave rise to modern place names, such as the city of Ichinomiya, Aichi. Overview The term "Ichinomiya" literally means "first shrine" and is popularly regarded as the highest ranking shrine in each province, with the second ranking shrine referred to as the "Ninomiya" and third ranking shrine as "Sannomiya", and so on. However, there is no documentary material stipulating on how the shrines in each province are to be ranked, or even when this ranking system was created. As a general rule, all shrines designated "Ichinomiya" are of ancient origin and are listed in the ''Engishiki'' records completed in 927AD. However, the shrine selected is not necessarily the largest, or oldest, in that province, and is not necessarily one of the "Meishin Taisha", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoists'', although adherents rarely use that term themselves. There is no central authority in control of Shinto, with much diversity of belief and practice evident among practitioners. A polytheistic and animistic religion, Shinto revolves around supernatural entities called the . The are believed to inhabit all things, including forces of nature and prominent landscape locations. The are worshiped at household shrines, family shrines, and ''jinja'' public shrines. The latter are staffed by priests, known as , who oversee offerings of food and drink to the specific enshrined at that location. This is done to cultivate harmony between humans and and to solicit the latter's blessing. Other common rituals include the dances, rites of pass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokubun-ji
were Buddhist temples established in each of the provinces of Japan by Emperor Shōmu during the Nara period (710 – 794). History Shōmu (701 – 756?) decreed both a ''kokubun-ji'' for monks and a for nuns to be established in each province. Tōdai-ji, the provincial temple of Yamato Province, served as the head of all ''kokubun-ji'', and Hokke-ji held that duty for the ''kokubunni-ji''. Modern place names Modern place names based on this etymology include: *Kokubunji, Kagawa *Kokubunji, Tokyo *Kokubunji, Tochigi See also * 735–737 Japanese smallpox epidemic * Fuchū * Glossary of Japanese Buddhism * Ichinomiya is a Japanese historical term referring to the Shinto shrines with the highest rank in a province. Shrines of lower rank were designated , , , and so forth. ''Encyclopedia of Shinto'' ''Ichi no miya'' retrieved 2013-5-14. The term gave rise t ... References Buddhist temples in Japan Buddhist archaeological sites in Japan Former provinces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bizen Province
was a province of Japan on the Inland Sea side of Honshū, in what is today the southeastern part of Okayama Prefecture. It was sometimes called , with Bitchū and Bingo Provinces. Bizen borders Mimasaka, Harima, and Bitchū Provinces. Bizen's original center was in the modern city of Okayama. From an early time Bizen was one of Japan's main centers for sword smithing. Historical record In the 3rd month of the 6th year of the '' Wadō era'' (713), the land of Bizen''-no kuni'' was administratively separated from Mimasaka Province (美作国). In that same year, Empress Genmei's ''Daijō-kan'' continued to organize other cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara period. In ''Wadō'' 6, Tanba Province (丹波国) was sundered from Tango Province (丹後国); and Hyūga Province (日向国) was divided from Ōsumi Province (大隈国).Titsingh, Isaac. (1834) In ''Wadō'' 5 (712), Mutsu Province (陸奥国) had been severed from Dewa Province (出羽国). In the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suō Province
was a province of Japan in the area that is today the eastern part of Yamaguchi Prefecture. It was sometimes called . Suō bordered on Aki, Iwami, and Nagato Provinces. The ancient provincial capital was in Hōfu. Suō was ruled for much of the Muromachi period by the Ōuchi clan, who built a castle at Yamaguchi. In the Sengoku period it was conquered by the Mōri clan, and was ruled remotely by them for much of the Edo period. Shrines and temples ''Tamanoya jinja'' was the chief Shinto shrine (''ichinomiya'') of Suō. retrieved 2012-11-20. Historical districts * ** ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dazaifu (term)
The is a Japanese term for the regional government in Kyushu from the 8th to the 12th centuries. The name may also refer to the seat of government which grew into the modern city of Dazaifu in Fukuoka Prefecture."Dazaifu" at Japan-guide.com retrieved 2013-3-5. History The ''Dazaifu'' was established in northwest Kyushu the late 7th century. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Dazaifu" in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 150. The town of Dazaifu grew up around the civil and military headquarters of the regional government. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin Shi Huang of the Qin dynasty, China's first emperor, held his imperial court, and constructed his massive mausoleum guarded by the Terracotta Army. From its capital at Xianyang, the Qin dynasty ruled a larger area than either of the preceding dynasties. The imperial city of Chang'an during the Han dynasty was located northwest of today's Xi'an. During the Tang dynasty, the area that came to be known as Chang'an included the area inside the Ming Xi'an fortification, plus some small areas to its east and west, and a substantial part of its southern suburbs. Thus, Tang Chang'an was eight times the size of the Ming Xi'an, which was reconstructed upon the site of the former imperial quarters of the Sui and Tang city. During its heyday, Chang'an w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Zhou dynasty (690–705), Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
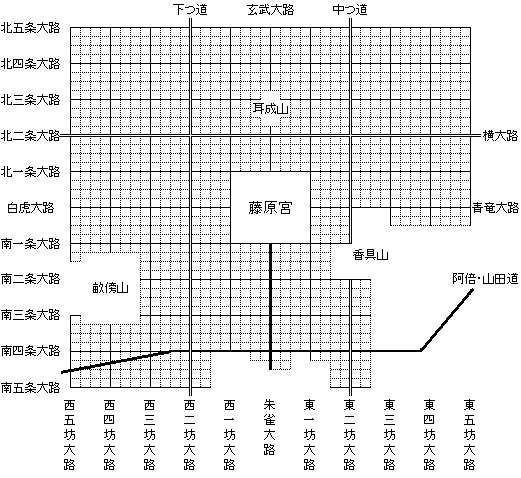
Fujiwara-kyō
was the Imperial capital of Japan for sixteen years, between 694 and 710. It was located in Yamato Province (present-day Kashihara, Nara, Kashihara in Nara Prefecture), having been moved from nearby Asuka, Yamato, Asuka. However, the name Fujiwara-kyō was never used in the ''Nihon Shoki''. During those times it was recorded as Aramashi-kyō (新益京). As of 2006, ongoing excavations have revealed construction on the site of Fujiwara-kyō as early as 682, near the end of the reign of Emperor Tenmu. With a brief halt upon Emperor Tenmu's death, construction resumed under Empress Jitō, who officially moved the capital in 694. Fujiwara-kyō remained the capital for the reigns of Emperor Monmu and Empress Genmei, but in 710 the Imperial court moved to the Heijō Palace in Nara, Nara, Nara, beginning the Nara period. History Fujiwara was Japan's first capital built in a grid pattern on the Chinese model (条坊制 ''jōbō-sei''); recent investigation has revealed that the city c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |