|
Klang (Stockhausen)
''Klang'' ()—''Die 24 Stunden des Tages'' (Sound—The 24 Hours of the Day) is a cycle of compositions by Karlheinz Stockhausen, on which he worked from 2004 until his death in 2007. It was intended to consist of 24 chamber-music compositions, each representing one hour of the day, with a different colour systematically assigned to every hour. The cycle was unfinished when the composer died, so that the last three "hours" are lacking. The 21 completed pieces include solos, duos, trios, a septet, and Stockhausen's last entirely electronic composition, ''Cosmic Pulses''. The fourth composition is a theatre piece for a solo percussionist, and there are also two auxiliary compositions which are not part of the main cycle. The completed works bear the work (opus) numbers 81–101. History and character After having spent 27 years composing the opera-cycle '' Licht'' (1977–2004), Stockhausen felt he was shifting his focus from the visible world of the eyes—''Licht'' is the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycle Of Compositions
Cycle has several meanings in the field of music. Acoustics, Acoustically, it refers to one complete vibration, the base unit of Hertz being one cycle per second. Theoretically, an interval cycle is a collection of pitch classes created by a sequence of identical intervals. Individual pieces that aggregate into larger works are considered cycles, for example, the Movement (music), movements of a suite, symphony, sonata, or string quartet. This definition can apply to everything from settings of the Mass or a song cycle to an opera cycle. Cycle also applies to the complete performance of an individual composer's work in one genre. Harmonic cycles—repeated sequences of a harmonic progression—are at the root of many musical genres, such as the twelve-bar blues. In compositions of this genre, the chord progression may be repeated indefinitely, with melodic and lyrical variation forming the musical interest. The form theme and variations is essentially of this type, but generally on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western States of Germany, state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 million people in the Cologne Bonn Region, urban region. Centered on the left bank of the Rhine, left (west) bank of the Rhine, Cologne is about southeast of NRW's state capital Düsseldorf and northwest of Bonn, the former capital of West Germany. The city's medieval Catholic Cologne Cathedral (), the third-tallest church and tallest cathedral in the world, constructed to house the Shrine of the Three Kings, is a globally recognized landmark and one of the most visited sights and pilgrimage destinations in Europe. The cityscape is further shaped by the Twelve Romanesque churches of Cologne, and Cologne is famous for Eau de Cologne, that has been produced in the city since 1709, and "col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milan Cathedral
Milan Cathedral ( it, Duomo di Milano ; lmo, Domm de Milan ), or Metropolitan Cathedral-Basilica of the Nativity of Saint Mary ( it, Basilica cattedrale metropolitana di Santa Maria Nascente, links=no), is the cathedral church of Milan, Lombardy, Italy. Dedicated to the Nativity of St Mary (''Santa Maria Nascente''), it is the seat of the Archbishop of Milan, currently Archbishop Mario Delpini. The cathedral took nearly six centuries to complete: construction began in 1386, and the final details were completed in 1965. It is the largest church in the Italian Republic—the larger St. Peter's Basilica is in the State of Vatican City, a sovereign state—and possibly the second largest in Europe and the third largest in the world (its size and position remain a matter of debate). History Milan's layout, with streets either radiating from the Duomo or circling it, reveals that the Duomo occupies what was the most central site in Roman Mediolanum, that of the public bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duomo Di Milano Keski
''Duomo'' (, ) is an Italian term for a church with the features of, or having been built to serve as, a cathedral, whether or not it currently plays this role. Monza Cathedral, for example, has never been a diocesan seat and is by definition not a cathedral. On the other hand, the city of Trevi no longer has a bishop, although it once did, and the erstwhile cathedral of Emilianus of Trevi is now a mere church. By contradistinction, the Italian word for a cathedral ''sensu stricto'' is ''cattedrale''. There is no direct translation of "duomo" into English, leading to many such churches being erroneously called "cathedral" in English, regardless of whether the church in question hosts a bishop. Many people refer to particular churches simply as ''il Duomo'', the ''Duomo'', without regard to the full proper name of the church. Similar words exist in other European languages: ''Dom'' (German), ''dom'' (Romanian), ''dóm'' ( Hungarian and Slovak), ''dôme'' ( French), ''domo'' (P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
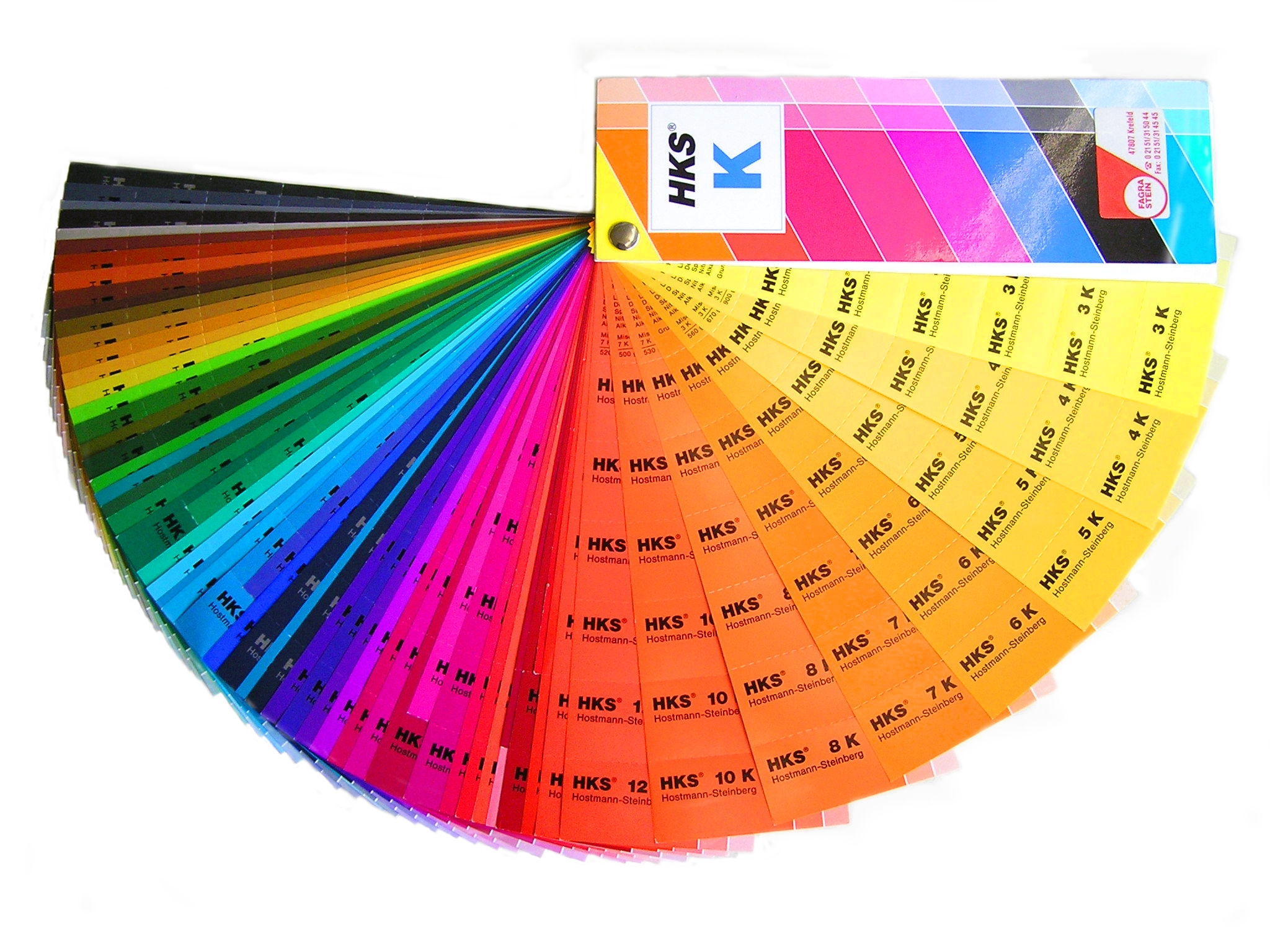
HKS (colour System)
The HKS is a colour system which contains 120 spot colours and 3520 tones for coated and uncoated paper. HKS is an abbreviation of three German colour manufacturers: Hostmann-Steinberg Druckfarben, Kast + Ehinger Druckfarben, and H. Schmincke & Co. The association of those three companies have defined the colours of the HKS system since 1968. HKS colours, similar to Pantone colours, can be used in any kind of print publication to produce predictable colours. As in the Pantone colour system, there are HKS colours that cannot be reproduced using the CMYK colour space, like bright orange or certain tones of blue. The HKS colour system is based on the euroscale colourspace. It follows the guidelines of ISO 12647:2 2002 and the FOGRA Standards (such as Fogra27L). This means HKS colours are available on all paper types of the 12647 standard. This makes it easier to print the colours in offset Offset or Off-Set may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * "Off-Set", a song b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Ostwald
Friedrich Wilhelm Ostwald (; 4 April 1932) was a Baltic German chemist and German philosophy, philosopher. Ostwald is credited with being one of the founders of the field of physical chemistry, with Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff, Walther Nernst, and Svante Arrhenius. He received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1909 for his scientific contributions to the fields of catalysis, chemical equilibria and Reaction velocity, reaction velocities. Following his 1906 retirement from academic life, Ostwald became much involved in philosophy, art, and politics. He made significant contributions to each of these fields. He has been described as a polymath. Early life and education Ostwald was born ethnically Baltic German in Riga, Russian Empire (now Latvia) to cooper (profession), master-cooper Gottfried Wilhelm Ostwald (1824–1903) and Elisabeth Leuckel (1824–1903). He was the middle child of three, born after Eugen (1851–1932) and before Gottfried (1855–1918). Ostwald developed an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
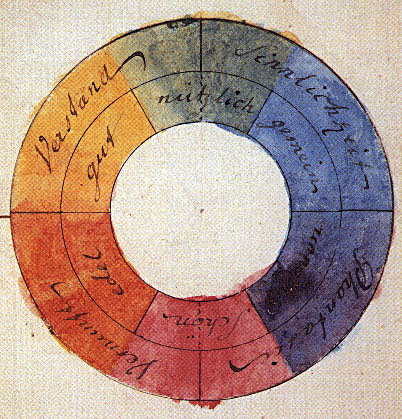
Color Wheel
A color wheel or color circle is an abstract illustrative organization of color hues around a circle, which shows the relationships between primary colors, secondary colors, tertiary colors etc. Some sources use the terms ''color wheel'' & ''color circle'' interchangeably; however, one term or the other may be more prevalent in certain fields or certain versions as mentioned above. For instance, some reserve the term ''color wheel'' for mechanical rotating devices, such as color tops, filter wheels or Newton disc. Others classify various color wheels as ''color disc'', ''color chart'', and ''color scale'' varieties. History In his book ''Opticks'', Isaac Newton presented a color circle to illustrate the relations between these colors. The original color circle of Isaac Newton showed only the spectral hues and was provided to illustrate a rule for the color of mixtures of lights, that these could be approximately predicted from the center of gravity of the numbers of "rays" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Theory
In the visual arts, color theory is the body of practical guidance for color mixing and the visual effects of a specific color combination. Color terminology based on the color wheel and its geometry separates colors into primary color, secondary color, and tertiary color. The understanding of color theory dates to antiquity. Aristotle (d. 322 BCE) and Claudius Ptolemy (d. 168 CE) already discussed which and how colors can be produced by mixing other colors. The influence of light on color was investigated and revealed further by al-Kindi (d. 873) and Ibn al-Haytham (d.1039). Ibn Sina (d. 1037), Nasir al-Din al-Tusi (d. 1274), and Robert Grosseteste (d. 1253) discovered that contrary to the teachings of Aristotle, there are multiple color paths to get from black to white. More modern approaches to color theory principles can be found in the writings of Leone Battista Alberti (c. 1435) and the notebooks of Leonardo da Vinci (c. 1490). A formalization of "color theory" began in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liturgy Of The Hours
The Liturgy of the Hours (Latin: ''Liturgia Horarum'') or Divine Office (Latin: ''Officium Divinum'') or ''Opus Dei'' ("Work of God") are a set of Catholic prayers comprising the canonical hours, often also referred to as the breviary, of the Latin Church. The Liturgy of the Hours forms the official set of prayers "marking the hours of each day and sanctifying the day with prayer." The term "Liturgy of the Hours" has been retroactively applied to the practices of saying the canonical hours in both the Christian East and West–particularly within the Latin liturgical rites–prior to the Second Vatican Council, and is the official term for the canonical hours promulgated for usage by the Latin Church in 1971. Before 1971, the official form for the Latin Church was the ''Breviarium Romanum'', first published in 1568 with major editions through 1962. The Liturgy of the Hours, like many other forms of the canonical hours, consists primarily of psalms supplemented by hymns, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canonical Hours
In the practice of Christianity, canonical hours mark the divisions of the day in terms of fixed times of prayer at regular intervals. A book of hours, chiefly a breviary, normally contains a version of, or selection from, such prayers. In the Roman Rite of the Catholic Church, canonical hours are also called ''offices'', since they refer to the official set of prayers of the Church, which is known variously as the ("divine service" or "divine duty"), and the ("work of God"). The current official version of the hours in the Roman Rite is called the Liturgy of the Hours ( la, liturgia horarum) in North America or divine office in Ireland and Britain. In Lutheranism and Anglicanism, they are often known as the daily office or divine office, to distinguish them from the other "offices" of the Church (e.g. the administration of the sacraments). In the Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Catholic Churches, the canonical hours may be referred to as the divine services, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostwald Color
Ostwald may refer to: * Friedrich Wilhelm Ostwald, the physico-chemist (awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, 1909) # Ostwald's rule of polymorphism: in general, the least stable polymorph crystallizes first # The Ostwald Process, a synthesis method for making nitric acid from ammonia # Ostwald ripening, a crystallization effect # Ostwald color system * Wolfgang Ostwald, chemist and biologist, son of Friedrich Wilhelm Ostwald. He studied colloids * Martin Ostwald, a German-American classical scholar * Ostwald (crater), a crater on the far side of the moon * Ostwald, Bas-Rhin, a commune in the Bas-Rhin ''département'' in France See also * Oswald (other) Oswald may refer to: People * Oswald (given name), including a list of people with the name *Oswald (surname), including a list of people with the name Fictional characters *Oswald the Reeve, who tells a tale in Geoffrey Chaucer's '' The Canterb ... * Ozwald Boateng {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Cloisters
The Cloisters, also known as the Met Cloisters, is a museum in the Washington Heights, Manhattan, Washington Heights neighborhood of Upper Manhattan, New York City. The museum, situated in Fort Tryon Park, specializes in European medieval art and medieval architecture, architecture, with a focus on the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque and Gothic architecture, Gothic periods. Governed by the Metropolitan Museum of Art, it contains a large collection of medieval artworks shown in the architectural settings of French monasteries and abbeys. Its buildings are centered around four cloisters—the Cuxa, Saint-Guilhem, Bonnefont and Trie—that were acquired by American sculptor and art dealer George Grey Barnard in France before 1913, and moved to New York. Barnard's collection was bought for the museum by financier and philanthropist John D. Rockefeller, Jr. Other major sources of objects were the collections of J. P. Morgan and Joseph Brummer. The museum's building was designed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |