|
King Of Mann
The King of Mann () was the title taken between 1237 and 1504 by the various rulers, both sovereign and suzerain, over the Kingdom of Mann – the Isle of Man which is located in the Irish Sea, at the centre of the British Isles. Since 1504, the head of state has been known as the Lord of Mann. Celtic Kings of Ynys Manaw (before 836) * Tutagual Theodovellaunus (c. 485–c. 495); son of Cinuit, also king of Alt Clut and Galwyddel *Dingat (c. 495); son of Tutagual, also king of Galwyddel * (c. 550); son of Dingat, exiled king of Galwyddel * (c. 575), son of Sennylt Hael *Diwg (c. 600s), client king of Áedán mac Gabráin of Dál Riata * Edwin of Northumbria (620–633), also king of Bernicia and Deira * (until c. 682), descendant of Magnus Maximus * (from c. 682), son of Merfyn Fawr * (c. 710), son of Anarawd *Sandde (c. 730), descendant of Llywarch Hen of Rheged, husband of Celemion daughter of Tudwal *Elidyr (c. 790), son of Sandde * Gwriad (until 825), son of Elidyr, mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir John Stanley, Lord Lieut Of Ireland, Titular King Of Man, KG
''Sir'' is a formal honorific address in English for men, derived from Sire in the High Middle Ages. Both are derived from the old French "Sieur" (Lord), brought to England by the French-speaking Normans, and which now exist in French only as part of "Monsieur", with the equivalent "My Lord" in English. Traditionally, as governed by law and custom, Sir is used for men titled as knights, often as members of orders of chivalry, as well as later applied to baronets and other offices. As the female equivalent for knighthood is damehood, the female equivalent term is typically Dame. The wife of a knight or baronet tends to be addressed as Lady, although a few exceptions and interchanges of these uses exist. Additionally, since the late modern period, Sir has been used as a respectful way to address a man of superior social status or military rank. Equivalent terms of address for women are Madam (shortened to Ma'am), in addition to social honorifics such as Mrs, Ms or Miss. Etymol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llywarch Hen
Llywarch Hen (, "Llywarch the Old"; c. 534 – c. 608), was a prince and poet of the Brythonic kingdom of Rheged, a ruling family in the Hen Ogledd or "Old North" of Britain (modern southern Scotland and northern England). Along with Taliesin, Aneirin, and Myrddin, he is held to be one of the four great bards of early Welsh poetry. Whether he actually wrote the poems attributed to him is unknown, and most of what is known about his life is derived from early medieval poems which may or may not be historically accurate. Life Llywarch Hen was the son of Elidurus, chief of Argoed (in the Rheged region, later Cumberland). In the genealogy known as "Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd (The Descent of the Men of the North)" he is listed as a descendant of Coel Hen (King Cole), and is first cousin to King Urien Rheged. It is thought that he may have been a monarch himself, with Urien ruling northern Rheged, and Llywarch ruling the south. In his 1953 book ''The Derbyshire Dales'', Norman Price link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. While the rights and obligations of a vassal are called vassalage, and the rights and obligations of a suzerain are called suzerainty. The obligations of a vassal often included military support by knights in exchange for certain privileges, usually including land held as a tenant or fief. The term is also applied to similar arrangements in other feudal societies. In contrast, fealty (''fidelitas'') was sworn, unconditional loyalty to a monarch. European vassalage In fully developed vassalage, the lord and the vassal would take part in a commendation ceremony composed of two parts, the homage and the fealty, including the use of Christian sacraments to show its sacred importance. According to Eginhard's brief description, the ''commenda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olaf The Black
Óláfr Guðrøðarson (died 1237) (Scottish Gaelic: ''Amhlaibh Dubh''), also known as Olaf the Black, was a thirteenth-century King of the Isles, and a member of the Crovan dynasty. He was a son of Guðrøðr Óláfsson, King of the Isles and Fionnghuala Nic Lochlainn. Óláfr was a younger son of his father; Óláfr's elder brother, Rǫgnvaldr, probably had a different mother. According to the ''Chronicle of Mann'', Guðrøðr appointed Óláfr as heir since he had been born "in lawful wedlock". Whether or not this is the case, after Guðrøðr's death in 1187 the Islesmen instead appointed Rǫgnvaldr as king, as he was a capable adult and Óláfr was a mere child. Rǫgnvaldr ruled the island-kingdom for almost forty years, during which time the half-brothers vied for the kingship. Óláfr appears to have held authority on the island of Lewis and Harris. At some point, Óláfr appears to have confronted Rǫgnvaldr for a larger stake in the kingdom, after which Rǫgnvaldr had h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrides
The Hebrides (; gd, Innse Gall, ; non, Suðreyjar, "southern isles") are an archipelago off the west coast of the Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner and Outer Hebrides. These islands have a long history of occupation (dating back to the Mesolithic period), and the culture of the inhabitants has been successively influenced by the cultures of Celtic-speaking, Norse-speaking, and English-speaking peoples. This diversity is reflected in the various names given to the islands, which are derived from the different languages that have been spoken there at various points in their history. The Hebrides are where much of Scottish Gaelic literature and Gaelic music has historically originated. Today, the economy of the islands is dependent on crofting, fishing, tourism, the oil industry, and renewable energy. The Hebrides have less biodiversity than mainland Scotland, but a significant number of seals an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clann Somhairle
Clann Somhairle, sometimes anglicised as Clan Sorley, refers to those Scottish and Irish dynasties descending from the famous Norse-Gaelic leader Somerled, King of Mann and the Isles, son of Gillabrigte (†1164) and ancestor of Clann Domhnaill. Primarily they are the Clan Donald, formerly known as the Lord of the Isles, and the mainland Clan MacDougall, and all their numerous branches. Clan Macruari are their lost sept. Origins The origin of Somerled, from whom the clan derives, is obscure. Only the name of his father is directly attested in early records. He was later portrayed as having Gaelic ancestry, with late pedigrees from the 14th and 15th century tracing him from legendary Colla Uais and hence from Conn of the Hundred Battles, and some versions apparently including the legendary founder of the Scottish state of Dál Riata, Fergus Mór. Historians have distrusted this derivation, though in the 1960s, David Sellar defended a Gaelic derivation. More recently, his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somerled
Somerled (died 1164), known in Middle Irish as Somairle, Somhairle, and Somhairlidh, and in Old Norse as Sumarliði , was a mid-12th-century Norse-Gaelic lord who, through marital alliance and military conquest, rose in prominence to create the Kingdom of Argyll and the Isles. Little is certain of Somerled's origins, although he may have been born in northern Ireland and appears to have belonged to a Norse–Gaelic family of some prominence. His father, GilleBride, of royal Irish ancestry, appears to have conducted a marriage alliance with Máel Coluim mac Alaxandair, son of Alexander I of Scotland, and claimant to the Scottish throne. During a period of alliance with David I of Scotland, Somerled married Ragnhild, daughter of Óláfr Guðrøðarson, King of Man and the Isles in 1140. In 1153, Olaf of Man died and was succeeded by his son, Godred. But Godred Olafsson was a very unpopular ruler. Somerled was asked by Thorfinn Ottarson, a Manx chief, to allow Somerled's son, Dug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rulers Of The Kingdom Of The Isles
The Kingdom of the Isles comprised the Hebrides, the islands of the Firth of Clyde and the Isle of Man from the 9th to the 13th centuries AD. The islands were known to the Norse as the , or "Southern Isles" as distinct from the or Northern Isles of Orkney and Shetland. The historical record is incomplete and the kingdom was probably not a continuous entity throughout the entire period. The islands concerned are sometimes referred to as the "Kingdom of Mann and the Isles", although only some of the later rulers claimed that title. At times the rulers were independent of external control, although for much of the period they had overlords in Norway, Ireland, England, Scotland or Orkney. At times there also appear to have been competing claims for all or parts of the territory. The islands involved have a total land area of over and extend for more than from north to south. Viking influence in the area commenced in the late 8th century, and whilst there is no doubt that the Uí � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of The Isles
The Kingdom of the Isles consisted of the Isle of Man, the Hebrides and the islands of the Firth of Clyde from the 9th to the 13th centuries AD. The islands were known to the Norse as the , or "Southern Isles" as distinct from the or Northern Isles of Orkney and Shetland. In Scottish Gaelic, the kingdom is known as . The historical record is incomplete, and the kingdom was not a continuous entity throughout the entire period. The islands concerned are sometimes referred to as the Kingdom of Mann and the Isles, although only some of the later rulers claimed that title. At times the rulers were independent of external control, although for much of the period they had overlords in Norway, Ireland, England, Scotland or Orkney. At times there also appear to have been competing claims for all or parts of the territory. The islands involved have a total land area of over and extend for more than from north to south. Viking influence in the area commenced in the late 8th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Mann And The Isles-en
Kingdom commonly refers to: * A monarchy ruled by a king or queen * Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy Kingdom may also refer to: Arts and media Television * ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama starring Stephen Fry * ''Kingdom'' (American TV series), a 2014 US television drama starring Frank Grillo * ''Kingdom'' (South Korean TV series), a 2019 South Korean television series *'' Kingdom: Legendary War'', a 2021 South Korean television series Music * Kingdom (group), a South Korean boy group * ''Kingdom'' (Koda Kumi album), 2008 * ''Kingdom'' (Bilal Hassani album), 2019 * ''Kingdom'' (Covenant Worship album), 2014 * ''Kingdoms'' (Life in Your Way album), 2011 * ''Kingdoms'' (Broadway album), 2009 * ''Kingdom'' (EP), a 1998 EP by Vader * "Kingdom" (Dave Gahan song), 2007 * "Kingdom" (Maverick City Music and Kirk Franklin song), 2022 * "Kingdom", a song by Battle Beast on their 2013 album '' Battle Beast'' * "Kingdom", a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merfyn Frych
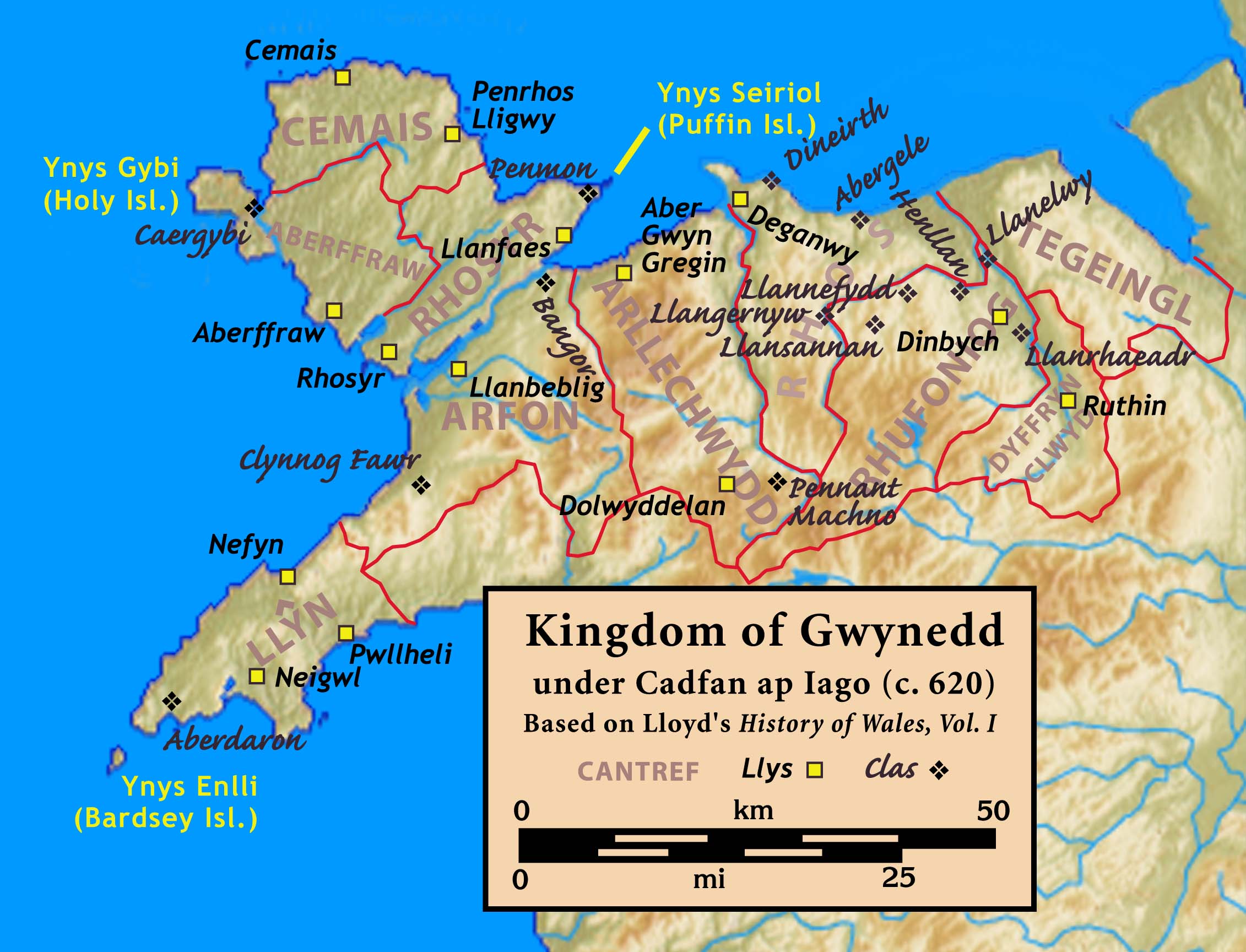
Merfyn Frych ('Merfyn the Freckled'; Old Welsh ''Mermin''), also known as Merfyn ap Gwriad ('Merfyn son of Gwriad') and Merfyn Camwri ('Merfyn the Oppressor'), was King of Gwynedd from around 825 to 844, the first of its kings known not to have descended from the male line of King Cunedda. Little is known of his reign, and his primary notability is as the father of Rhodri the Great and founder of his dynasty, which was sometimes called the Merfynion after him. Merfyn came to the throne in the aftermath of a bloody dynastic struggle between two rivals named Cynan and Hywel generally identified with the sons of Rhodri Molwynog. The ''Annales Cambriae'' say Merfyn died around 844, the same year in which a battle occurred at Cetyll, but it is unclear whether those were two unrelated events or he fell in battle. Political background The times leading up to Merfyn's reign were unsettled for both Gwynedd and neighbouring Powys. Both kingdoms were beset by internal dynastic strife, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
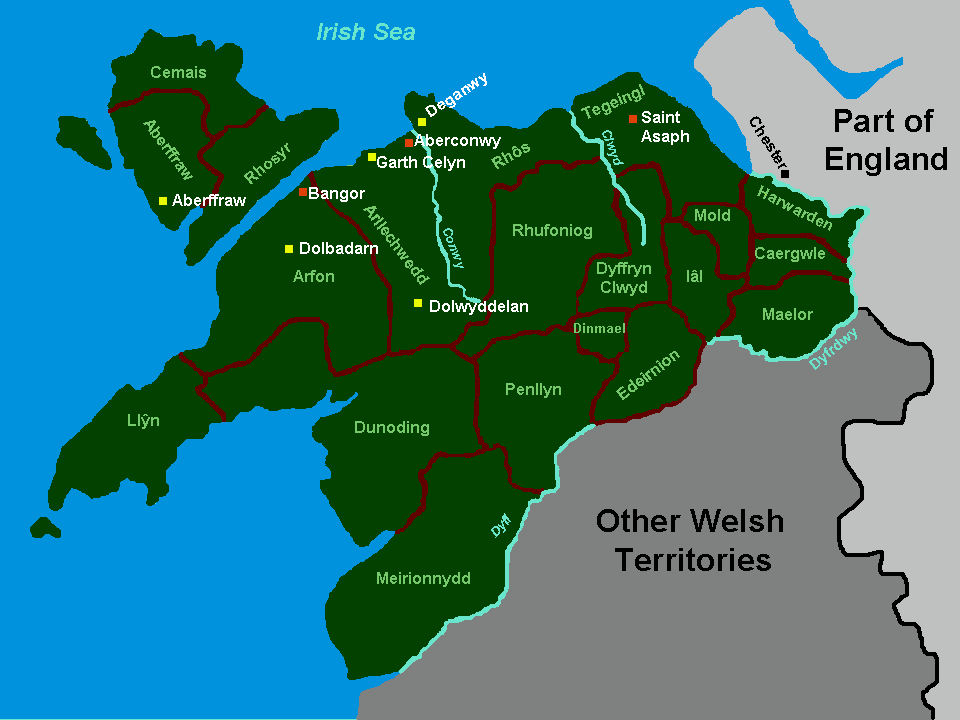
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as " King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llewelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted peace between the two but would also guarantee that Welsh self-rule would end upon Llewelyn's death, and so it represented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)