|
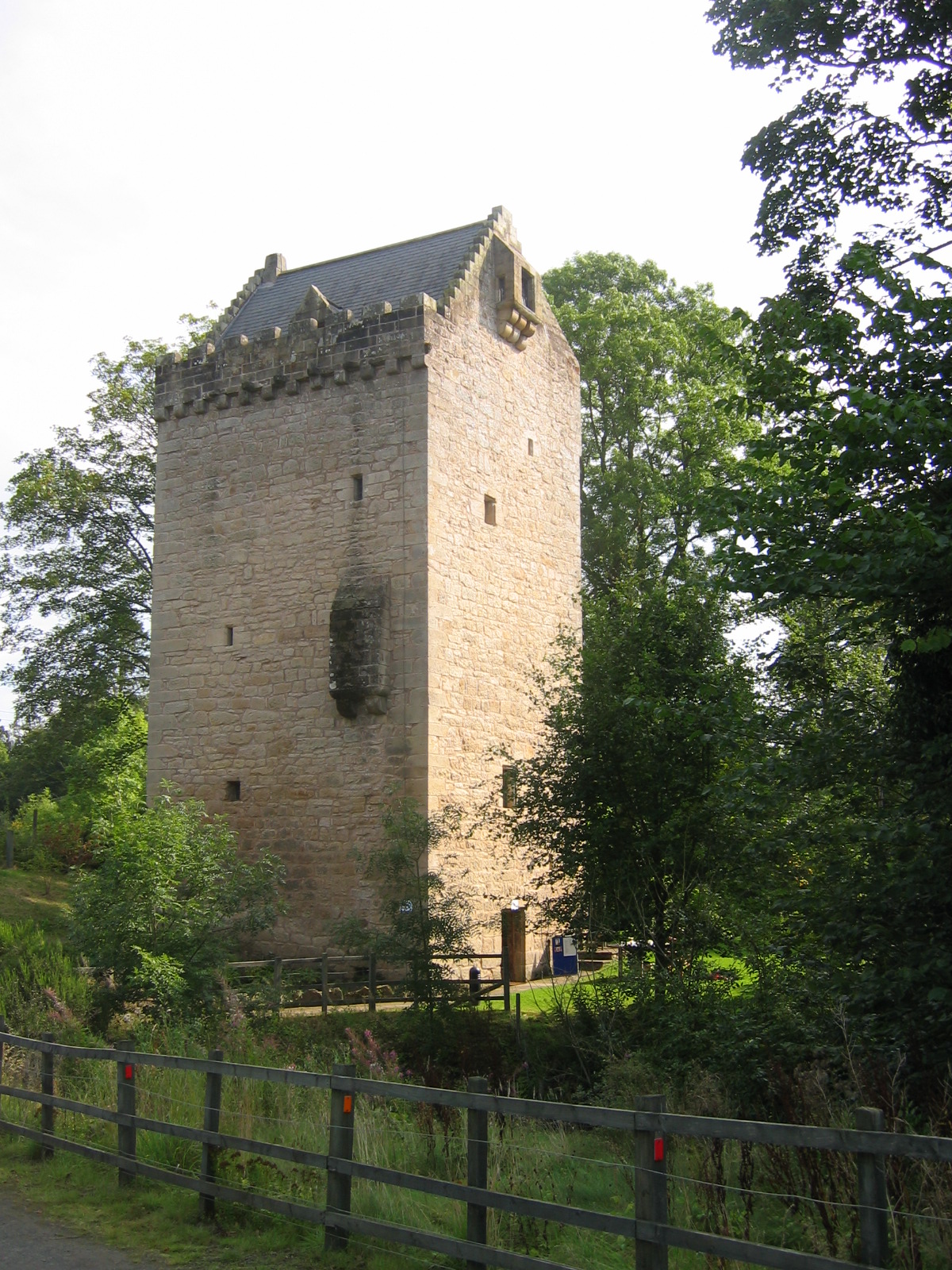
Kemnay House
Kemnay House is a 17th-century tower house, now incorporated in a later house, about south and west of Inverurie, Aberdeenshire, Scotland, and south of Kemnay, to the south of the River Don.Coventry, Martin (1997) ''The Castles of Scotland''. Goblinshead. p.219 History During the 16th century, Kemnay was a property of the Douglases of Glenbervie. It was acquired by the Crombie family, who built the present house. Thomas Burnett of Leys purchased it in 1688; he was subsequently imprisoned in the Bastille, Paris, at the instigation of Jacobite enemies. Alterations, including the extension of the wings, took place in 1833. The house is still occupied. Structure The original tower house was a tall L-plan building. The entrance in the reentrant angle, above which a stair turret arises this from the second floor, has been replaced. There is a vaulted basement, with the kitchen in the wing. The cream-washed walls are pierced by small windows. The three-storey wing, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tower House
A tower house is a particular type of stone structure, built for defensive purposes as well as habitation. Tower houses began to appear in the Middle Ages, especially in mountainous or limited access areas, in order to command and defend strategic points with reduced forces. At the same time, they were also used as an aristocrat's residence, around which a castle town was often constructed. Europe After their initial appearance in Ireland, Scotland, the Stins, Frisian lands, Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country and England during the High Middle Ages, tower houses were also built in other parts of western Europe, especially in parts of France and Italy. In Italian medieval communes, urban ''palazzi'' with a very tall tower were increasingly built by the local highly competitive Patrician (post-Roman Europe), patrician families as power centres during times of internal strife. Most north Italian cities had a number of these by the end of the Middles Ages, but few no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles In Great Britain And Ireland
Castles have played an important military, economic and social role in Great Britain and Ireland since their introduction following the Norman invasion of England in 1066. Although a small number of castles had been built in England in the 1050s, the Normans began to build motte and bailey and ringwork castles in large numbers to control their newly occupied territories in England and the Welsh Marches. During the 12th century the Normans began to build more castles in stone – with characteristic square keep – that played both military and political roles. Royal castles were used to control key towns and the economically important forests, while baronial castles were used by the Norman lords to control their widespread estates. David I invited Anglo-Norman lords into Scotland in the early 12th century to help him colonise and control areas of his kingdom such as Galloway; the new lords brought castle technologies with them and wooden castles began to be established over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basement
A basement or cellar is one or more floors of a building that are completely or partly below the ground floor. It generally is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the furnace, water heater, breaker panel or fuse box, car park, and air-conditioning system are located; so also are amenities such as the electrical system and cable television distribution point. In cities with high property prices, such as London, basements are often fitted out to a high standard and used as living space. In British English, the word ''basement'' is usually used for underground floors of, for example, department stores. The word is usually used with houses when the space below the ground floor is habitable, with windows and (usually) its own access. The word ''cellar'' applies to the whole underground level or to any large underground room. A ''subcellar'' is a cellar that lies further underneath. Purpose, geography, and history A basement can be used in almost exactly th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vault (architecture)
In architecture, a vault (French ''voûte'', from Italian ''volta'') is a self-supporting arched form, usually of stone or brick, serving to cover a space with a ceiling or roof. As in building an arch, a temporary support is needed while rings of voussoirs are constructed and the rings placed in position. Until the topmost voussoir, the keystone, is positioned, the vault is not self-supporting. Where timber is easily obtained, this temporary support is provided by centering consisting of a framed truss with a semicircular or segmental head, which supports the voussoirs until the ring of the whole arch is completed. Vault types Corbelled vaults, also called false vaults, with horizontally joined layers of stone have been documented since prehistoric times; in the 14th century BC from Mycenae. They were built regionally until modern times. The real vault construction with radially joined stones was already known to the Egyptians and Assyrians and was introduced into the buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-plan Castle
An L-plan castle is a castle or tower house in the shape of an L, typically built from the 13th to the 17th century. This design is found quite frequently in Scotland, but is also seen in England, Ireland, Romania, Sardinia, and other locations. The evolution of its design was an expansion of the blockhouse or simple square tower from the Early Middle Ages. As building techniques improved, it became possible to construct a larger building footprint and a more complex shape than the simple blockhouse tower. A more compelling motivation for the L plan was the ability to defend the entrance door by providing covering fire from the adjacent walls. This stratagem was particularly driven by the advent of cannon used by attackers. It was common for the union of the two wings to have very thick wall construction to support a major defensive tower in the union area. For example, the stone walls of Muchalls Castle in Scotland are over 14 feet thick at the ground level. Built in the 13t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kemnay House (geograph 1836648)
Kemnay House is a 17th-century tower house, now incorporated in a later house, about south and west of Inverurie, Aberdeenshire, Scotland, and south of Kemnay, to the south of the River Don.Coventry, Martin (1997) ''The Castles of Scotland''. Goblinshead. p.219 History During the 16th century, Kemnay was a property of the Douglases of Glenbervie. It was acquired by the Crombie family, who built the present house. In 1682 George Nicolson of Clunypurchased the Kemnay House and estate from Alexander Strachan of Glenkindie. On 5 July 1682 he was created a Senator of the College of Justice and adopted the title Lord Kemnay. Thomas Burnett of Leys purchased it from him in 1688; Thomas was subsequently imprisoned in the Bastille, Paris, at the instigation of Jacobite enemies. Alterations, including the extension of the wings, took place in 1833. The house is still occupied. Structure The original tower house was a tall L-plan building. The entrance in the reentrant angle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobitism
Jacobitism (; gd, Seumasachas, ; ga, Seacaibíteachas, ) was a political movement that supported the restoration of the senior line of the House of Stuart to the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British throne. The name derives from the first name of James II and VII, which in Latin translates as ''Jacobus (name), Jacobus''. When James went into exile after the November 1688 Glorious Revolution, the Parliament of England argued that he had abandoned the Kingdom of England, English throne, which they offered to his Protestant daughter Mary II, and her husband William III of England, William III. In April, the Convention of Estates (1689), Scottish Convention held that he "forfeited" the throne of Scotland by his actions, listed in the Articles of Grievances. The Revolution thus created the principle of a contract between monarch and people, which if violated meant the monarch could be removed. Jacobites argued monarchs were appointed by God, or Divine right of kings, divine right, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
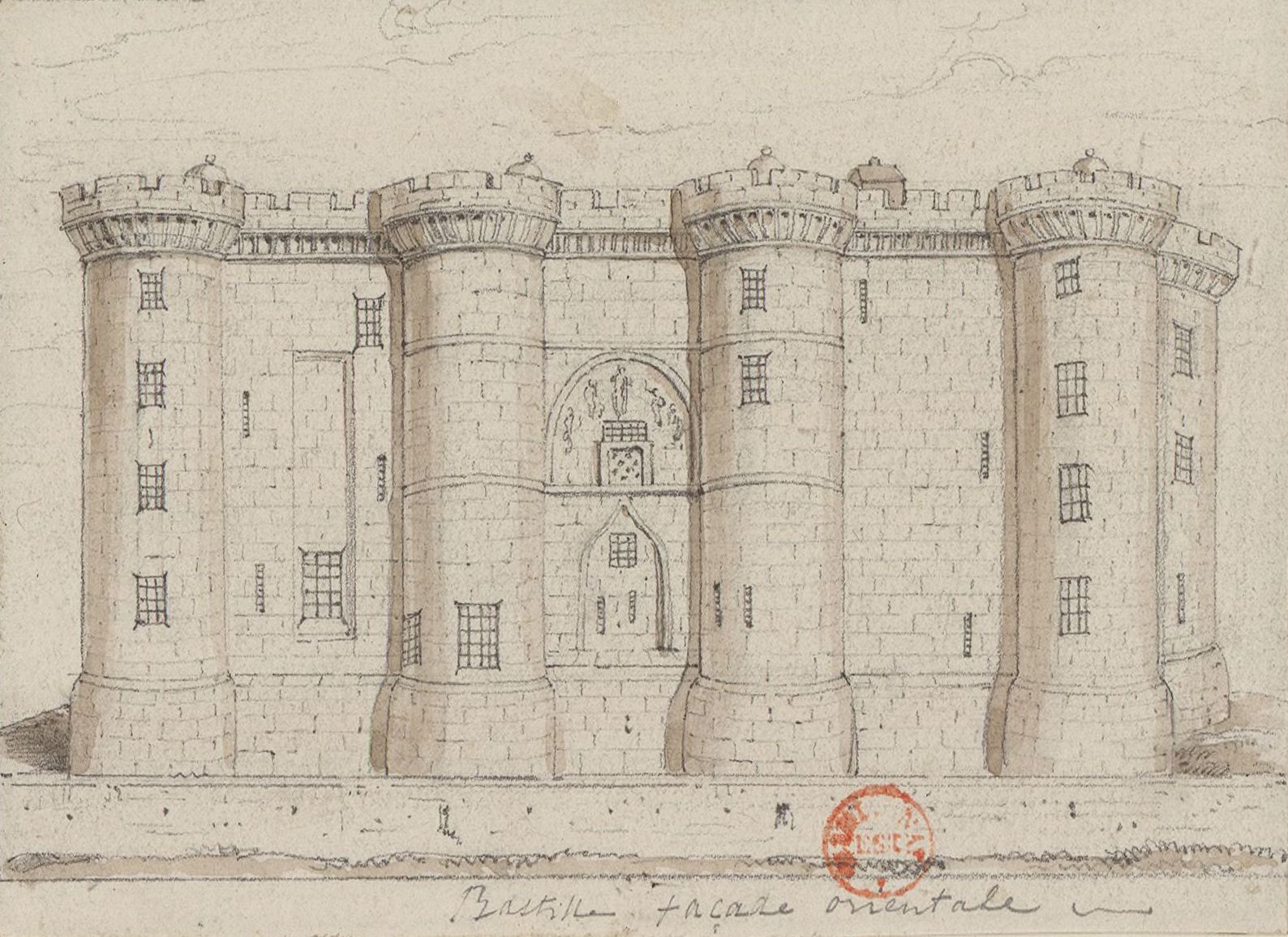
Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known formally as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was stormed by a crowd on 14 July 1789, in the French Revolution, becoming an important symbol for the French Republican movement. It was later demolished and replaced by the Place de la Bastille. The castle was built to defend the eastern approach to the city from potential English attacks during the Hundred Years' War. Construction was underway by 1357, but the main construction occurred from 1370 onwards, creating a strong fortress with eight towers that protected the strategic gateway of the Porte Saint-Antoine heading out to the east. The innovative design proved influential in both France and England and was widely copied. The Bastille figured prominently in France's domestic conflicts, including the fighting between the rival factions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverurie
Inverurie (Scottish Gaelic: ''Inbhir Uraidh'' or ''Inbhir Uaraidh'', 'mouth of the River Ury') is a town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland at the confluence of the rivers Ury and Don, about north-west of Aberdeen. Geography Inverurie is in the valley of the River Don at the centre of Aberdeenshire and is known locally as the Heart of the Garioch. It sits between the River Don and the River Ury and is only from the imposing hill of Bennachie. The town centre is triangular and is dominated by Inverurie Town Hall built in 1863. In the middle of the 'square' (as it is known locally) is the Inverurie and District War Memorial, capped by a lone Gordon Highlander looking out over the town. The main shopping areas include the Market Place and West High Street which branches off from the centre towards the more residential part of the town. South of the River Don is the village of Port Elphinstone, which is part of the Royal Burgh of Inverurie and is so called due to the proximity of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Burnett
The House of Burnett (Burnet, Burnette, Burnard, Bernard) is a Lowland and Border Scottish family composed of several branches. The Chief of the Name and Arms of Burnett is James Comyn Amherst Burnett of Leys. Origins of the name It remains uncertain if the name of Burnett is of Saxon or Norman origins. It has been suggested that the name Burnett is derived from the Old French ''burnete'', ''brunette'', which is a diminutive of ''brun'' meaning "brown", "dark brown". Another proposed origin of the name is from ''burnete'', a high quality wool cloth originally dyed to a dark brown colour.''Crannog to Castle; A History of the Burnett Family in Scotland'', ed. Eileen A. Bailey (Banchory: Leys Publishing, 2000), pp. 2-3 There is also evidence which suggests that Burnett stems from the English surname of ''Burnard'', a derivative of the Anglo-Saxon name "Beornheard". Spelling variations of the name in early documents show Burnet and Burnard/Bernard being used interchangeably for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenbervie
Glenbervie (Scottish Gaelic: ''Gleann Biorbhaidh'', Scots: ''Bervie'') is located in the north east of Scotland in the Howe o' the Mearns, one mile from the village of Drumlithie and eight miles south of Stonehaven in Aberdeenshire. The river Bervie runs through the village. The rural area is the location of Glenbervie House and estate. The parish was formerly named Overbervie.History of Glenbervie G H Kinnear, Montrose, 1895, retrieved 10 July 2017 The population fell from a peak of 1307 in 1796 to 887 in 1895. Many of the villagers had immigrated, especially the young to the nearby cities and towns. The in Glenbervie is the final resting plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)